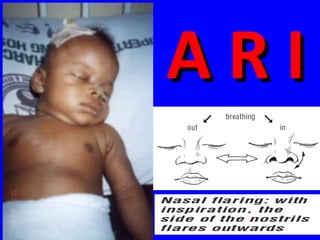
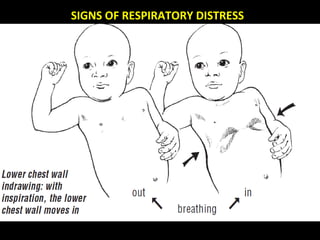
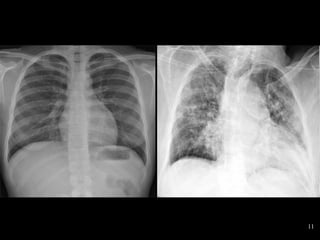
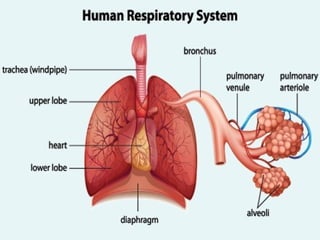
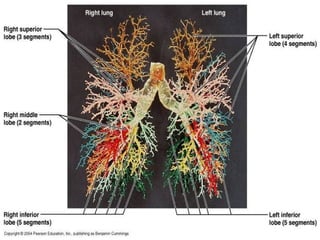
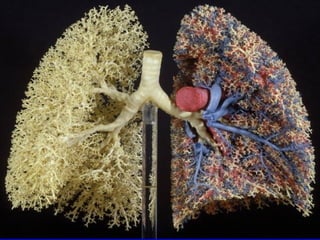
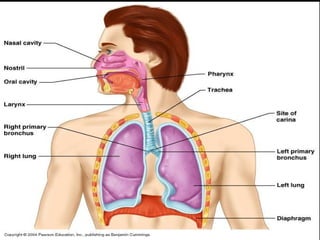
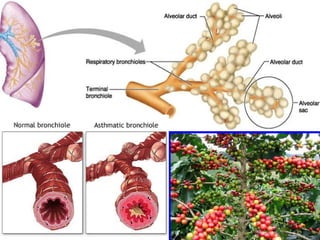
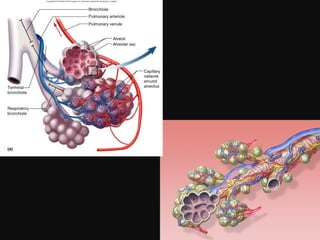
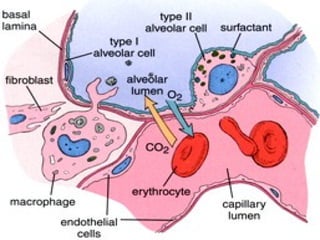
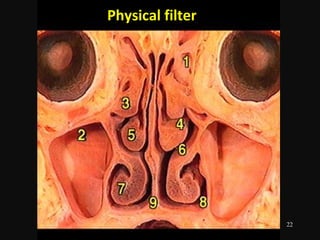
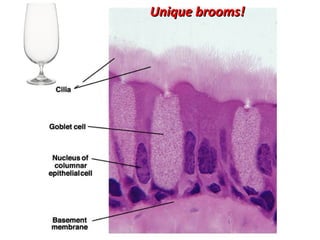
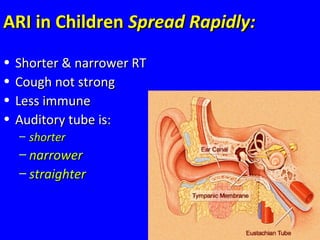
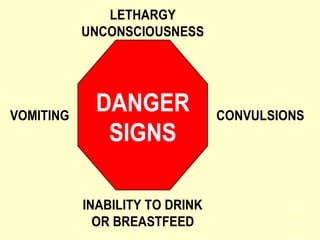
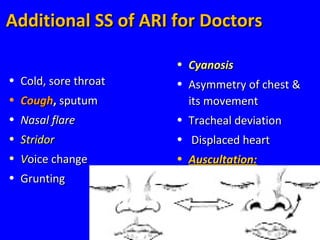
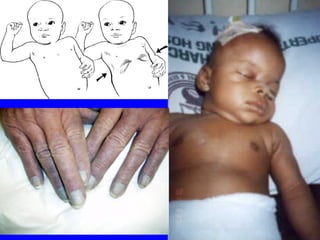
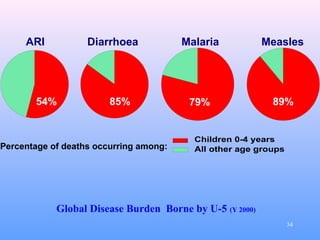
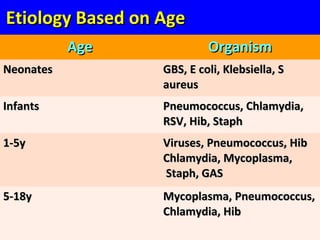
