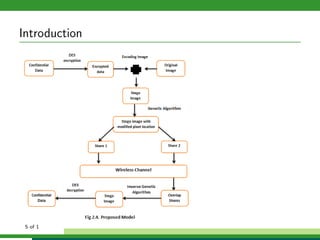
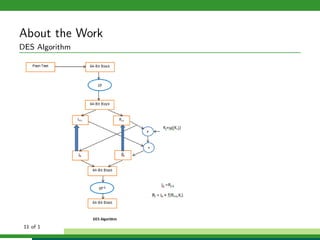
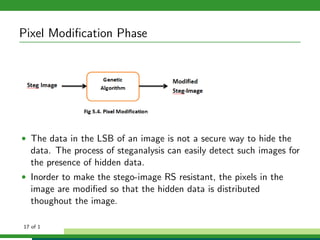
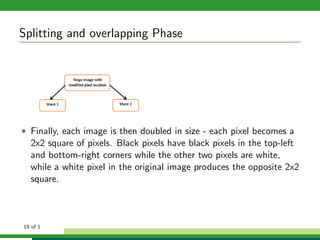
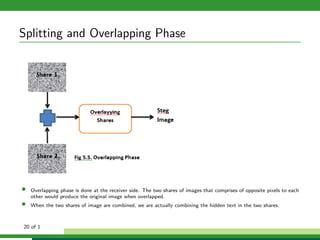
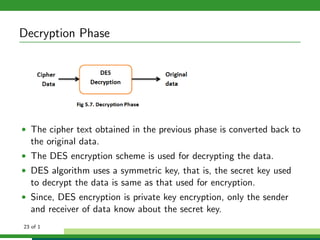
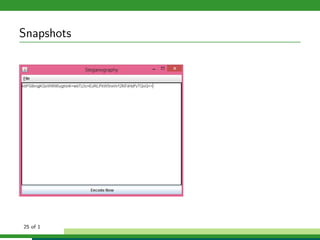
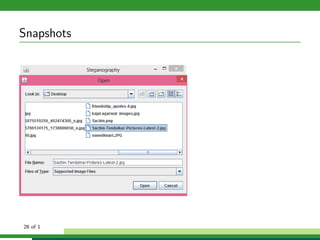
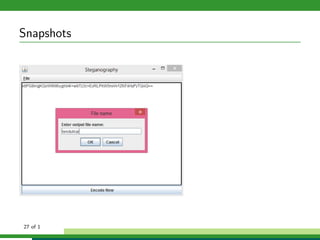
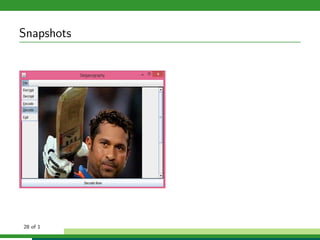
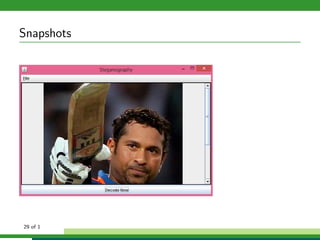
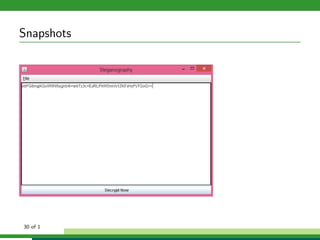
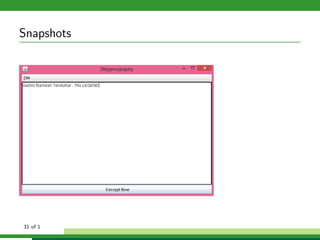
The document outlines a project focused on secure data hiding and transmission over wireless networks using a combination of least significant bit (LSB) steganography, genetic algorithms, and visual cryptography to enhance data security. It details the phases of the proposed system, including encryption, encoding, pixel modification, splitting, overlapping, decoding, and decryption, emphasizing the use of DES encryption and the complexity of message detection. The paper concludes that this enhanced secure algorithm significantly improves the reliability and security of hidden data transmission.