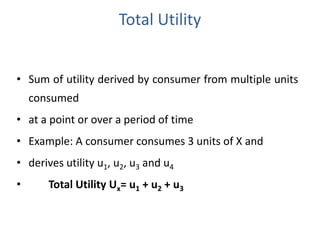
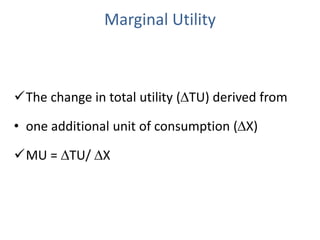
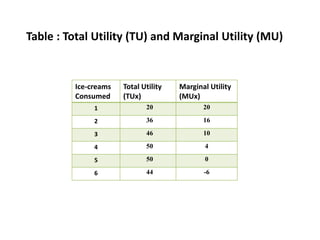
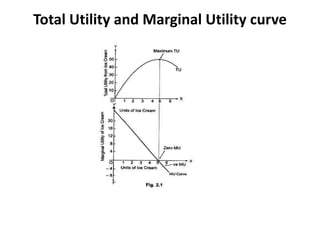
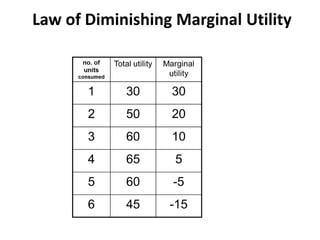
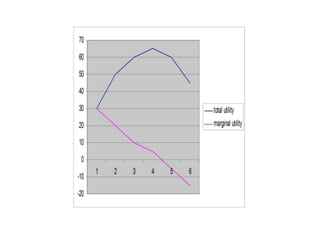
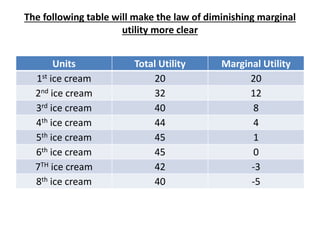
Utility is defined as the satisfaction or benefit derived from consuming goods and services. It can be measured in two ways: cardinal utility which assigns numerical values to satisfaction, and ordinal utility which ranks preferences without numbers. There are two types of utility: total utility which is the sum of utility from consuming multiple units of a good, and marginal utility which is the change in total utility from consuming one additional unit. As consumption of a good increases, marginal utility initially increases but then decreases, following the law of diminishing marginal utility. This is illustrated through an example showing total and marginal utility declining for additional ice cream consumption.