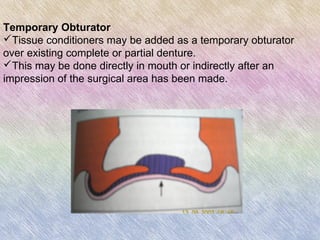
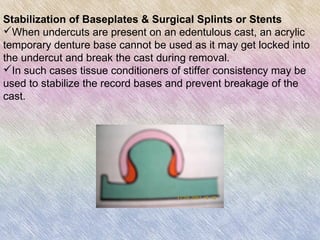
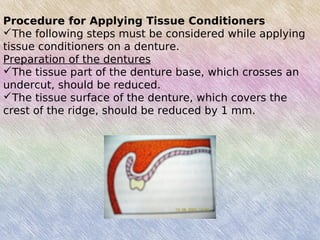
Tissue conditioners are temporary denture liners composed of polyethylmethacrylate and aromatic esters that form a gel when mixed. They have several uses: as adjuncts for tissue healing by protecting irritated tissues before denture fabrication; as temporary obturators over existing dentures; to stabilize denture bases and surgical splints; and to diagnose the effects of resilient denture liners. Tissue conditioners are applied by reducing the denture base, mixing the three components, and molding the material to the denture tissues. They require gentle cleaning to prevent tearing but only provide temporary relief due to loss of plasticizers over 4-8 weeks.