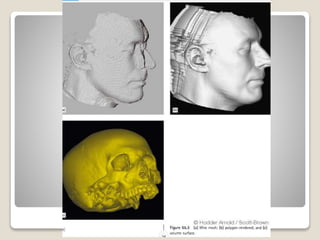
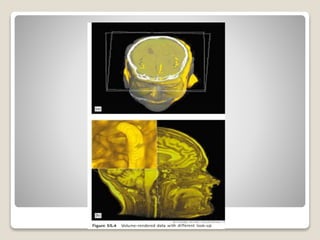
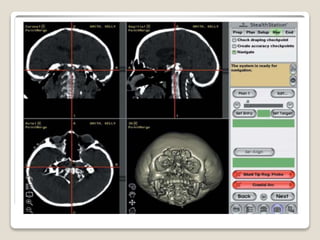
Image guided surgery involves using preoperative scans like MRI or CT to create 3D reconstructions of the surgical area. This information can be used for surgical planning, simulation, and navigation during the procedure. For navigation, the 3D models are registered to the patient in the operating room using probes to locate anatomical landmarks. This allows the surgeon to view internal structures and track the position of surgical tools to aid precision. Key benefits are improved accuracy, reduced risks to vital structures, and assistance for complex cases where normal anatomy is distorted.