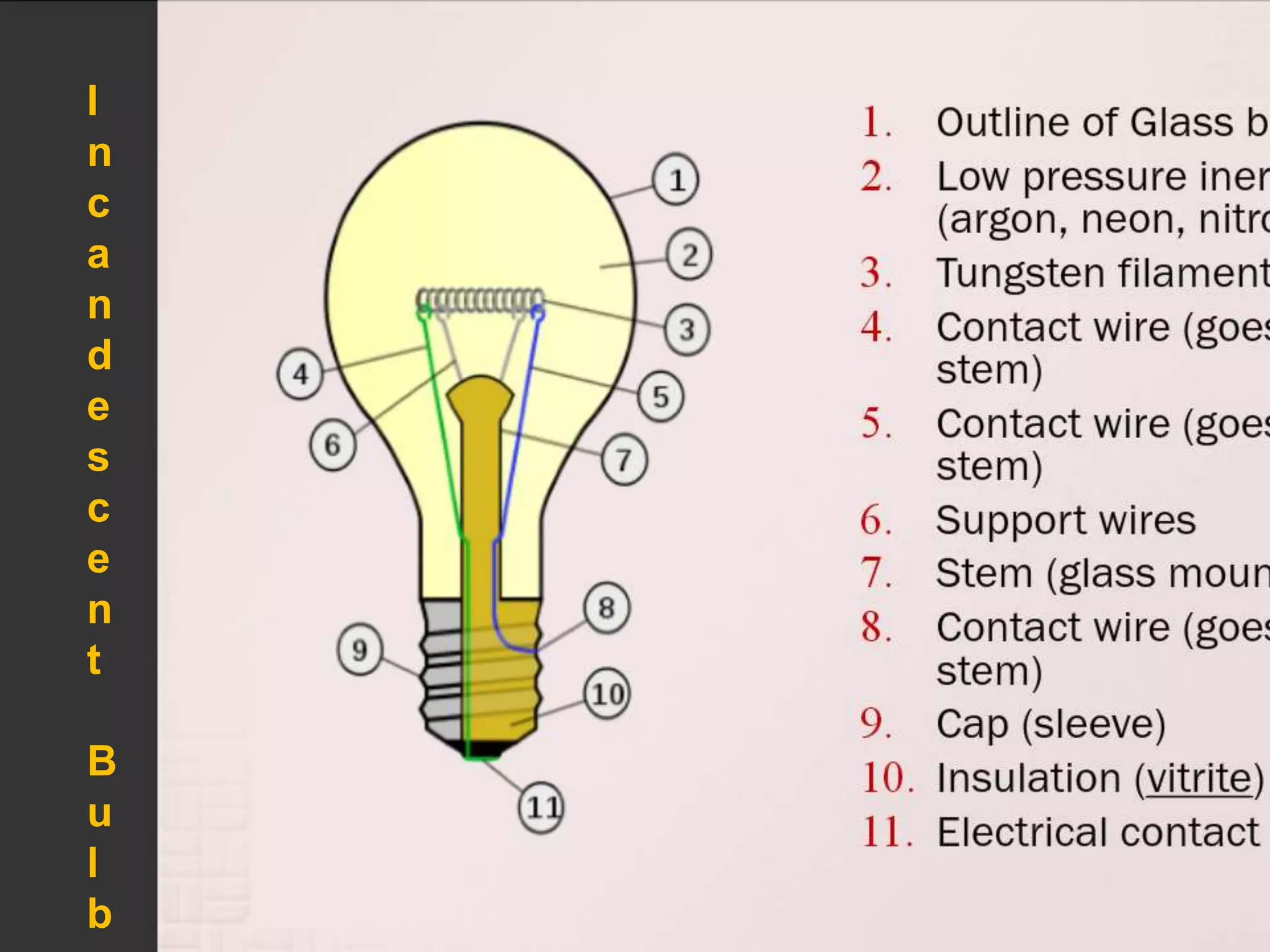
The document discusses the history and operation of incandescent light bulbs. It explains that in 1802, Humphry Davy demonstrated that running electricity through a thin metal strip could heat it enough to produce light. However, early light bulbs had short lifetimes due to filament burn up in air. Improvements were made to combat this, but generating electricity was costly. The document also describes how incandescent bulbs work, their availability in different sizes and voltages, their uses, and properties like color temperature.