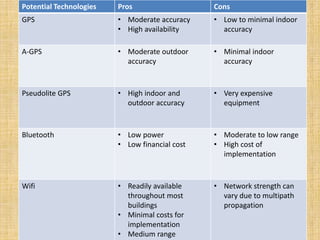
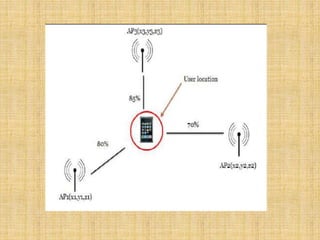
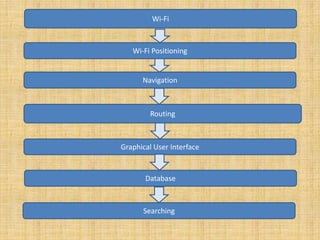
This document discusses and compares different indoor positioning techniques, focusing on Wi-Fi positioning. It describes how Wi-Fi positioning works by measuring the received signal strength from multiple access points and triangulating the user's position. Specifically, it presents an algorithm that uses the distances calculated from the signal strengths received from three access points to determine the coordinates of the user's location. The document also mentions using Dijkstra's algorithm for shortest path routing of indoor navigation once a user's position is determined.