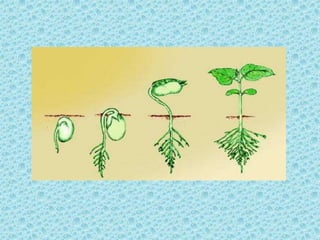
This document discusses the importance of water for living organisms. It states that water is essential for all life and is used by humans, plants and animals for various purposes. The document outlines how different types of organisms like aquatic animals, amphibians, and aquatic plants rely on water. It also describes how groundwater is extracted and how modern water supply systems work.