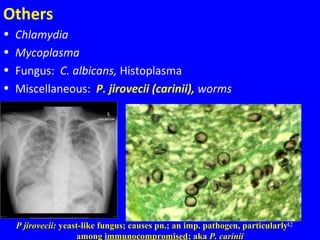
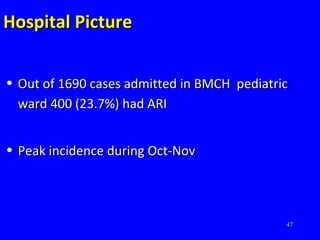
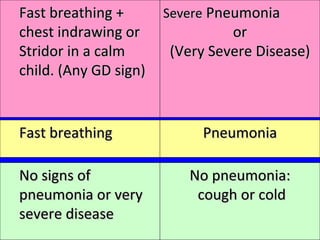
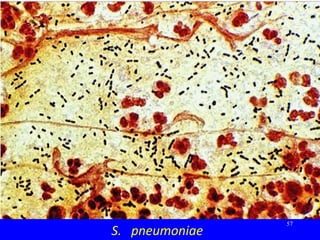
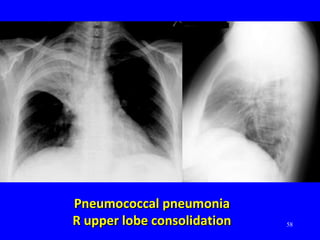
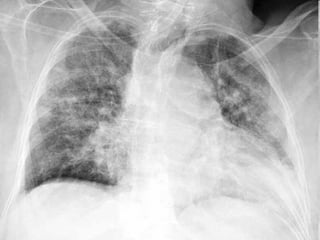
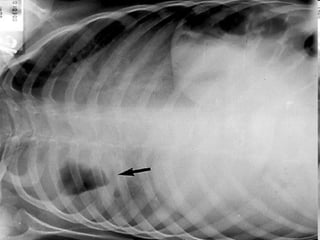
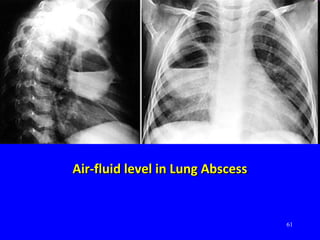
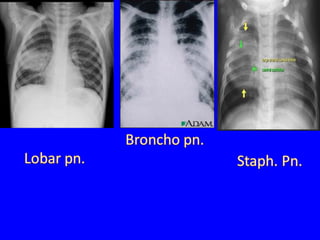
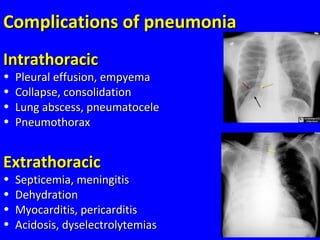
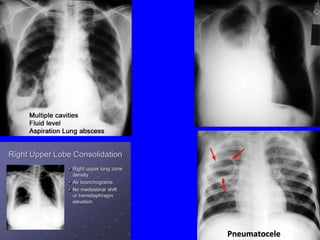
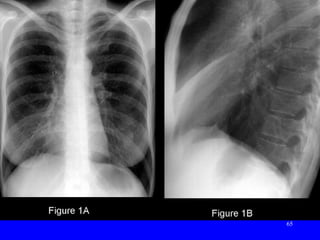
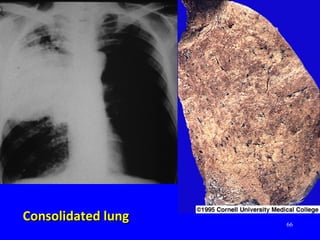
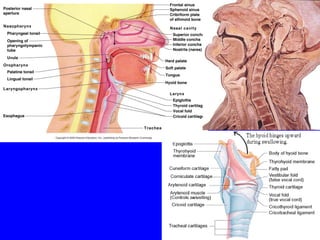
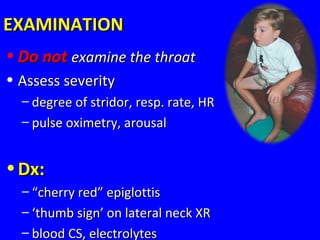
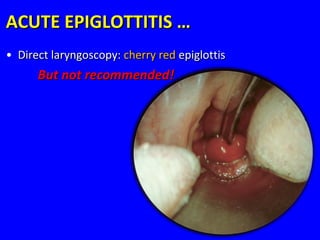
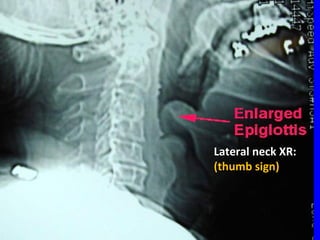
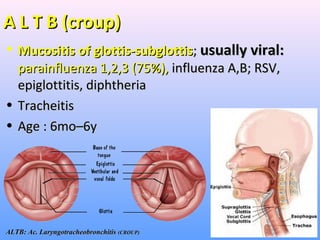
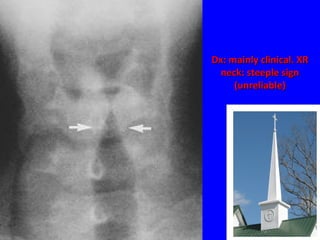
