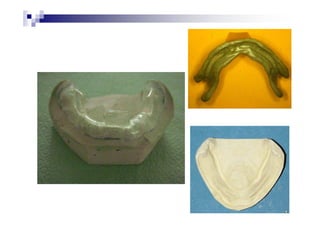
This document discusses different types of impression materials used in dentistry, including their properties and uses. It covers elastic materials like alginate, polyether, polysulfide, and silicone impressions that can record undercuts, as well as rigid materials like plaster, wax, and zinc oxide eugenol. Key properties discussed include accuracy, elasticity, dimensional stability, and setting characteristics. Hydrocolloids like alginate provide good detail but poor stability, while synthetic elastomers offer improved tear resistance and stability at the cost of potential allergic reactions or toxicity. Mixture, properties, advantages, and disadvantages are described for each major material type.