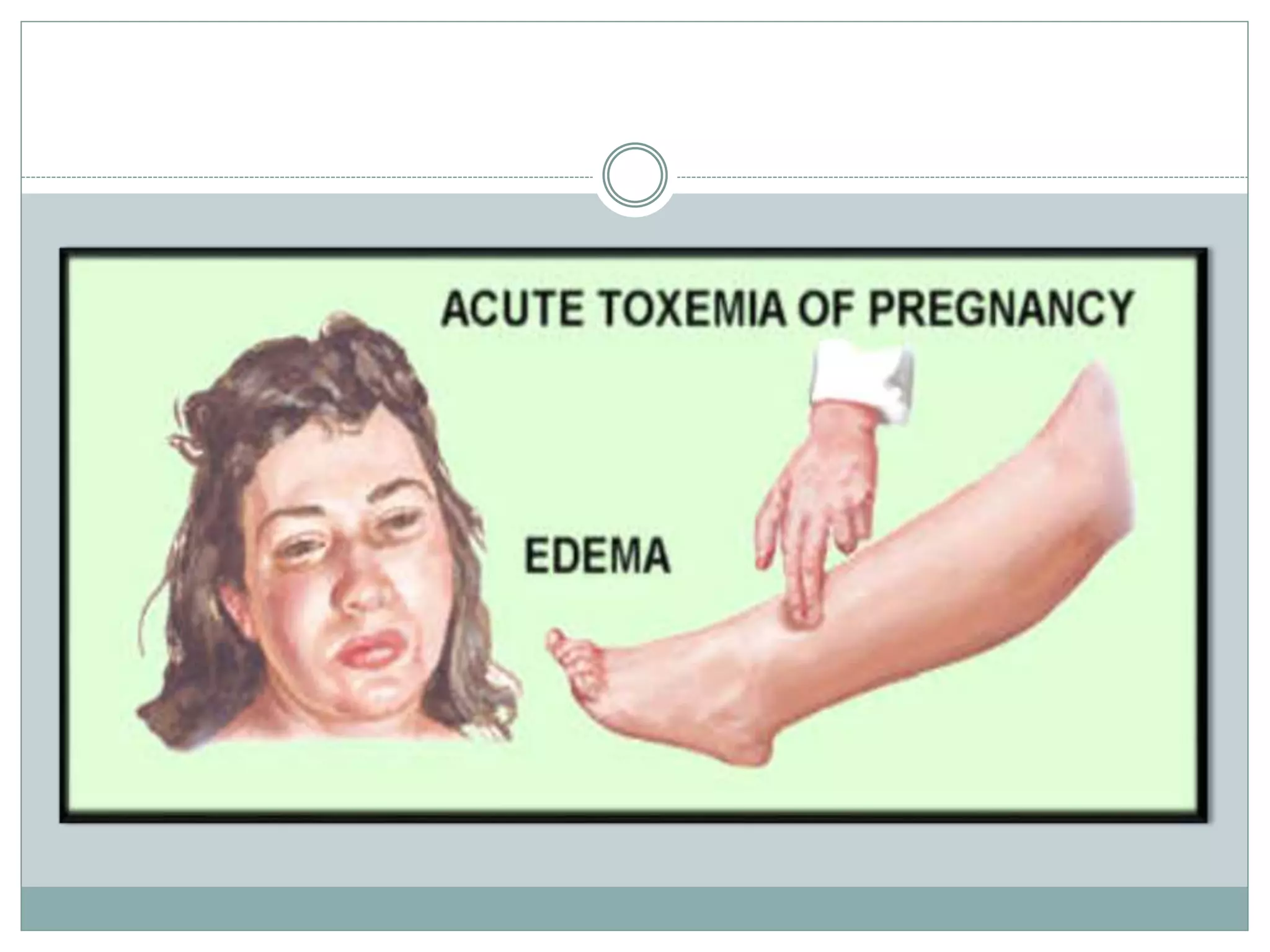
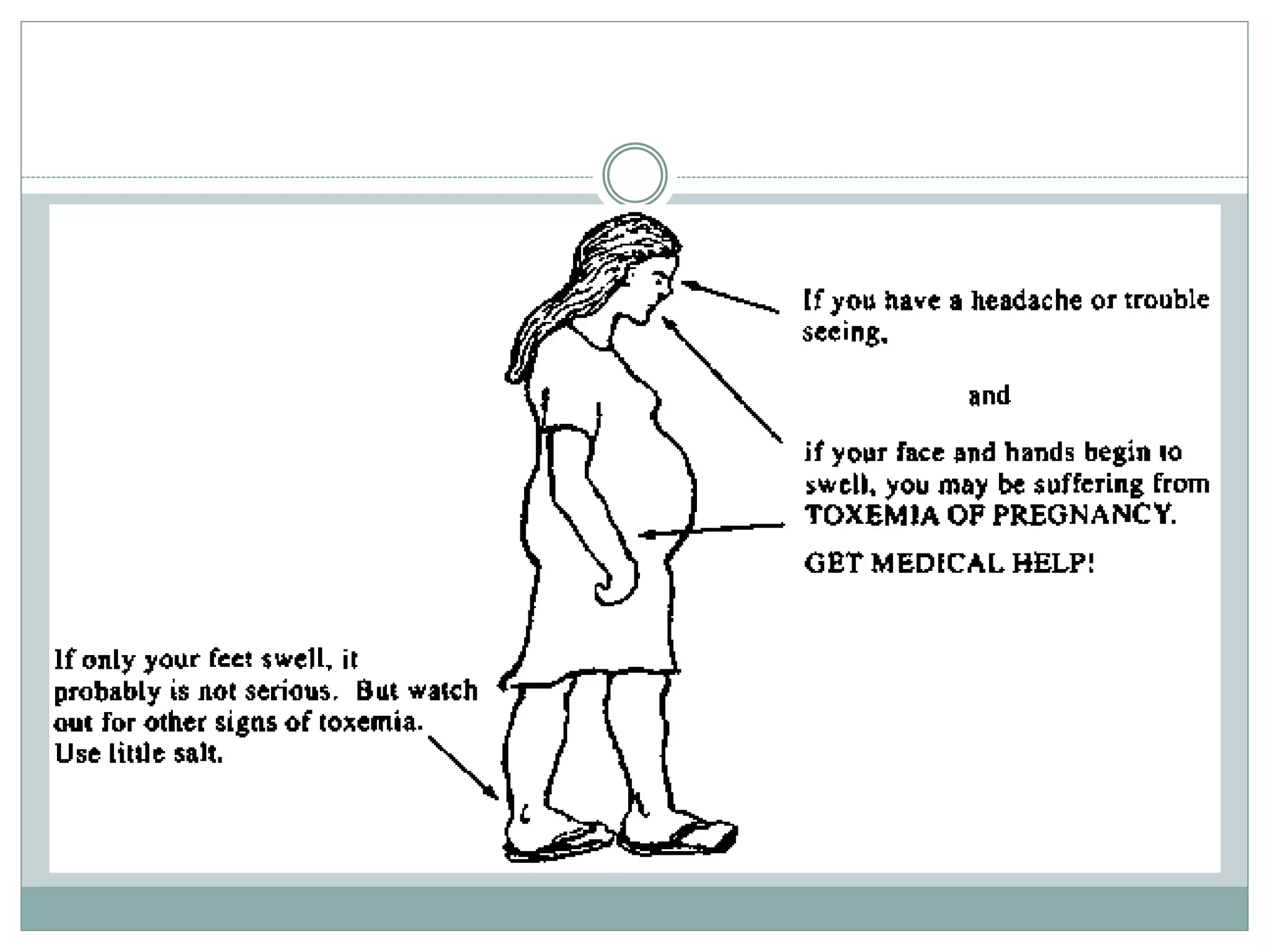
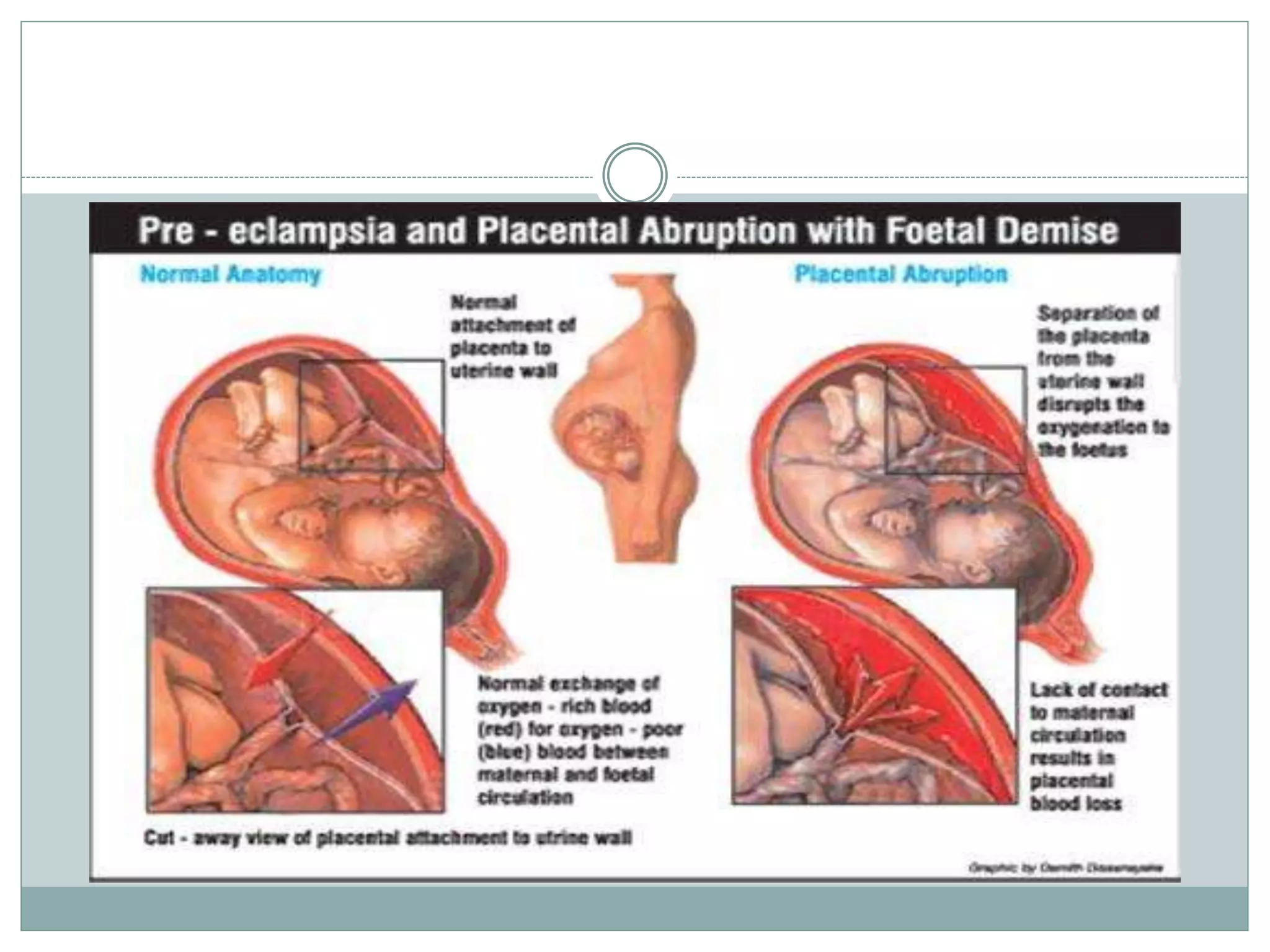
Toxemia in pregnancy, now called preeclampsia, is a condition characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine that affects 3-8% of pregnancies. It can threaten the health of the mother and baby. Symptoms include swelling, headaches, vision changes, and abdominal pain. Risk factors include first pregnancies, obesity, chronic high blood pressure, and a family history of preeclampsia. Treatment focuses on delivering the baby to resolve the condition, with close monitoring until then. Untreated preeclampsia can lead to serious maternal complications like seizures or organ damage and threaten the baby's growth and development.