Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


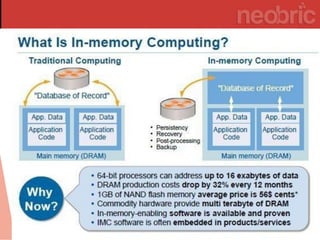

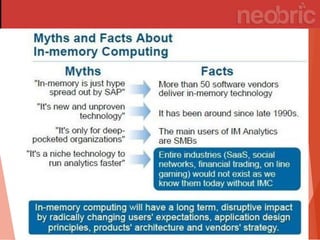

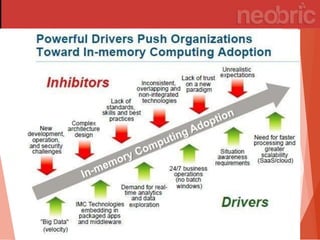








In-memory computing stores information in main RAM instead of slower disk drives, enabling rapid data analysis and operations, particularly benefiting industries like banking and utilities. Its popularity is rising due to decreasing memory costs and the increasing demand for speed in processing. However, challenges such as lack of standards, high migration costs, and data persistence concerns remain.














