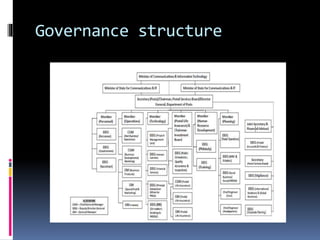
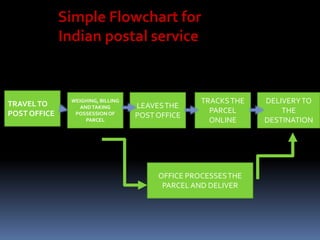
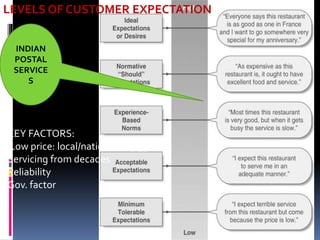
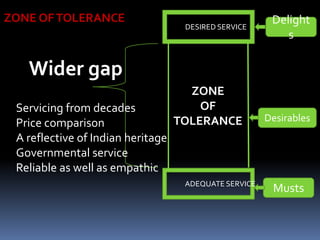
The document discusses India's large postal network, which has over 155,000 post offices, most in rural areas. It provides an overview of the services offered, including mail services, financial services, and retail services. It also discusses factors impacting the postal service like globalization and private competitors. A flowchart shows the process for sending a parcel. There are expectations for adequate and desired service levels. Strengths include a strong network and low prices, while weaknesses include outdated work culture and high customer dissatisfaction. Opportunities include more customers and technology, while threats include competitors and the internet.