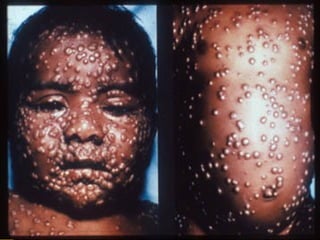
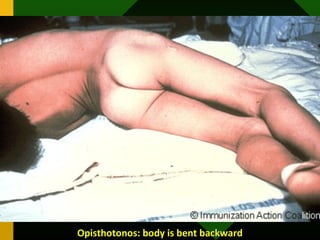
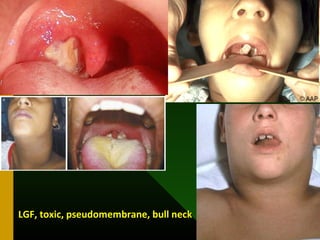
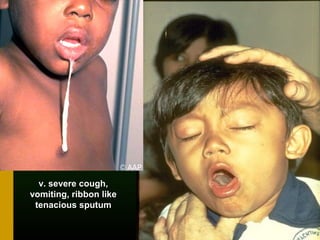
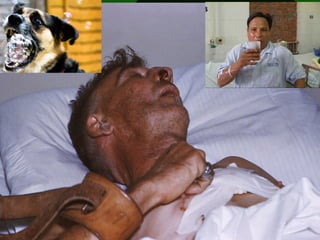
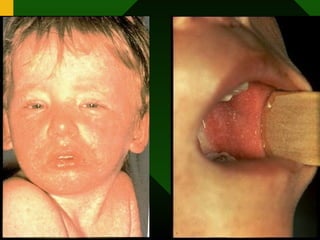
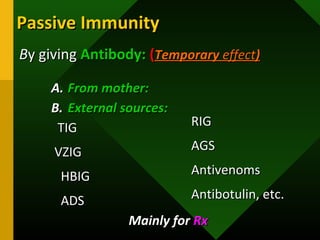
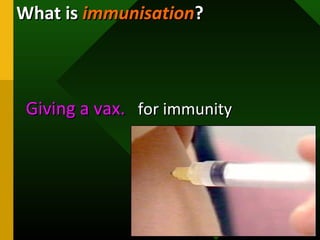
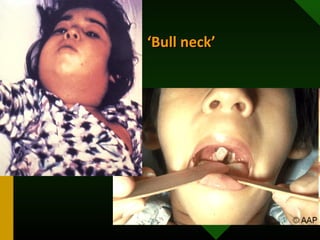
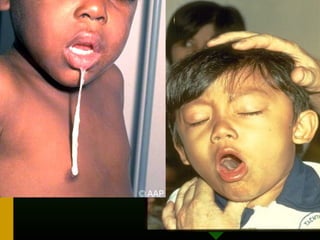
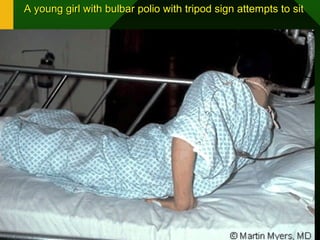
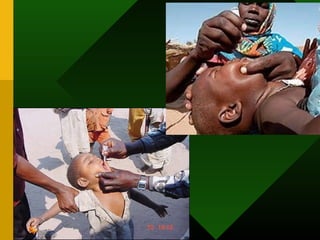
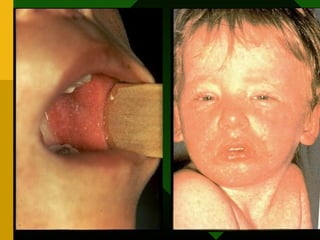
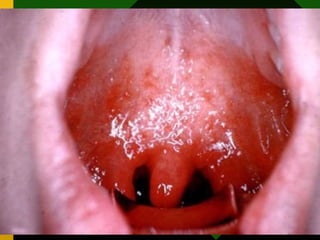
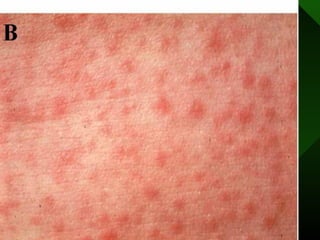
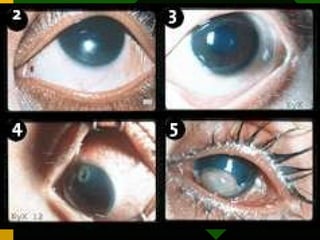
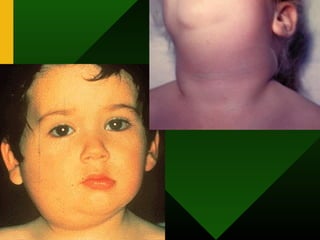
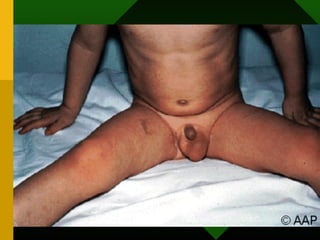
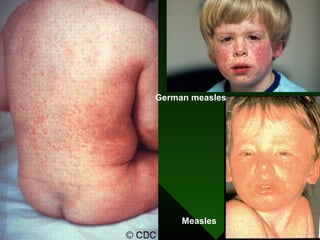
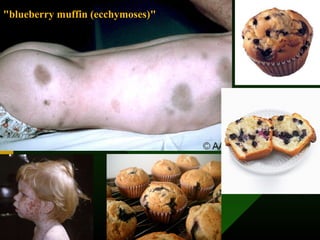
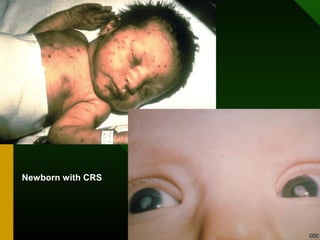
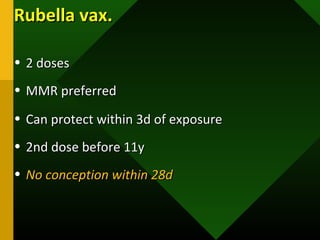
