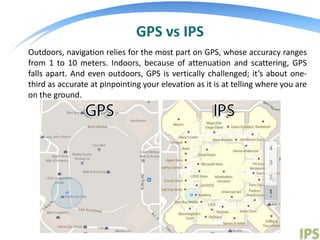
An indoor positioning system (IPS) uses wireless technologies like Wi-Fi to locate objects or people inside buildings, as GPS does not work well indoors. IPS relies on nearby nodes with known positions rather than satellites. Wi-Fi fingerprinting involves collecting and storing Wi-Fi signal strengths to develop location fingerprints. IPS has many potential uses including indoor navigation, location-based services, security, and analytics. Researchers are working to increase IPS accuracy by supplementing Wi-Fi with other sensor data.