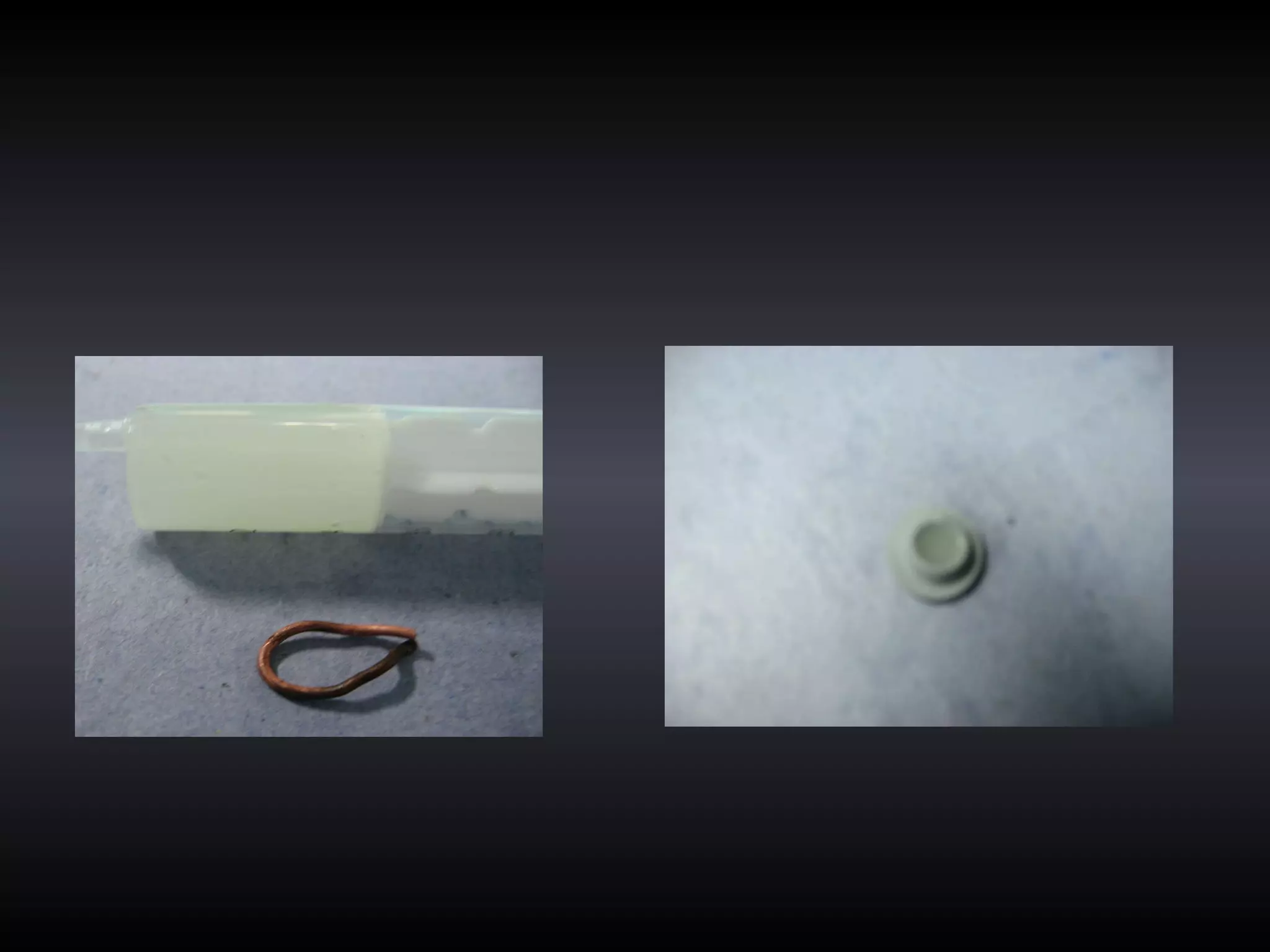
