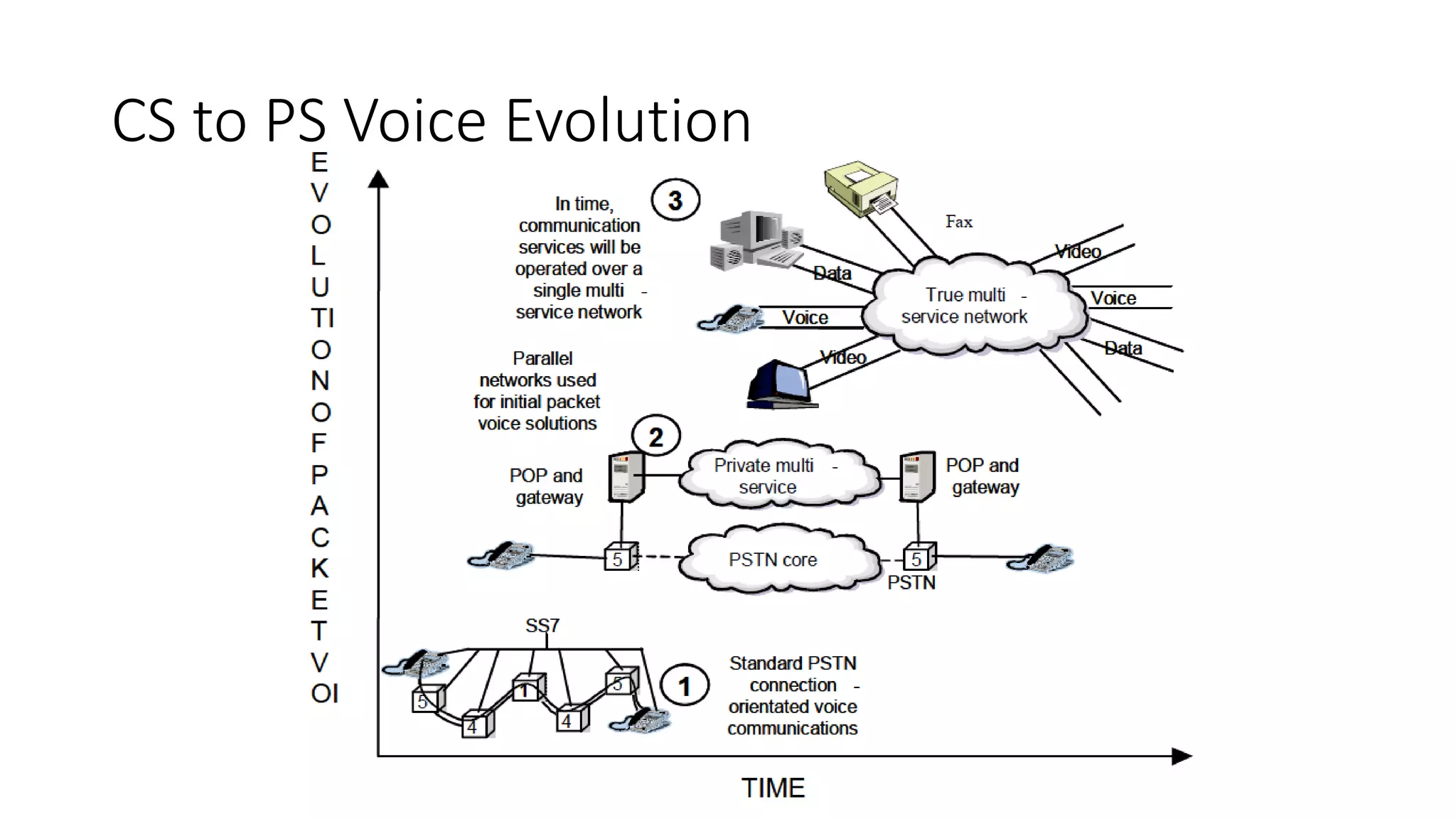
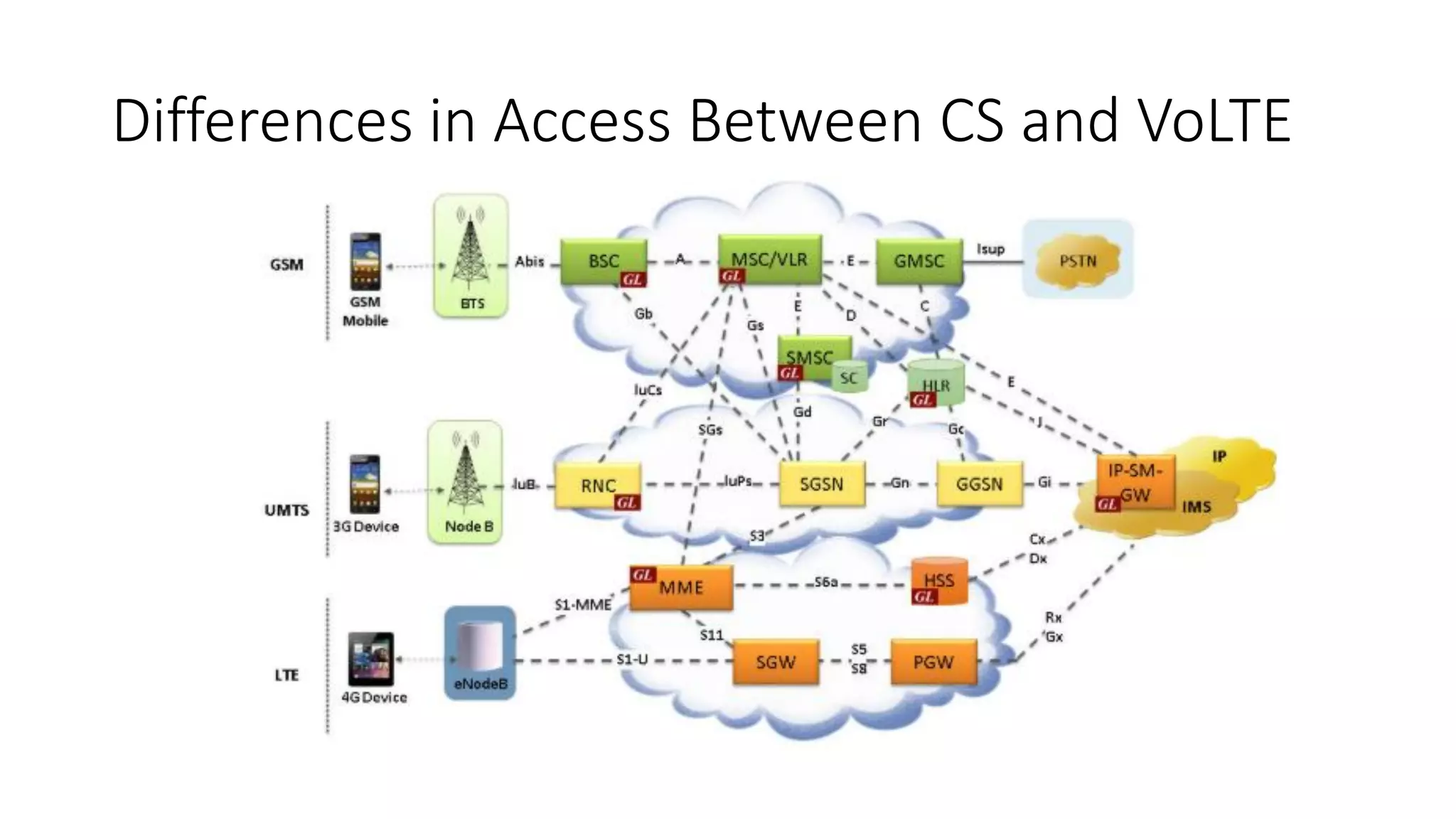
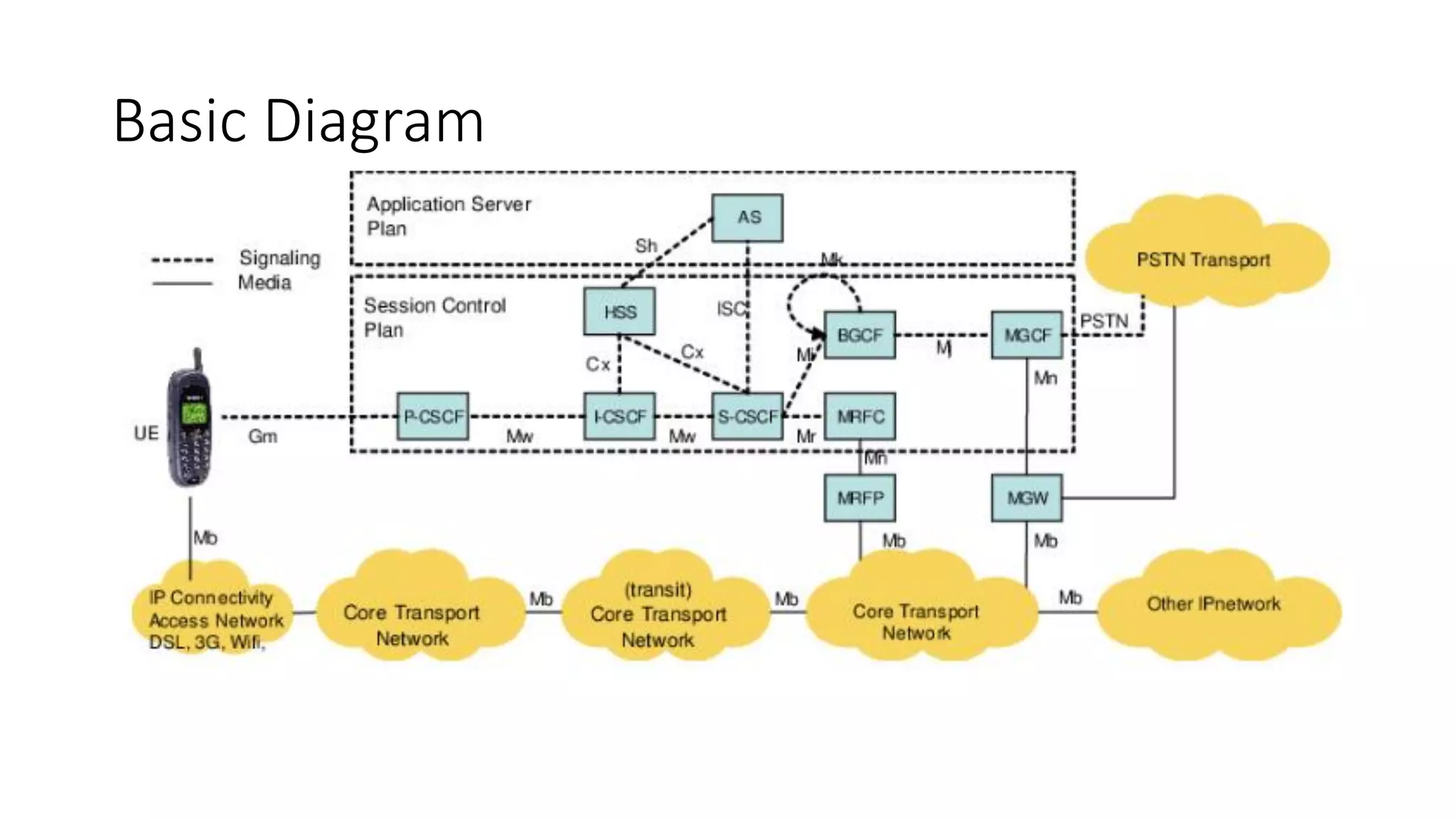
