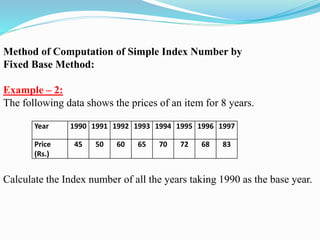
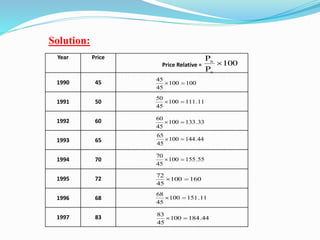
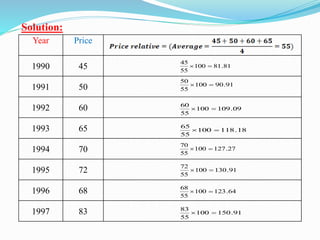
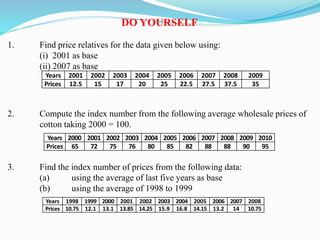
The document discusses index numbers which measure changes in variables over time. It defines simple and composite index numbers. The three main types of index numbers are price, quantity, and value indexes. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating price indexes using the fixed base method. Index numbers are calculated for different years using different base periods to compare price changes.