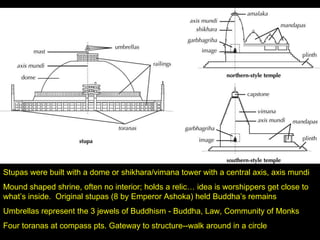
The document explores the interconnectedness of Indian and Southeast Asian arts, focusing on the cultural and philosophical influences of Hinduism and Buddhism. It details significant historical events, architectural styles, and artistic traditions, including temples, sculpture, and painting, emphasizing how these elements reflect religious beliefs and societal values. Additionally, it highlights the evolution of Buddhist and Hindu art, showcasing notable works and cultural practices throughout different historical periods.