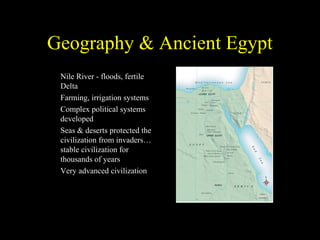
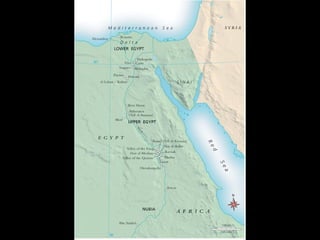
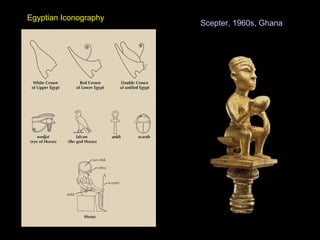
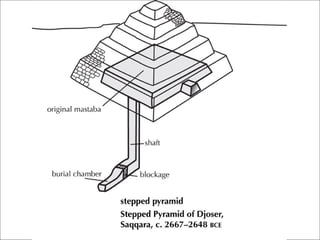
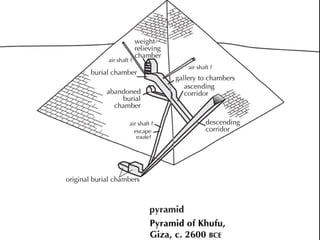
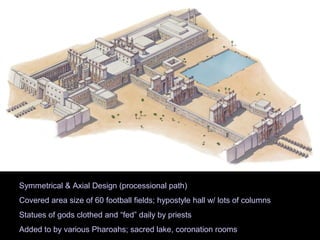
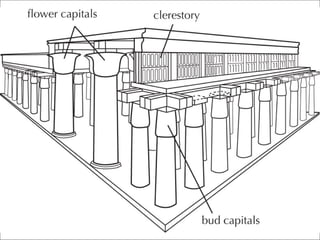
The document describes an ancient Egyptian funerary mask of Tutankhamun from 1327 BC made of gold inlaid with glass and semiprecious stones in the Cairo Museum, showing the artistic traditions from the New Kingdom period of ancient Egypt centered around religious beliefs involving judgment of the dead.