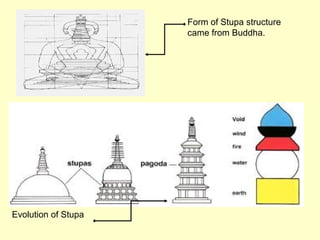
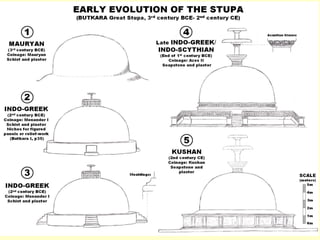
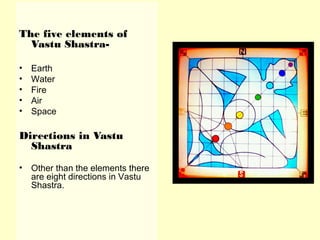
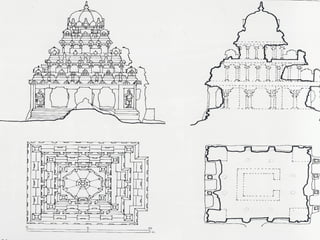
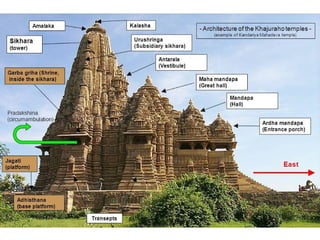
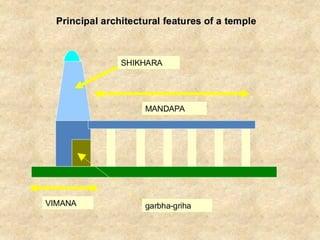
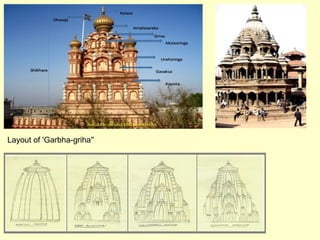
Hindu architecture evolved from a combination of indigenous Dravidian styles and those of invading Aryan groups. Key characteristics include ornate temples centered around a small inner shrine (garbha-griha) topped with a spire-shaped roof (sikhara) and surrounded by porch-like prayer halls (mandapas). Two major styles developed - the northern Nagara style using stone and emphasizing vertical elements, and the southern Dravidian style using stone for burial monuments and emphasizing horizontal lines. Important examples include the Sun Temple at Konark, known for its massive stone chariot-shaped structure, and early Chalukyan structural temples at Aihole that blended northern and southern features into a distinctive