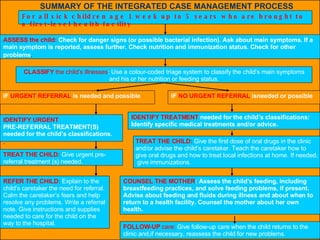
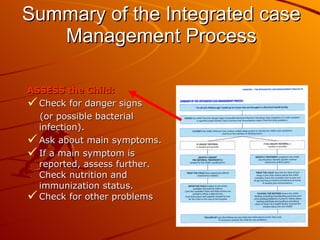
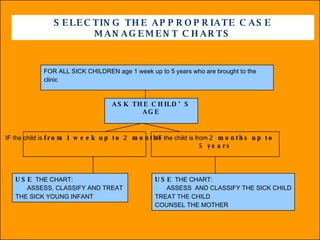
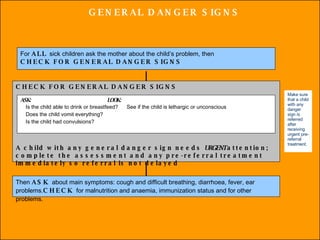
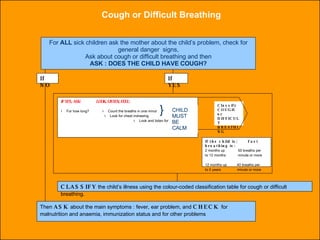
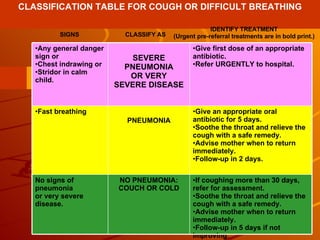
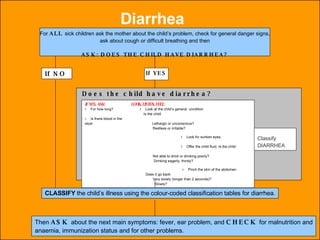
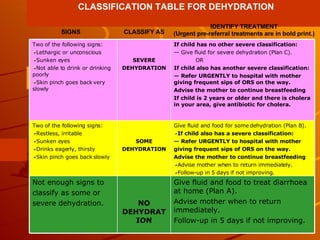
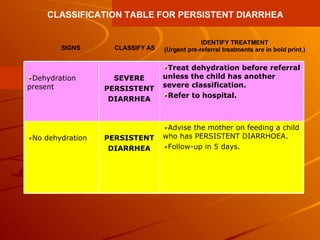
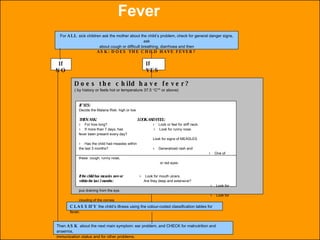
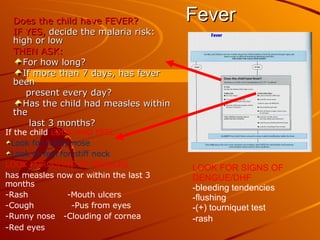
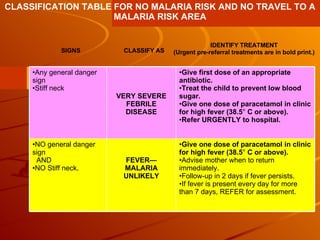
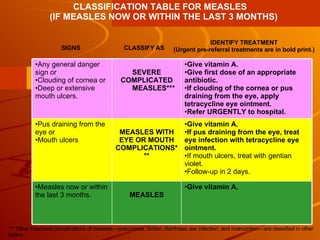
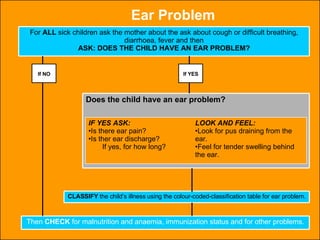
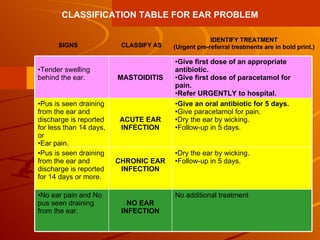
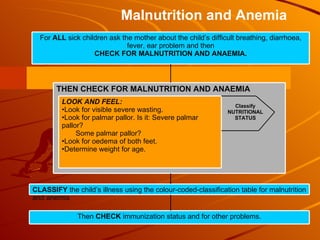
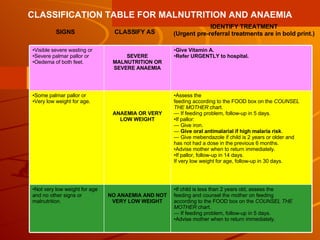
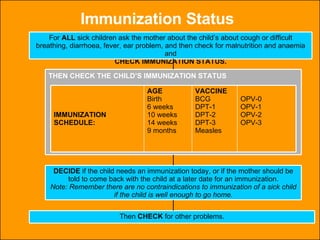
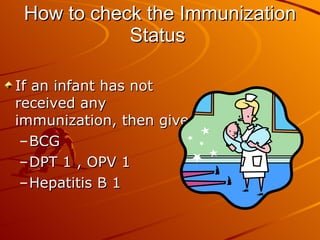
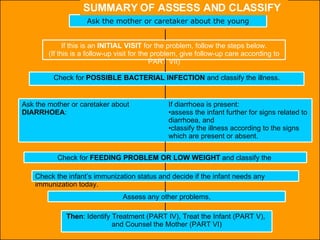
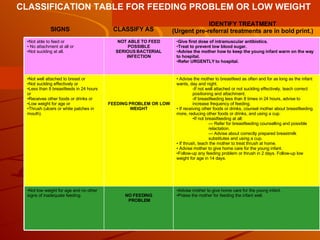
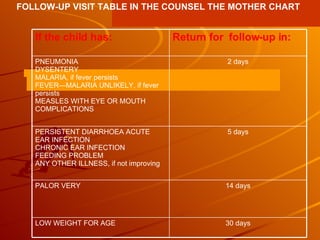
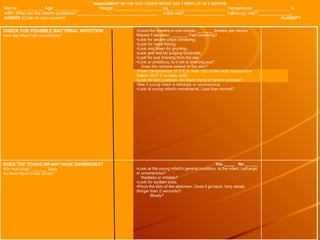
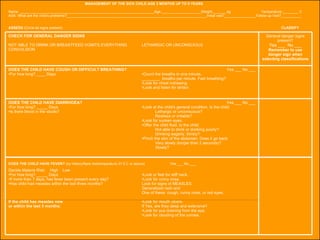
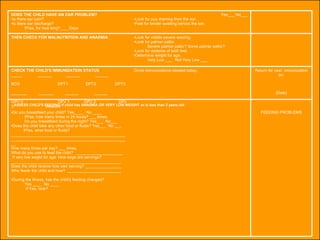
The integrated case management process is a standardized approach used to assess, classify, treat and provide follow-up care for sick children ages 1 week to 5 years who present at first-level health facilities. It involves assessing the child for symptoms and danger signs, classifying illnesses using color-coded charts, identifying and providing treatments, counseling the mother, and arranging follow-up care. The goal is to effectively manage the major causes of childhood illness and reduce mortality and morbidity.