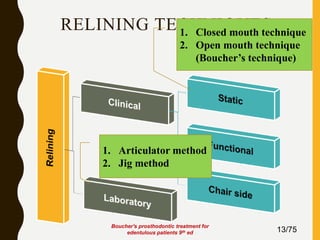
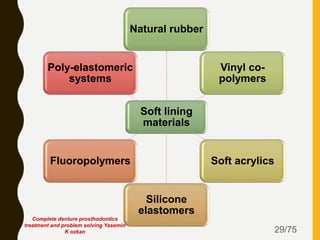
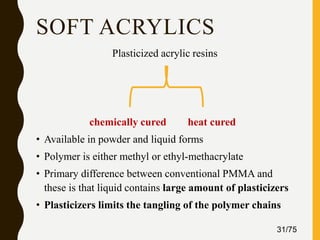
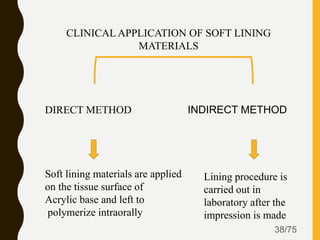
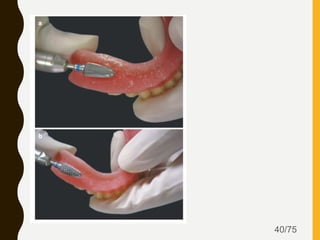
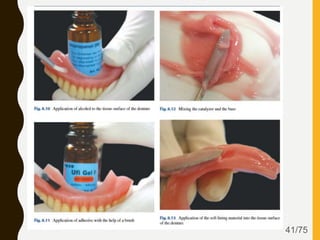
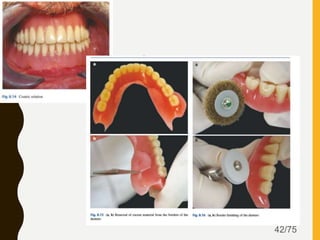
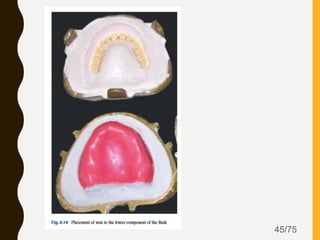
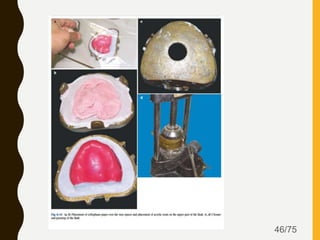
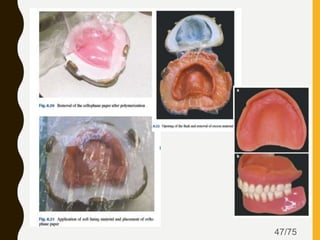
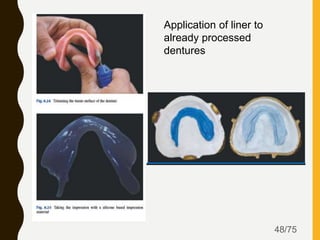
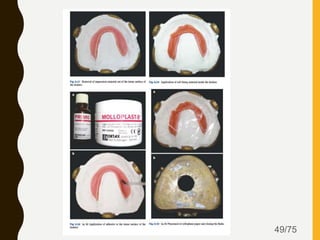
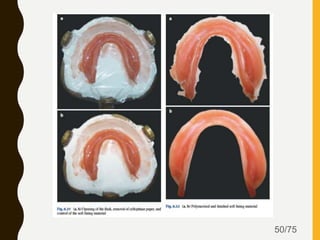
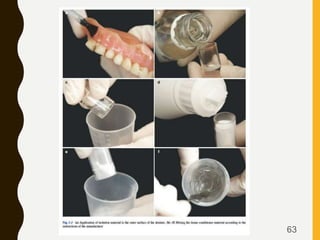
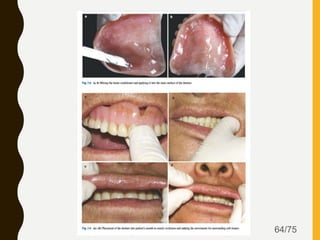
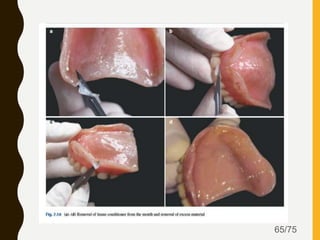
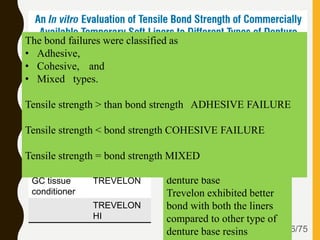
Tissue conditioners and denture liners are used to improve the fit and comfort of removable dentures. They can be classified based on their curing method, composition, durability, consistency and other properties. Tissue conditioners are temporary soft liners that help condition traumatized tissue, while hard and soft denture liners provide a more permanent resilient layer. Relining or rebasing dentures helps maintain proper fit as ridges resorb over time. Selection of the appropriate liner depends on the clinical situation and needs of the patient.