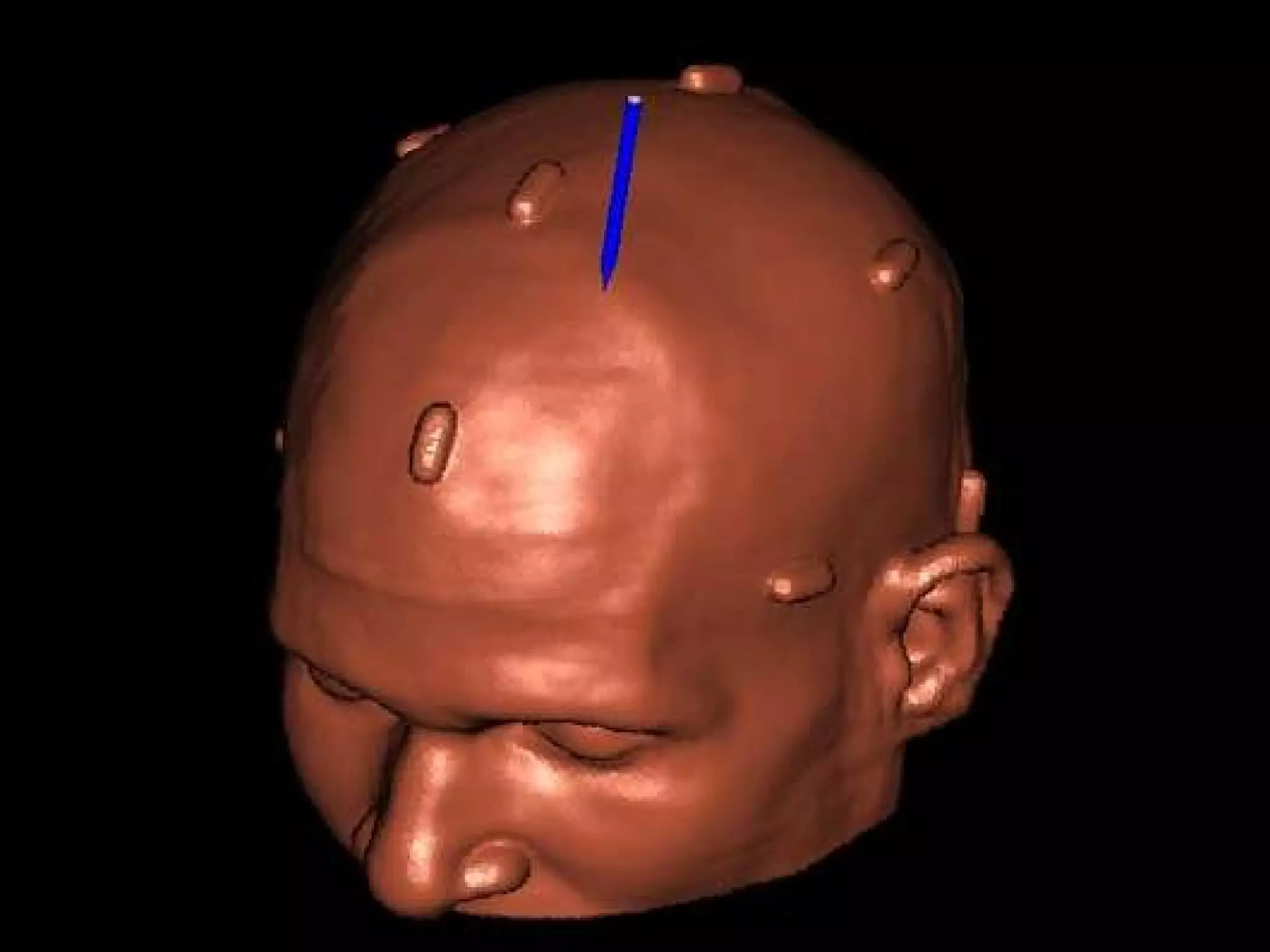
