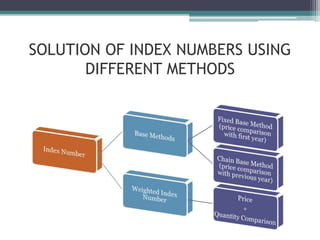
This document provides an introduction to index numbers and their uses and characteristics. It defines an index number as a method to measure changes in price levels over time, typically expressed as a percentage. Index numbers are specialized averages that measure changes in phenomena over periods of time and allow comparisons of prices, quantities, and values between different years by relating them to a base year. The document then discusses various methods for calculating index numbers, including fixed base methods, chain base methods, weighted index numbers using Laspeyres, Paaschee and Fisher's ideal formulas, and the Marshall-Edgeworth method.