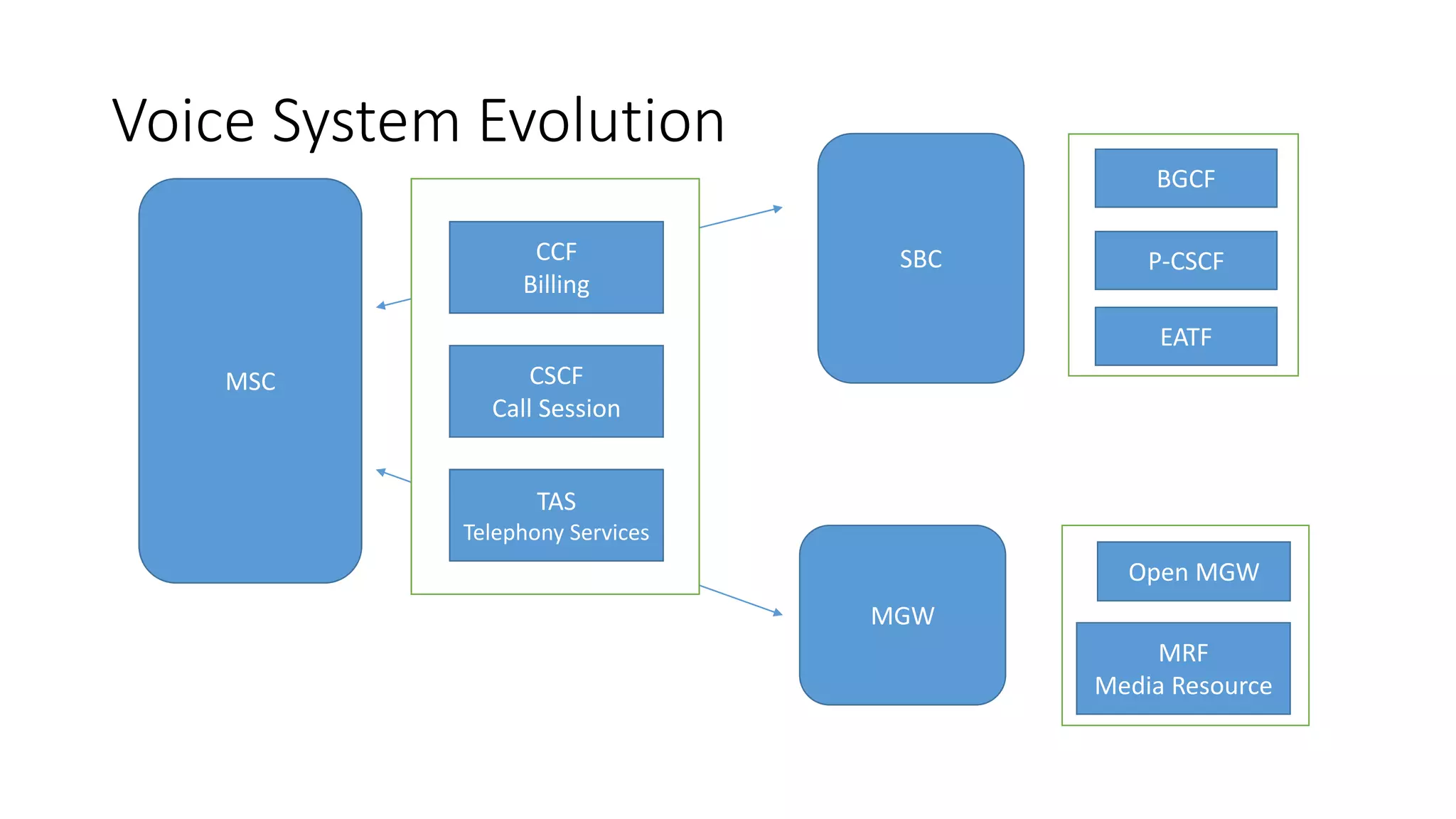
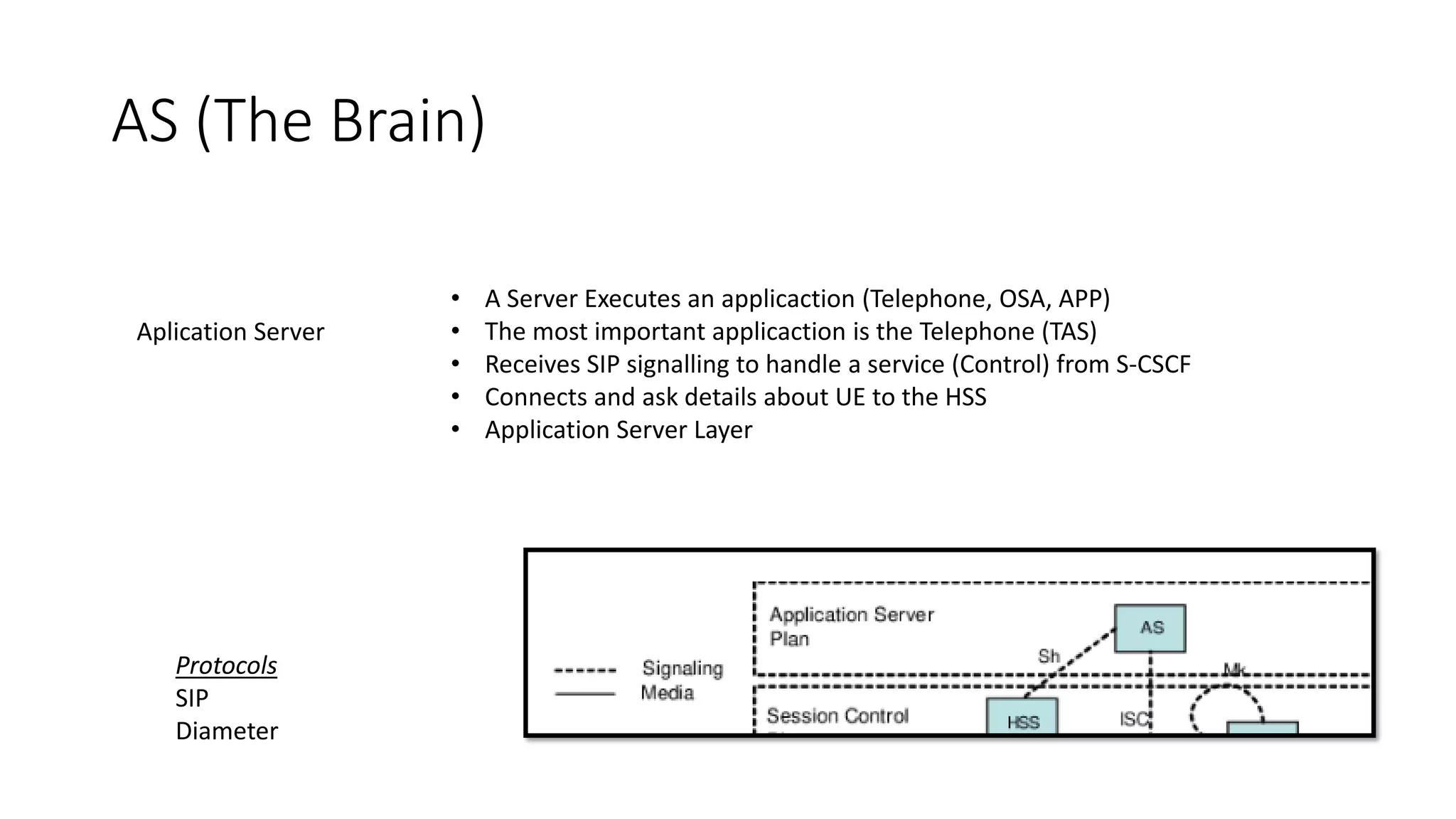
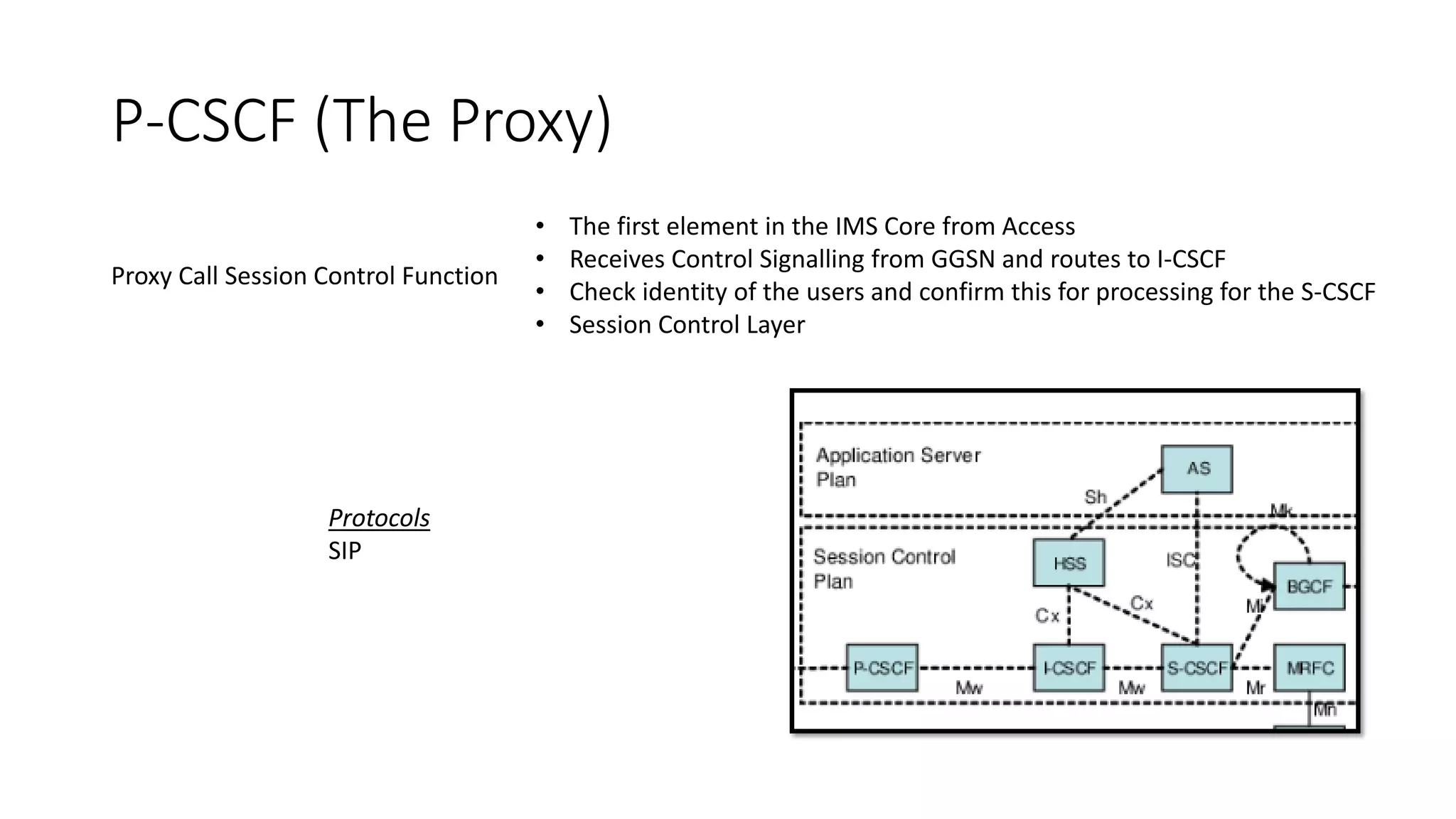
