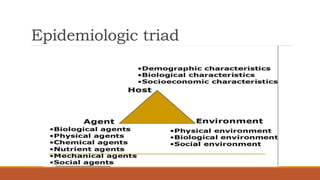
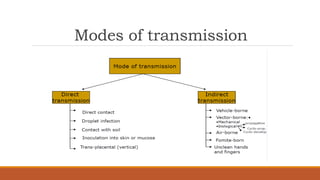
This document provides an introduction to a course on communicable and non-communicable diseases. The course aims to provide students with knowledge, skills, and attitudes to identify, prevent, and control various diseases. The course objectives are to describe key concepts of communicable diseases, signs and symptoms of communicable and non-communicable diseases, legislation related to diseases, neglected tropical diseases in Zambia, and factors influencing disease transmission and prevention. The course content will cover terminology, communicable disease agents and factors, and introduce communicable diseases.