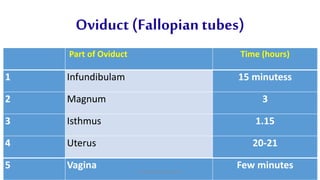
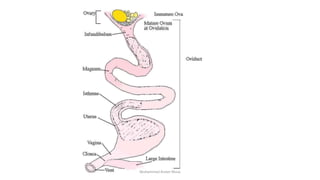
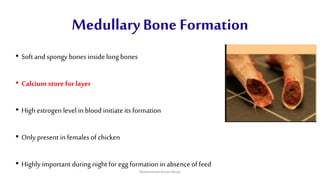
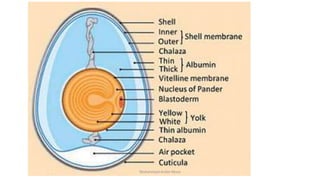
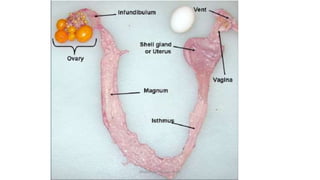
The egg formation process in chickens takes approximately 23-26 hours. The yolk develops first in the ovary over 10 days. Once matured, hormones cause the yolk to be released into the oviduct where various secretions are added over time in different sections to form the albumen and shell. This process is regulated by female reproductive hormones and results in a semi-solid nutritional mass being laid roughly every 25 hours.