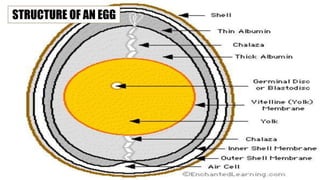
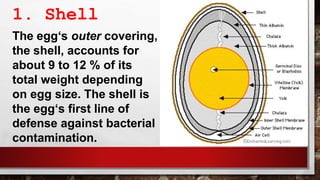
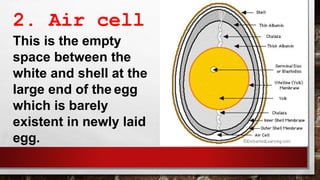
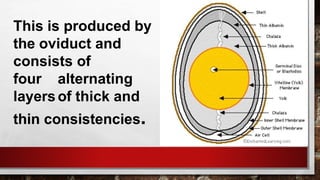
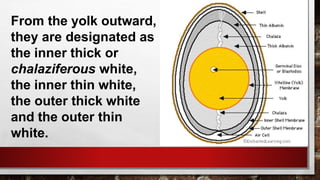
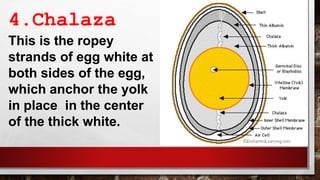
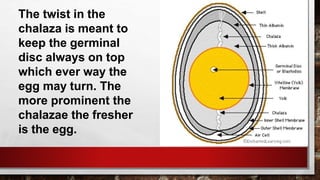
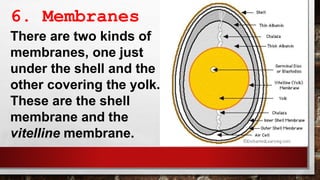
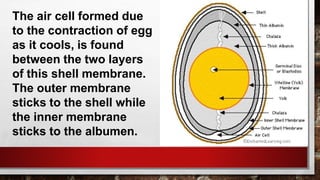
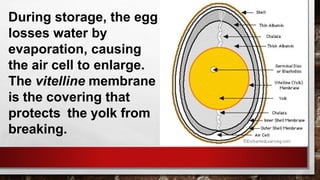
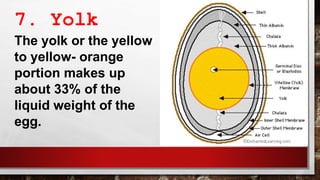
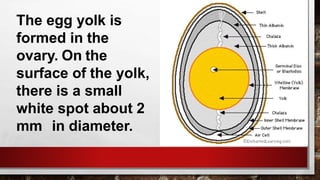
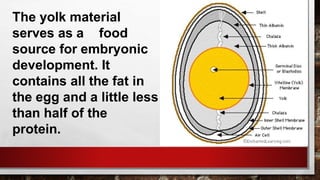
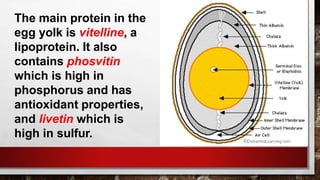
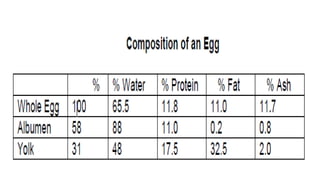
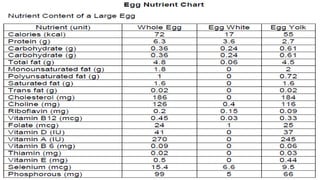
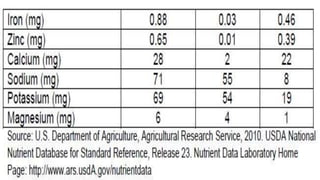
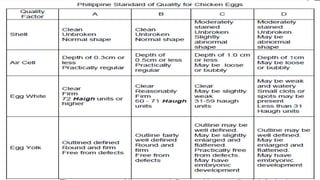
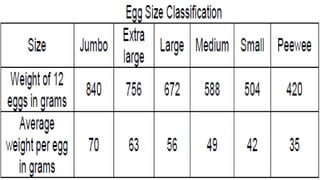
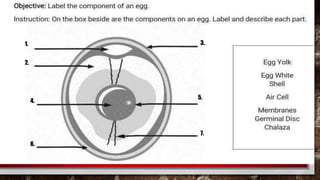
The document describes the physical structure and composition of eggs. It details the three main parts of an egg: the shell, egg white, and egg yolk. The egg white accounts for most of the egg's liquid weight at around 67% and consists of four alternating layers. The yolk makes up about 33% of the liquid weight and contains all of the egg's fat and around half of its protein.