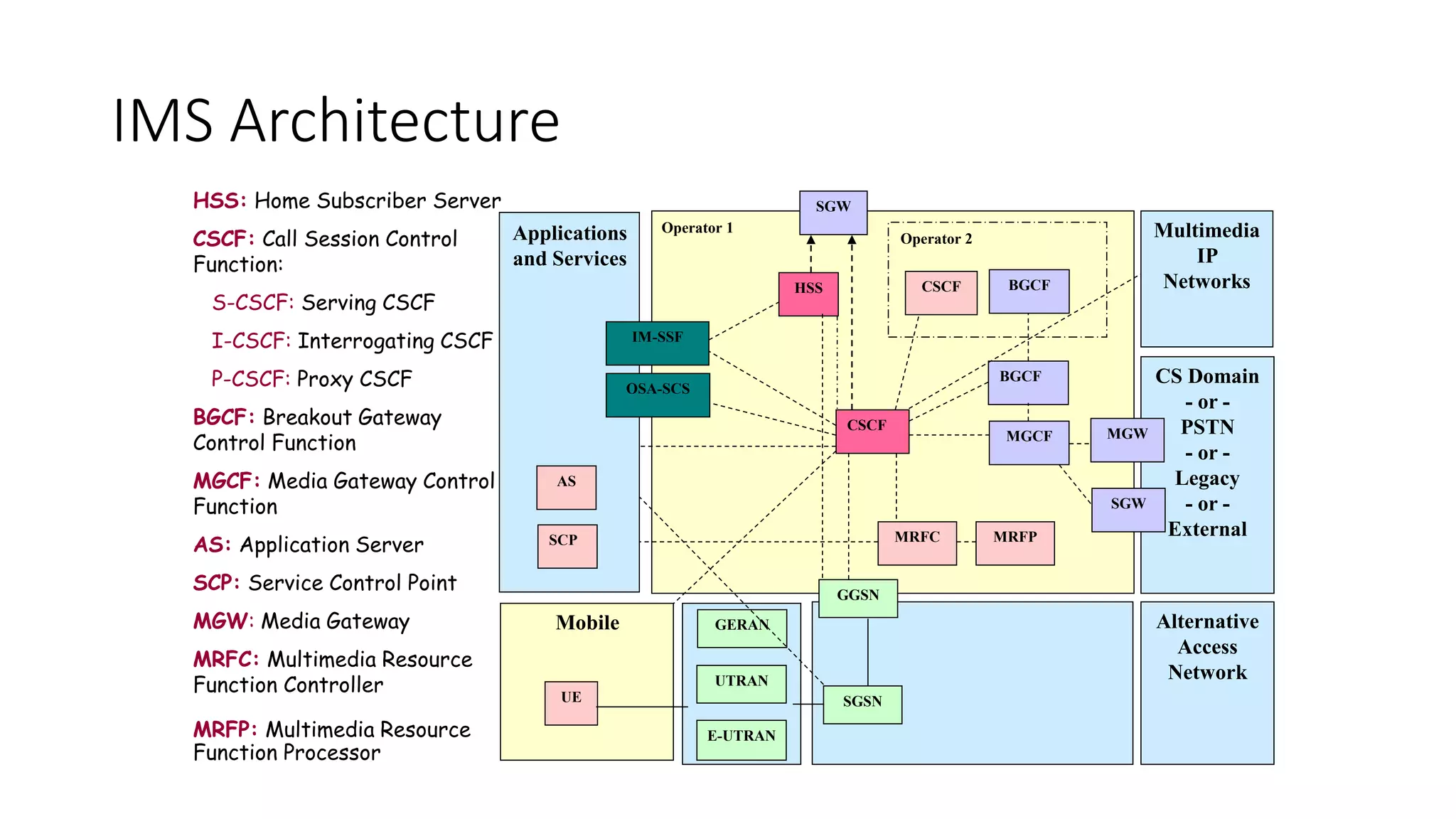
The document outlines the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS), which facilitates the convergence of voice, video, messaging, and data for both wireless and wireline users through specific functional elements and terminals. It details the architecture, requirements for quality of service, and the roles of various components such as the Call Session Control Function (CSCF) and the Home Subscriber Server (HSS). The IMS is designed to ensure interoperability and support for session-oriented applications across diverse access networks.