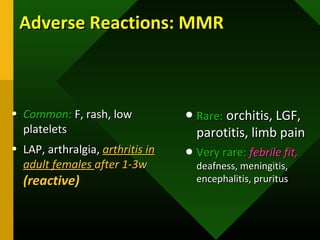
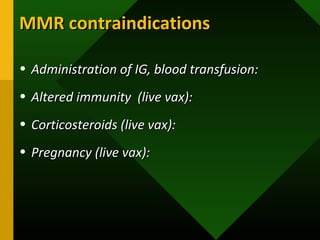
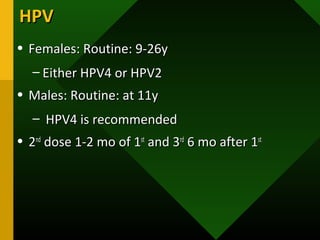
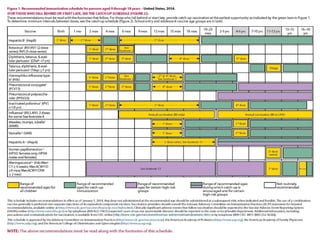
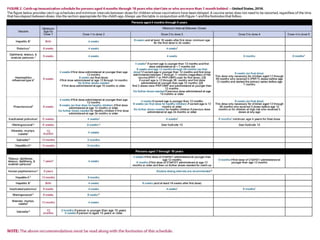
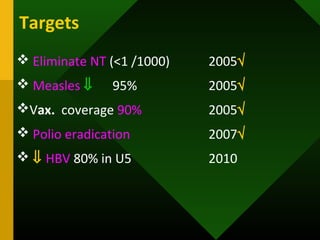
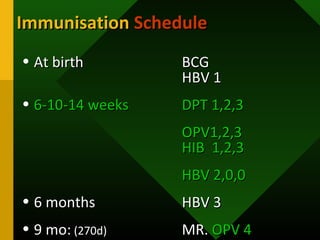
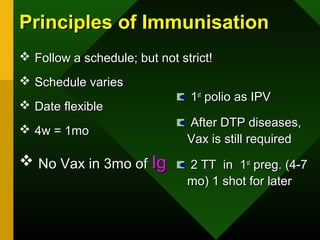
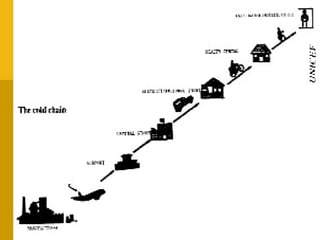
The document discusses various vaccines including their administration, effectiveness, and side effects. It notes that vaccines for diphtheria, pertussis, and tetanus (DPT) are given in a 3-dose series at 6-10-14 weeks and provide protection for 10 years. The measles vaccine is highly effective but needs to be given after 6 months of age to avoid interference from maternal antibodies. The mumps and rubella vaccines are part of the combined MMR vaccine. Rare side effects of the MMR include febrile seizures and deafness.