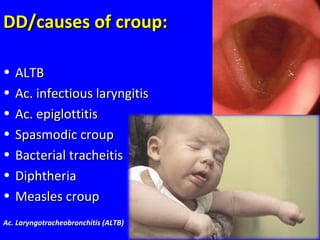
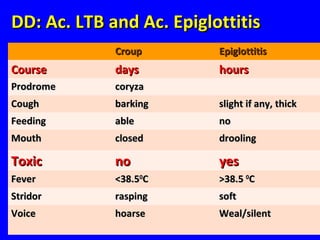
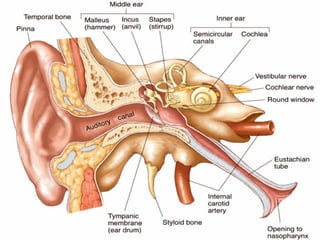
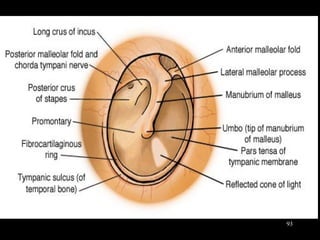
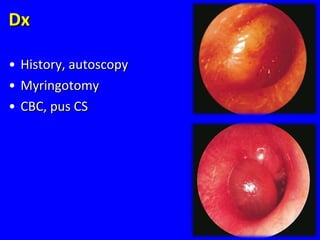
The document discusses acute respiratory infections (ARIs) in children under 5 years old. It defines ARI and describes the signs and symptoms, including fast breathing and chest indrawing. Common causes are viruses like RSV and bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae. ARIs often spread rapidly in young children due to anatomical factors. They are a major cause of mortality, responsible for around 900,000 child deaths per year. Proper treatment with low-cost measures can reduce the death toll from ARIs.