This document summarizes criminal and civil court procedures in India. It outlines the different types of criminal and civil courts, their jurisdictions, and powers. It also describes the key aspects of criminal procedure like FIR, investigation, arrest, and appeal. For civil procedures, it discusses topics like parties in a civil suit, notices, injunctions, judgments, appeals, and writ petitions that can be filed in high courts and the supreme court. It also provides an overview of government advocates and their roles in conducting government cases.


![Criminal Procedure
• Indian Penal Code,1860[IPC]
• The Code of Criminal
Procedure,1973[ Cr PC]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/courtprocedurepreparationofstatementoffacts-130812052006-phpapp01/75/Court-procedure-preparation-of-statement-of-facts-3-2048.jpg)



![Civil Procedure
Code of Civil
Procedure 1908
[C P C]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/courtprocedurepreparationofstatementoffacts-130812052006-phpapp01/75/Court-procedure-preparation-of-statement-of-facts-7-2048.jpg)
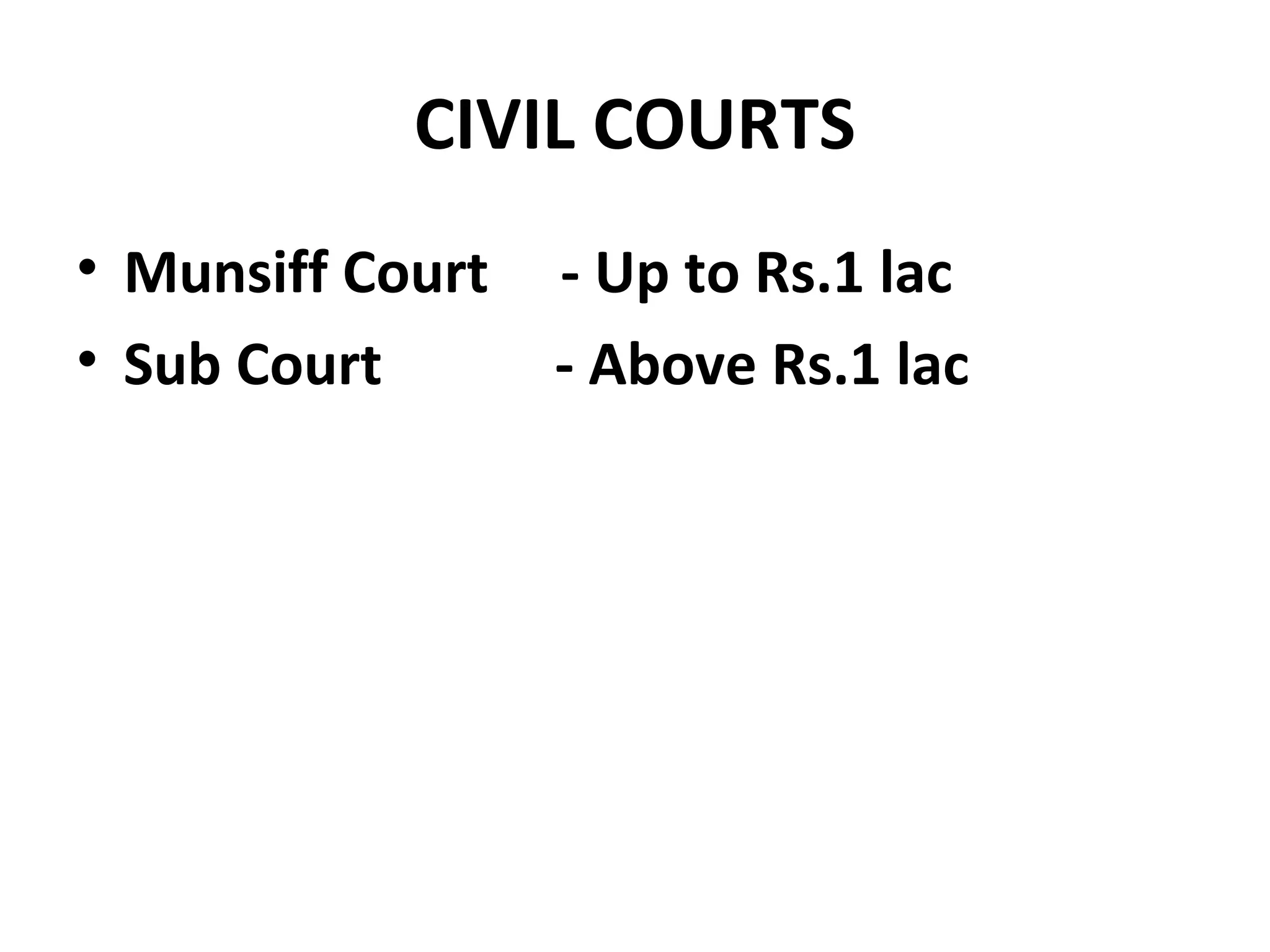
![CPC
Civil Courts, Its powers, Jurisdiction,
Suits[plaint & written statement],
Interim Orders, Judgment & Decree,
Execution of Decree etc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/courtprocedurepreparationofstatementoffacts-130812052006-phpapp01/75/Court-procedure-preparation-of-statement-of-facts-8-2048.jpg)





















![thanks
Chandrabos PV
Joint Secretary [Law] to Govt
O/D Associate Fellow,I M G
Mob-9497366502,Email-pvcbos@hotmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/courtprocedurepreparationofstatementoffacts-130812052006-phpapp01/75/Court-procedure-preparation-of-statement-of-facts-31-2048.jpg)