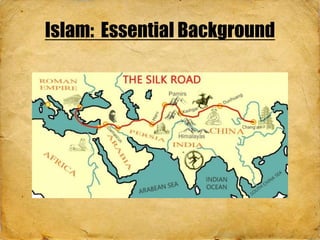
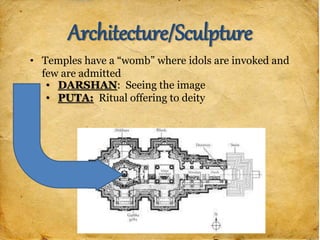
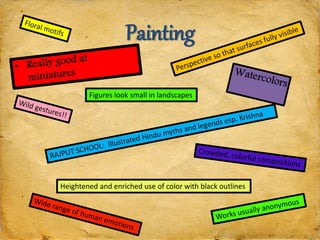
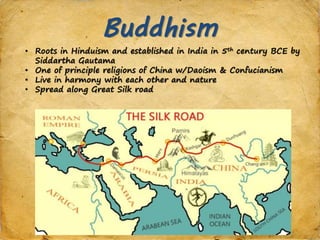
The document provides background information on various Asian religions and artworks. It discusses Islam, Buddhism, and Hinduism. Key details include how Islam spread through trade routes and conquest, core beliefs and deities of Hinduism like Brahma and Vishnu, and Buddhist concepts of suffering and enlightenment. The document examines architecture, sculpture, and paintings of regions in Asia, noting styles and religious symbolism. It also covers the influence of Chinese dynasties on art and the emphasis on calligraphy. The document aims to prepare the reader to answer exam questions on artworks of Asia.