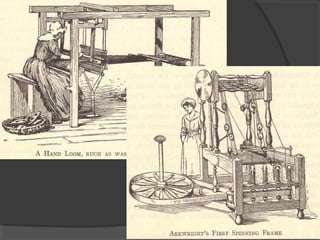
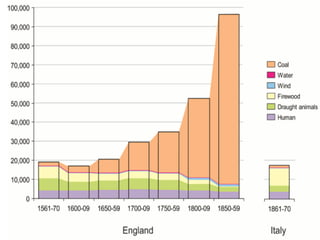
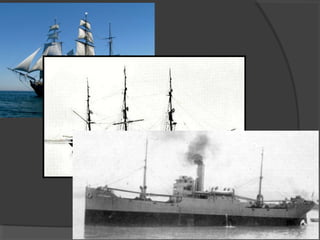
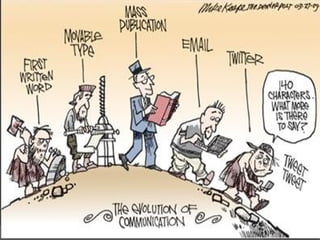
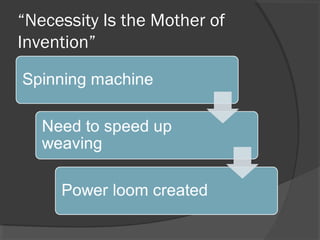
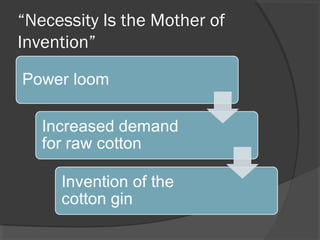
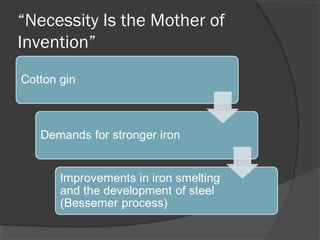
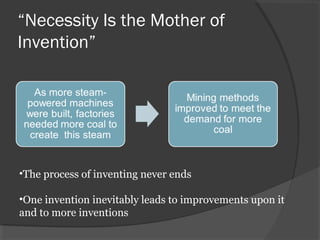
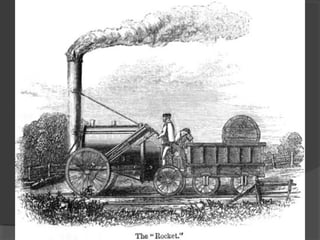
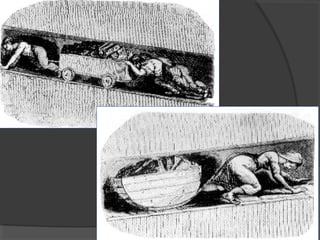
Here are some potential things that happened since newspapers became cheaper to produce:
- The cost of newspapers decreased, making them more affordable for common people.
- More newspapers could be produced, increasing circulation numbers and availability.
- Newspapers could be sold at a lower price point while still being profitable, opening the market up to a wider readership audience.
- Publishing newspapers became a more viable business since costs decreased, potentially leading to more newspapers being established.
- Literacy rates may have increased as newspapers were more accessible and affordable to the general public.