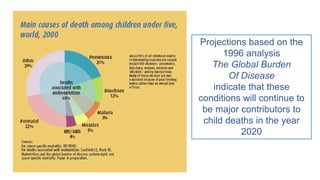
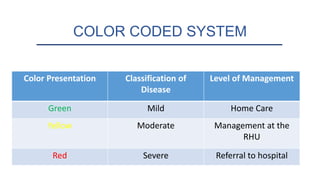
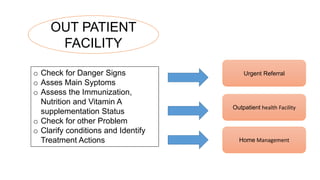
The Integrated Management of Childhood Illnesses (IMCI) is a strategy developed by WHO and UNICEF to address high child mortality rates. IMCI combines improved management of common childhood illnesses with nutrition, immunization, and other aspects of primary healthcare. It has three main components: improving health workers' case management skills through guidelines; strengthening health systems; and promoting better family/community practices. The IMCI case management process involves assessing children for danger signs, classifying illnesses, identifying treatments, providing counseling and follow up care.