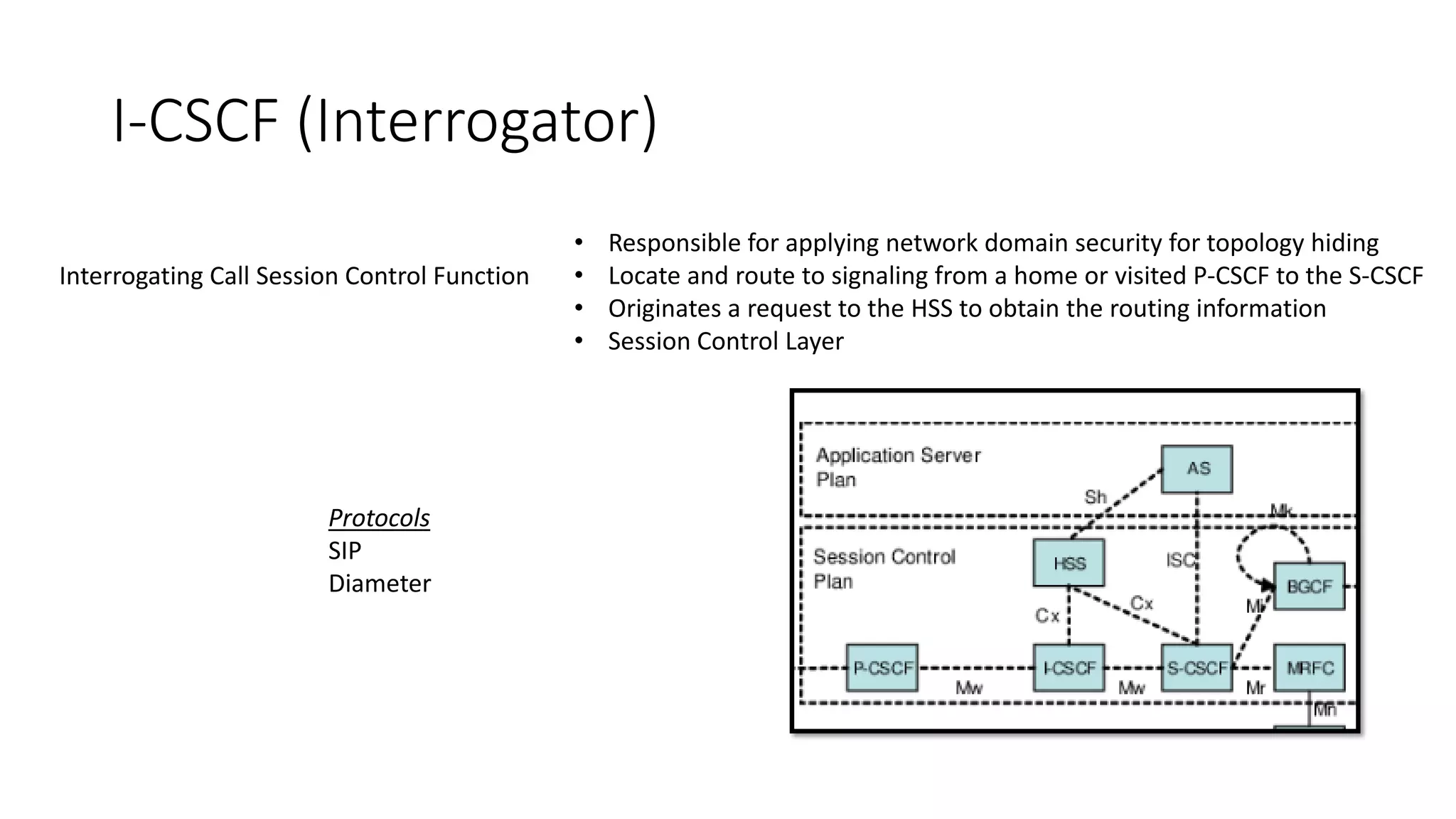
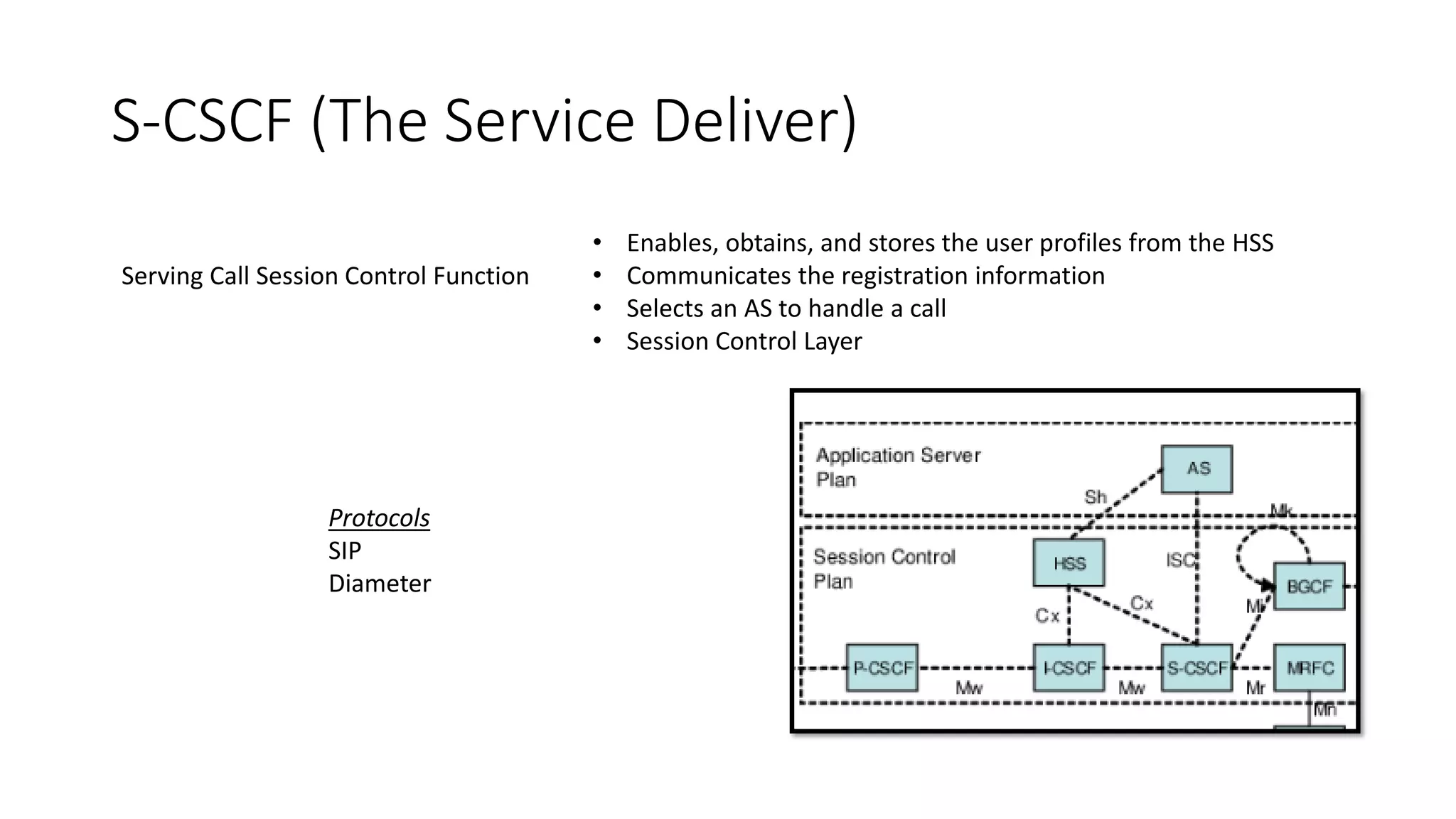
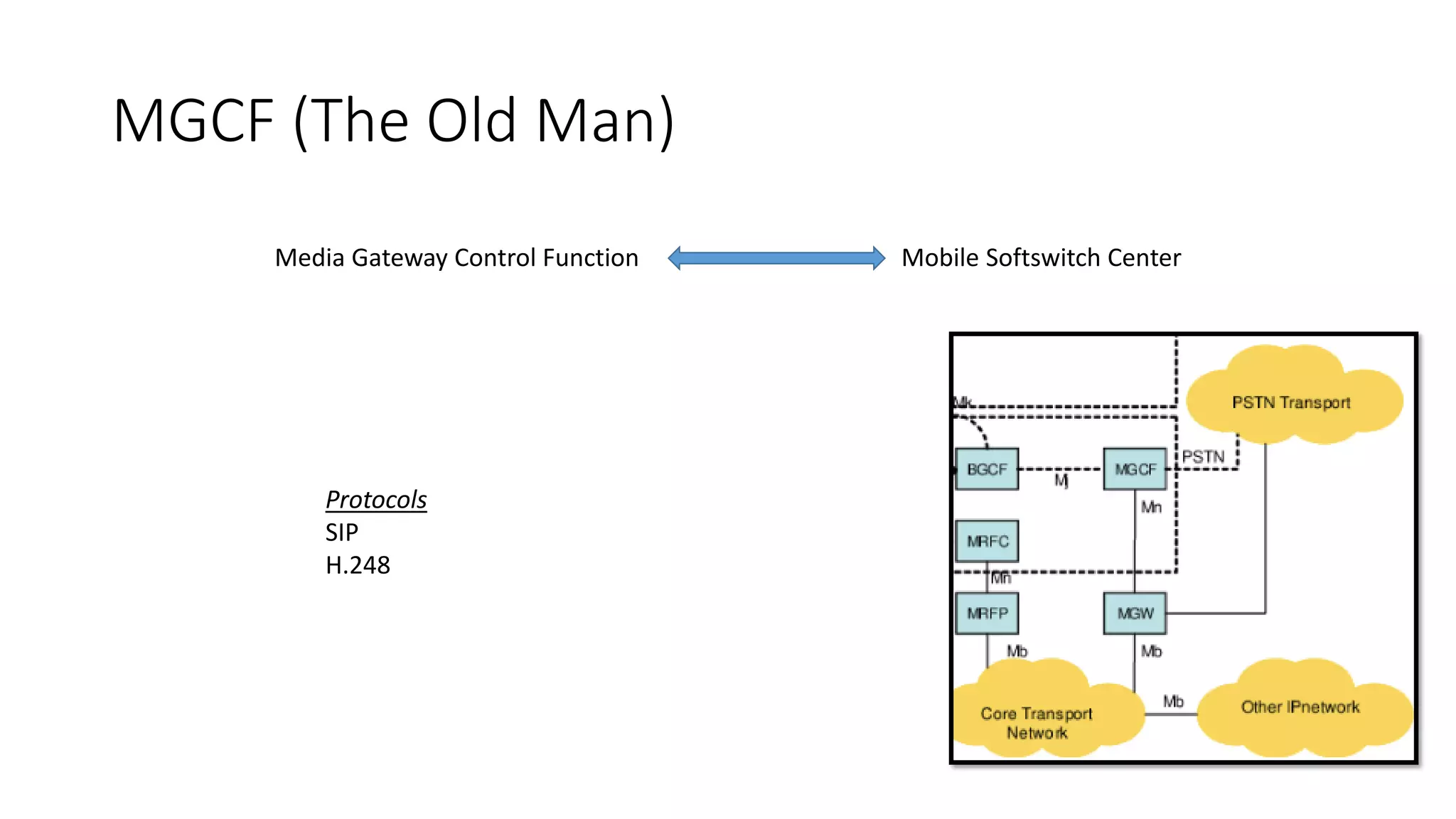
