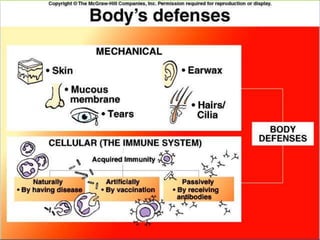
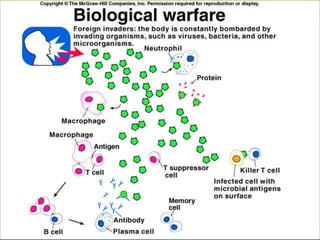
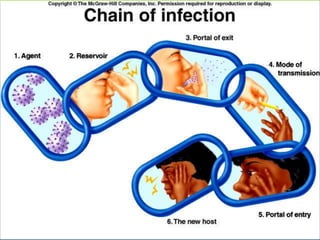
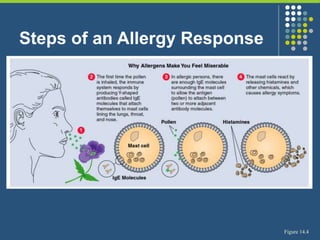
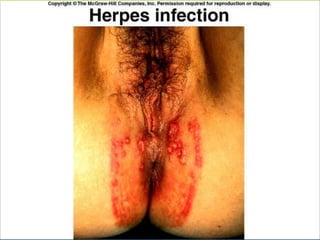
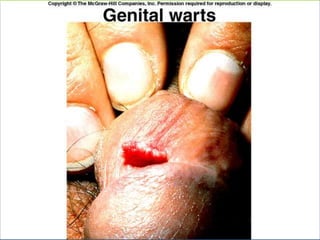
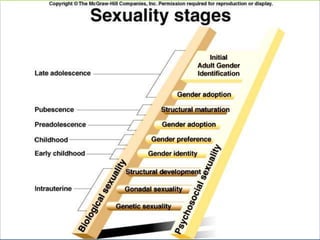
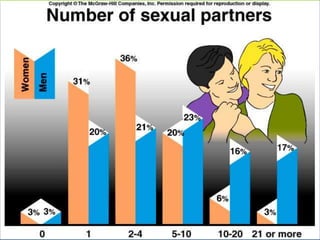
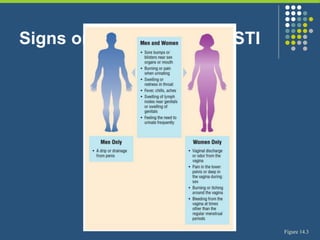
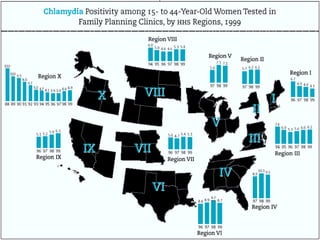
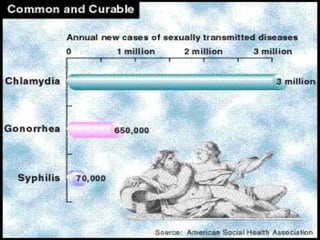
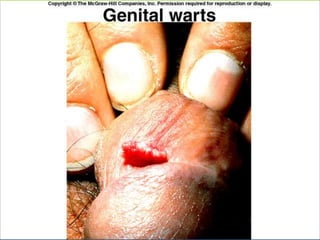
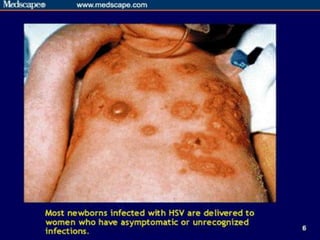
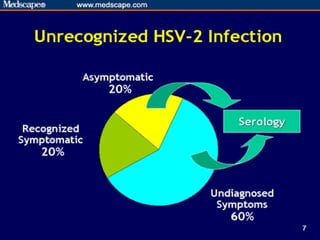
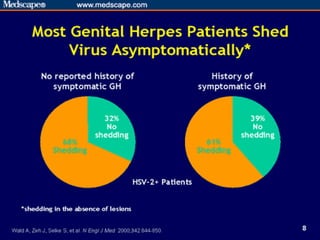
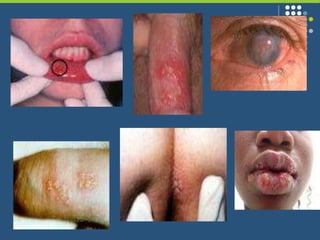
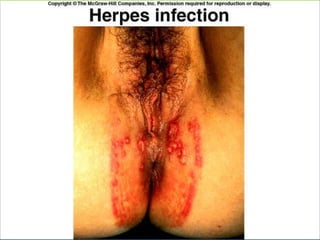
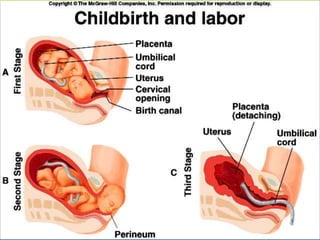
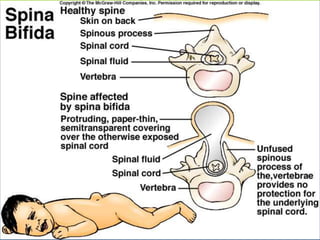
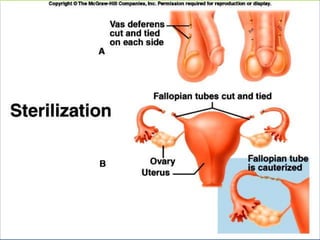
This document provides an overview of infectious and noninfectious diseases. It discusses topics such as immunity, risk factors, pathogens and routes of transmission for infectious diseases. It also addresses specific diseases like STIs (sexually transmitted infections), respiratory illnesses, neurological disorders, and musculoskeletal diseases. The document presents information on disease prevention, treatment, and the relationship between lifestyle factors and health risks.