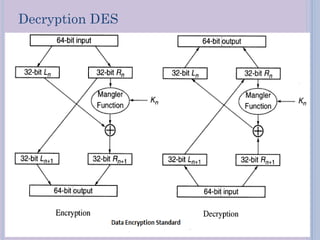
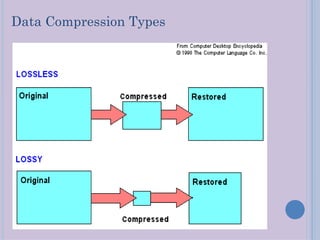
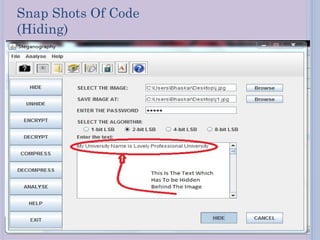
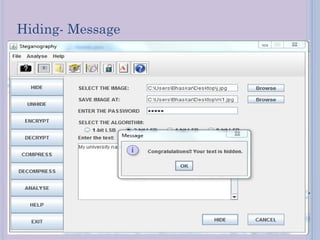
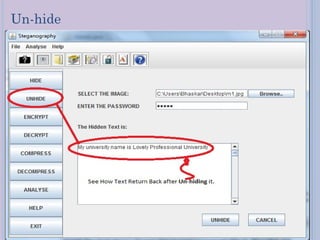
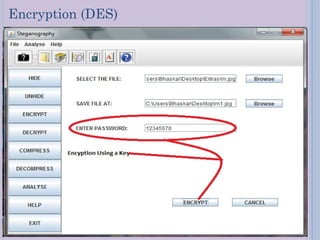
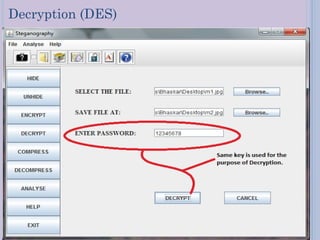
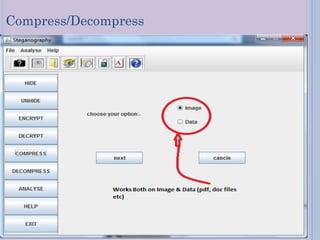
Steganography is a technique for hiding secret messages within other non-secret files like images, audio, or video. It works by embedding messages into the least significant bits of pixel data in an image or by masking digital signatures in portions of audio or video files. The document discusses steganography tools and algorithms for hiding data in images using techniques like LSB insertion and encryption algorithms like DES. It also covers data compression methods like Lempel-Ziv-Welch used for reducing file sizes.




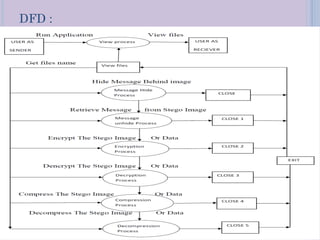
![ALGORITHM FOR HIDING MESSAGE
BEHIND IMAGE :-
Suppose my message is “hello” with the password
“12345”.
String p ,m;
Convert it into the binary form.
By using the pixel grabber class it take each pixel
of the image.
Which we will store in the in the array say a[ ].
Converting it into binary form it gives 32-bit.
Then we remove 8-bits which is of sign bit.
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/steganography-13344720859451-phpapp02-120415014329-phpapp02/85/Steganography-9-320.jpg)