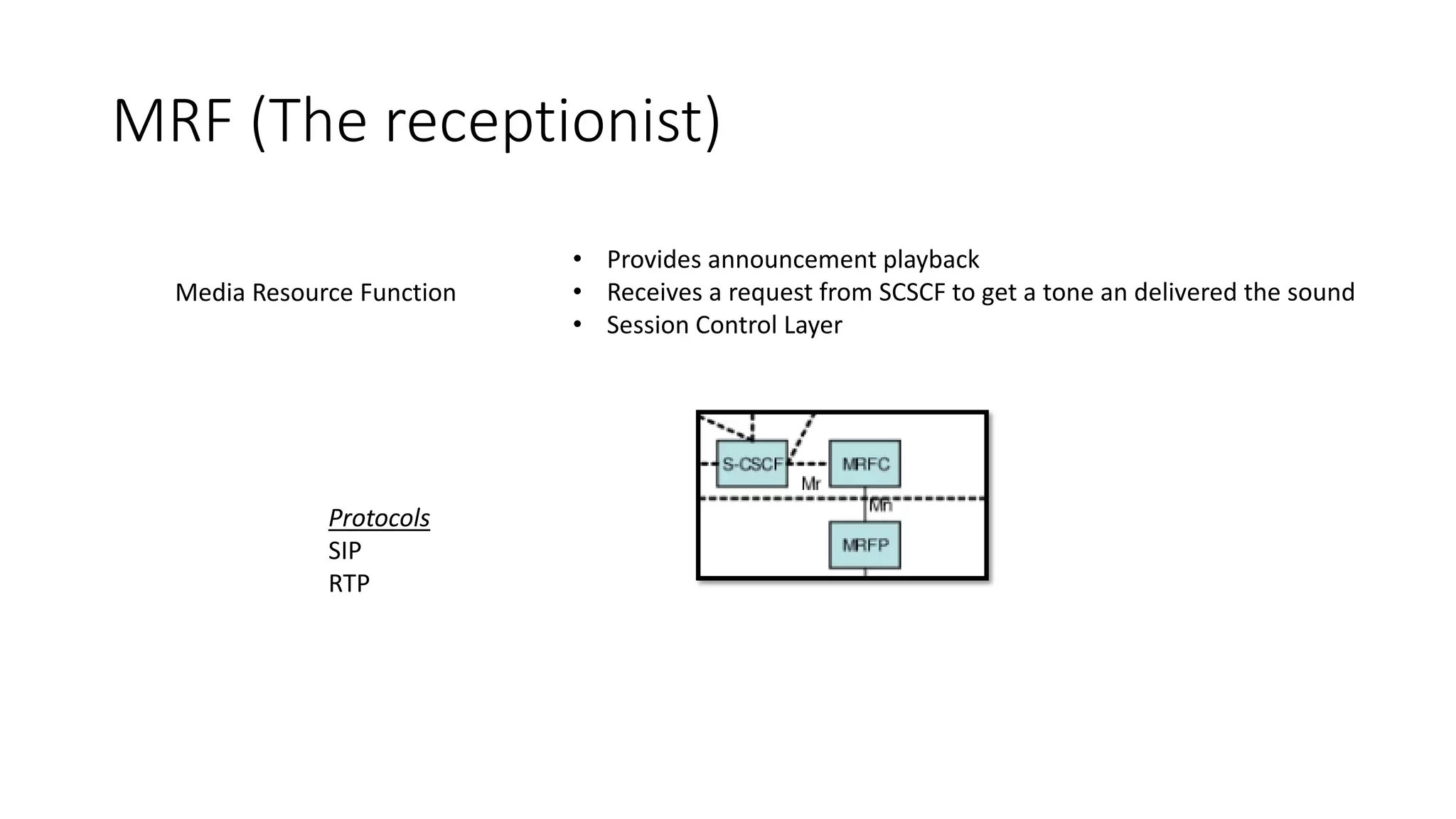
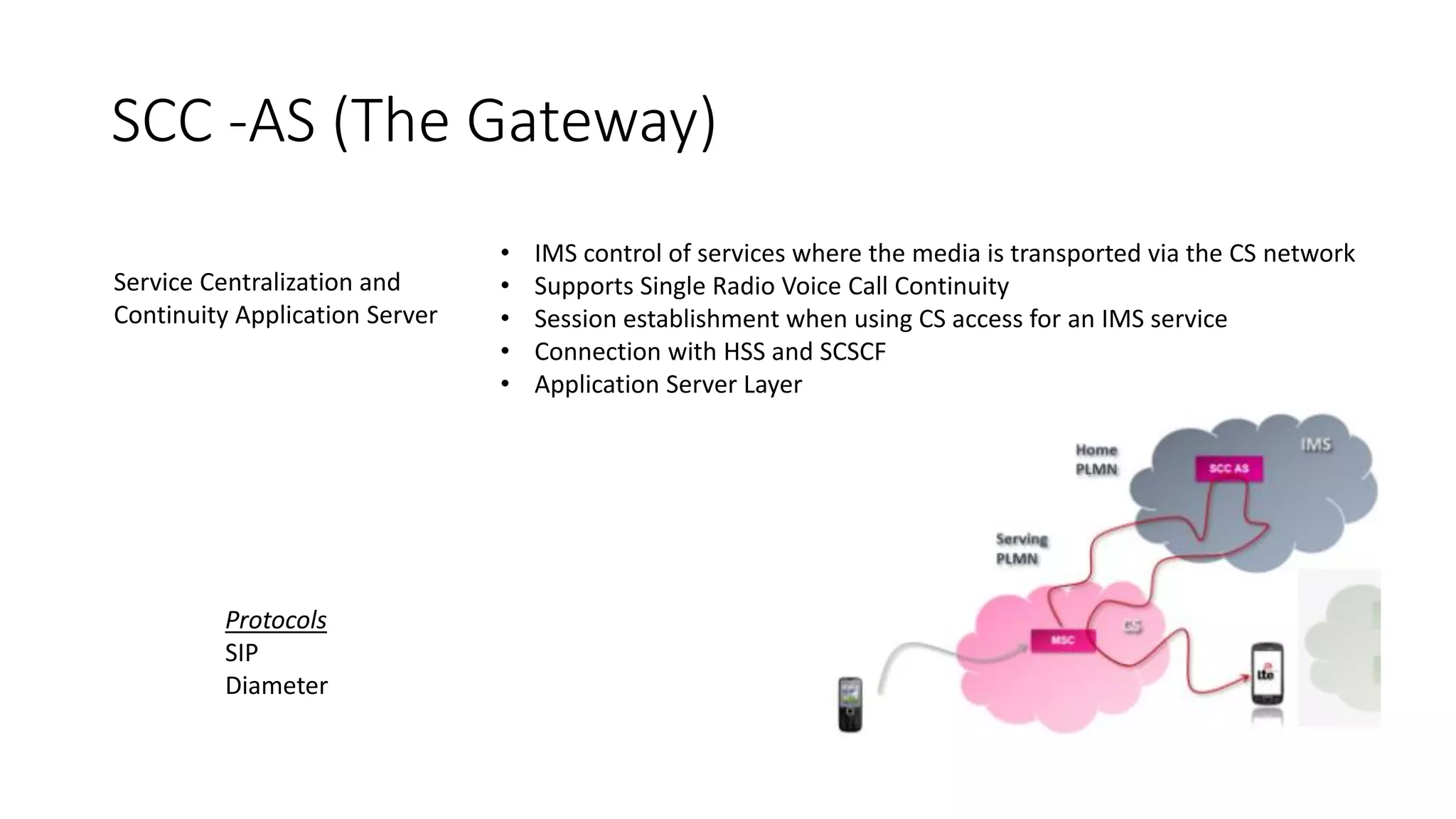
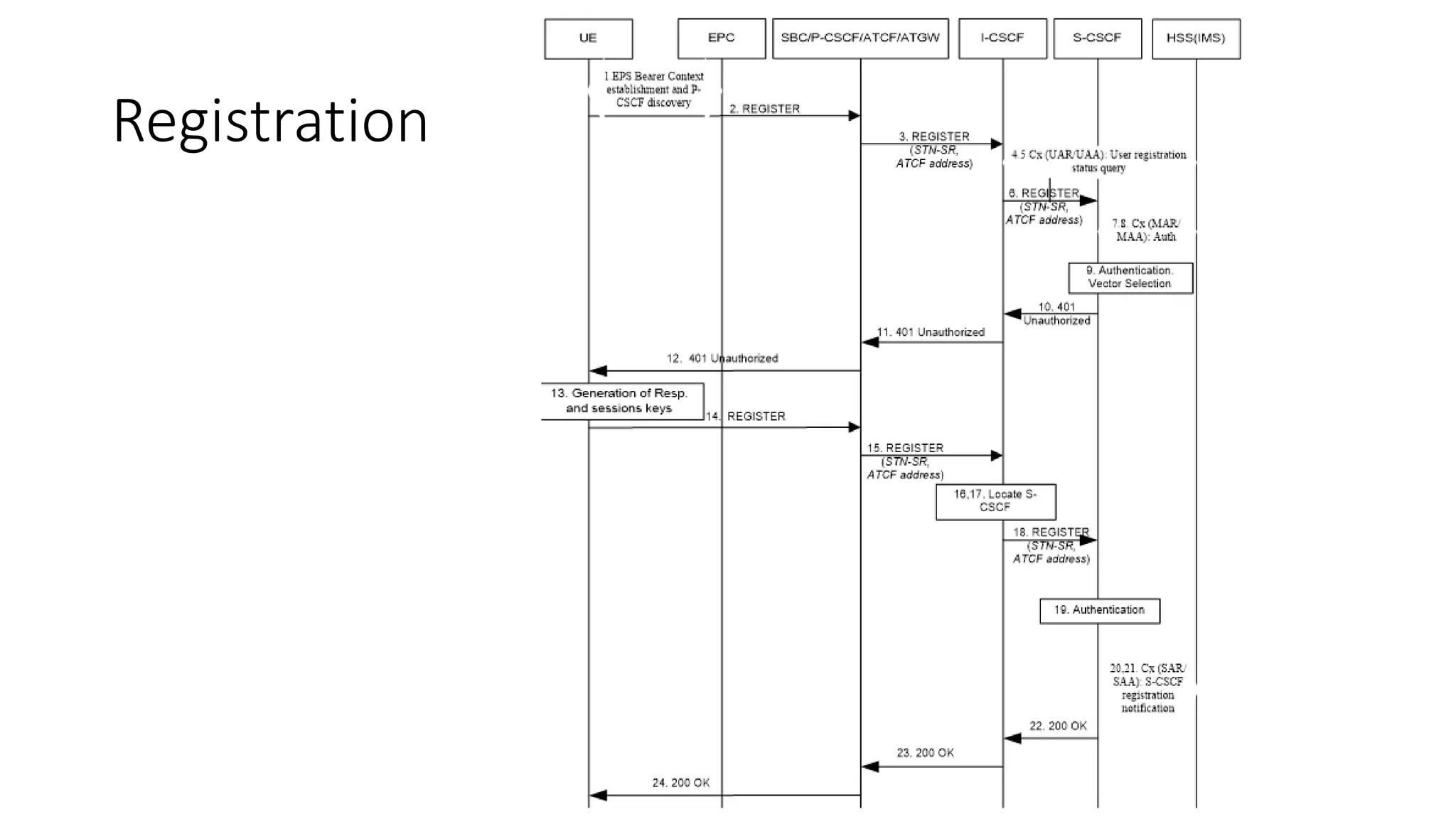
