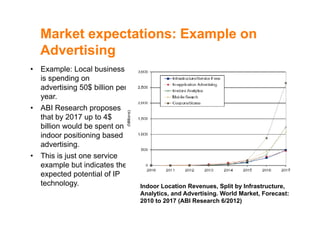
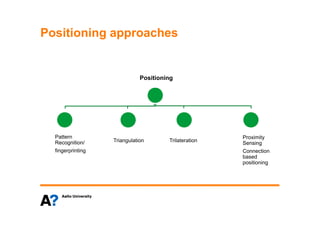
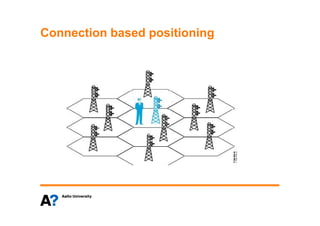
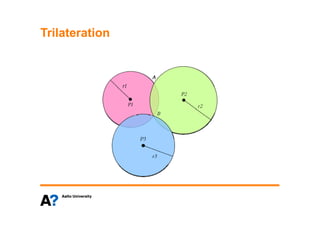
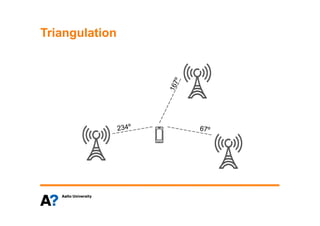
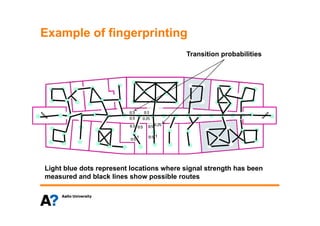
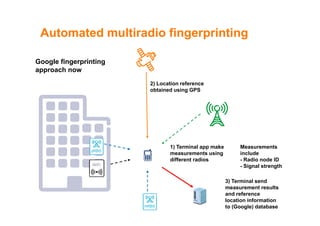
The document discusses indoor positioning solutions (IPS). It provides background on the growing indoor location market with over 130 companies working on indoor mapping, tracking, and navigation technologies. IPS can be used for navigation, emergency response, tracking people and assets, and user applications like social networking and shopping. Technical approaches to IPS include terminal-based methods using the device itself for positioning, infrastructure-based methods using dedicated indoor infrastructure or existing WiFi networks, and hybrid methods. Baseline positioning methods discussed are connection-based positioning using cell/access point IDs, trilateration/multilateration using signal strength or timing to estimate distance, triangulation using angle of arrival, and fingerprinting using spatial radio environment maps. Google aggregates WiFi