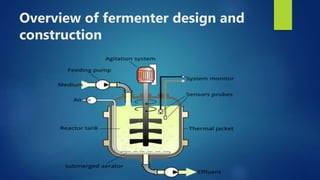
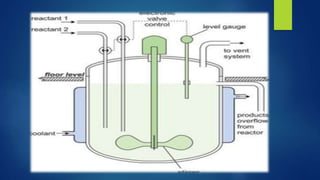
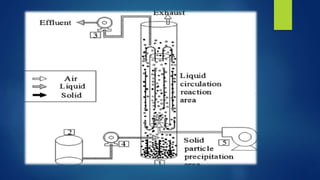
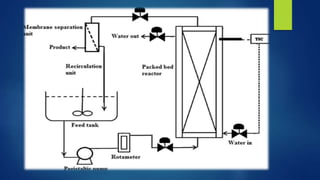
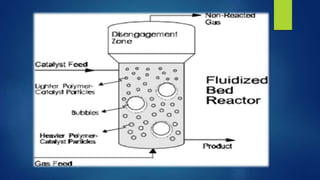
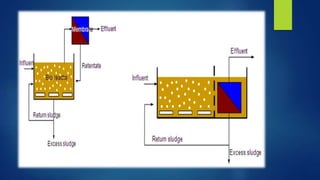
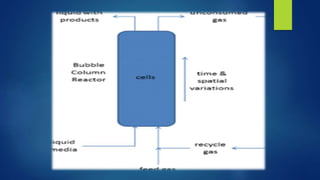
The document discusses different types of fermentors or bioreactors used in microbiology. It begins with an introduction to fermentors and their basic functions. It then describes various components of fermentor design including agitation systems, aeration systems, temperature control, and classifications of fermentors. Common types of fermentors are discussed such as continuous stirred tank reactors, airlift reactors, packed bed reactors, fluidized bed reactors, and membrane bioreactors. The advantages and disadvantages of different fermentor designs are highlighted.