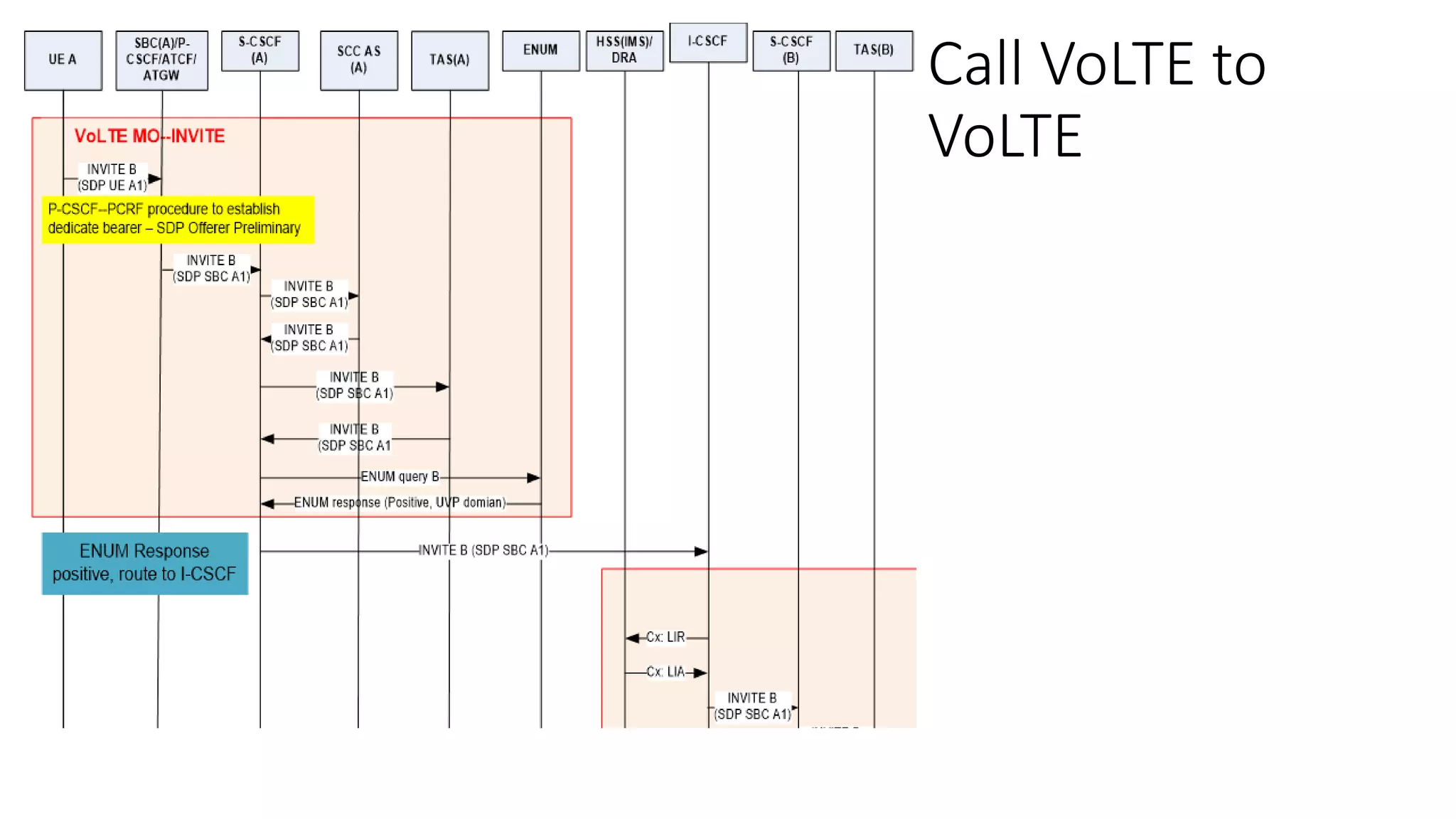
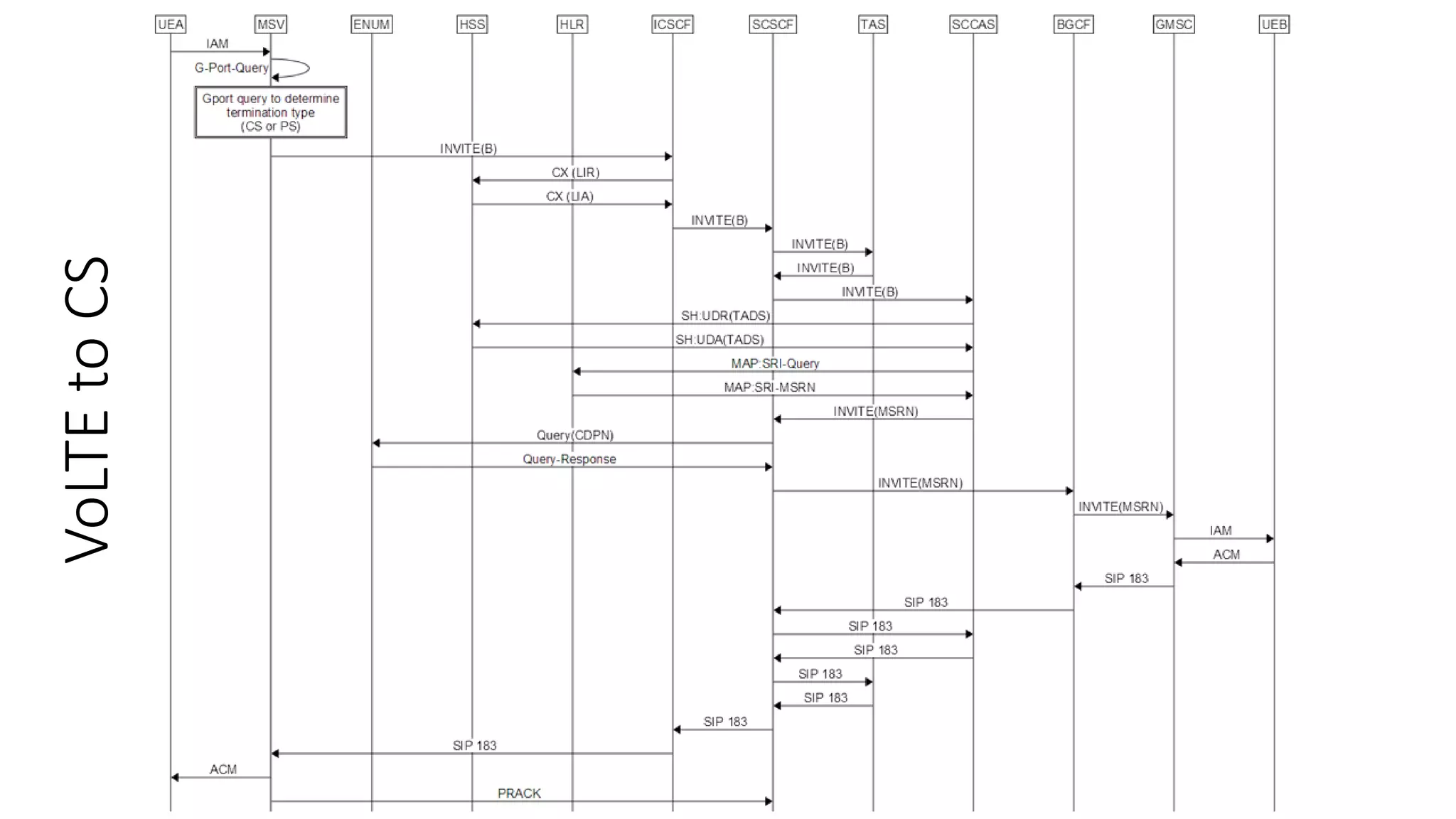
This document provides an introduction to the core IMS/VoLTE network elements and protocols. It describes the evolution from circuit-switched to packet-switched voice services and highlights key differences. The core elements discussed include the P-CSCF, I-CSCF, S-CSCF, AS, MRF, MGW, BGCF, and CCF. Basic call flows for registration and VoLTE-to-VoLTE and VoLTE-to-CS calls are presented to illustrate signaling and interactions between elements.