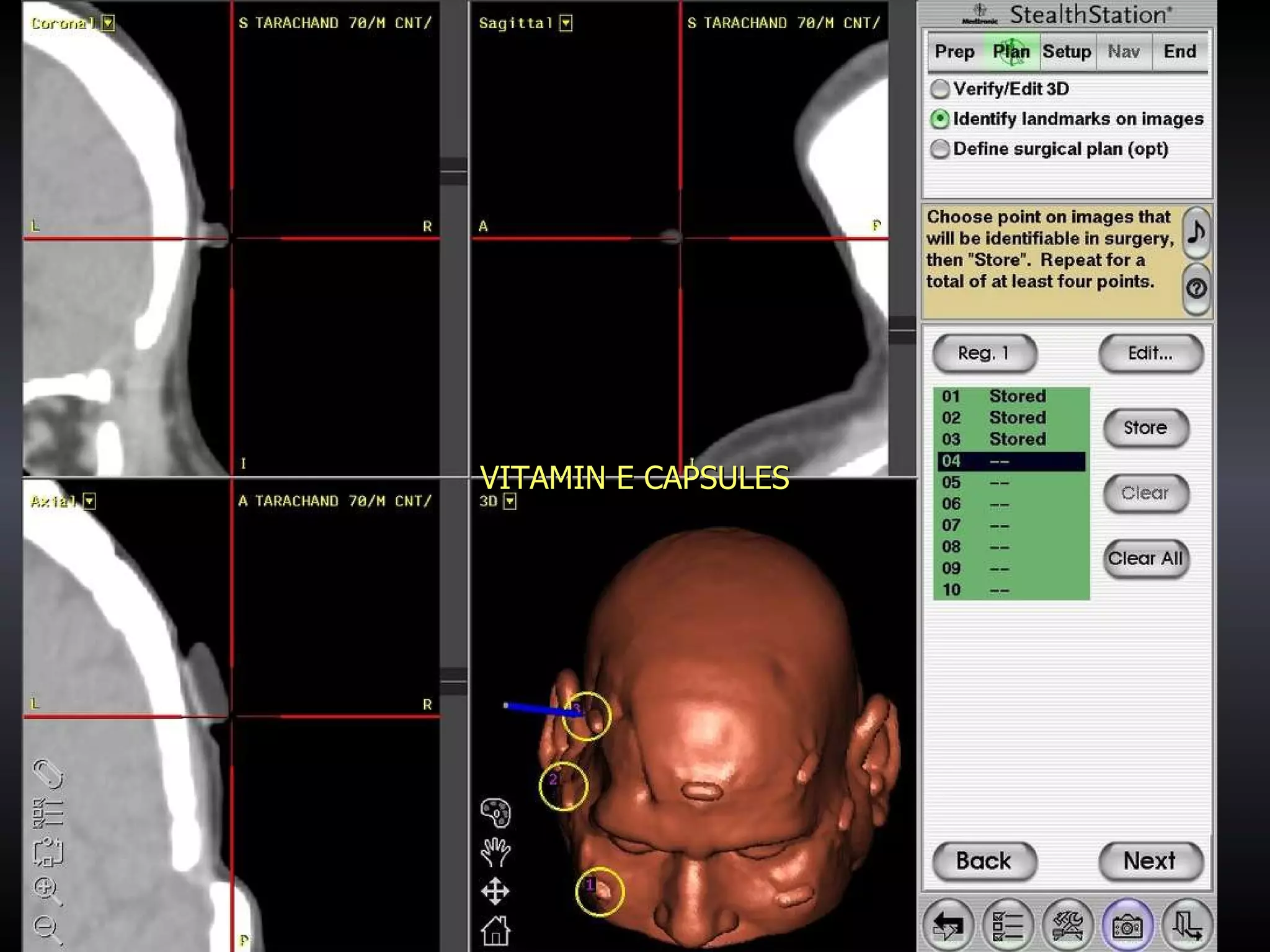
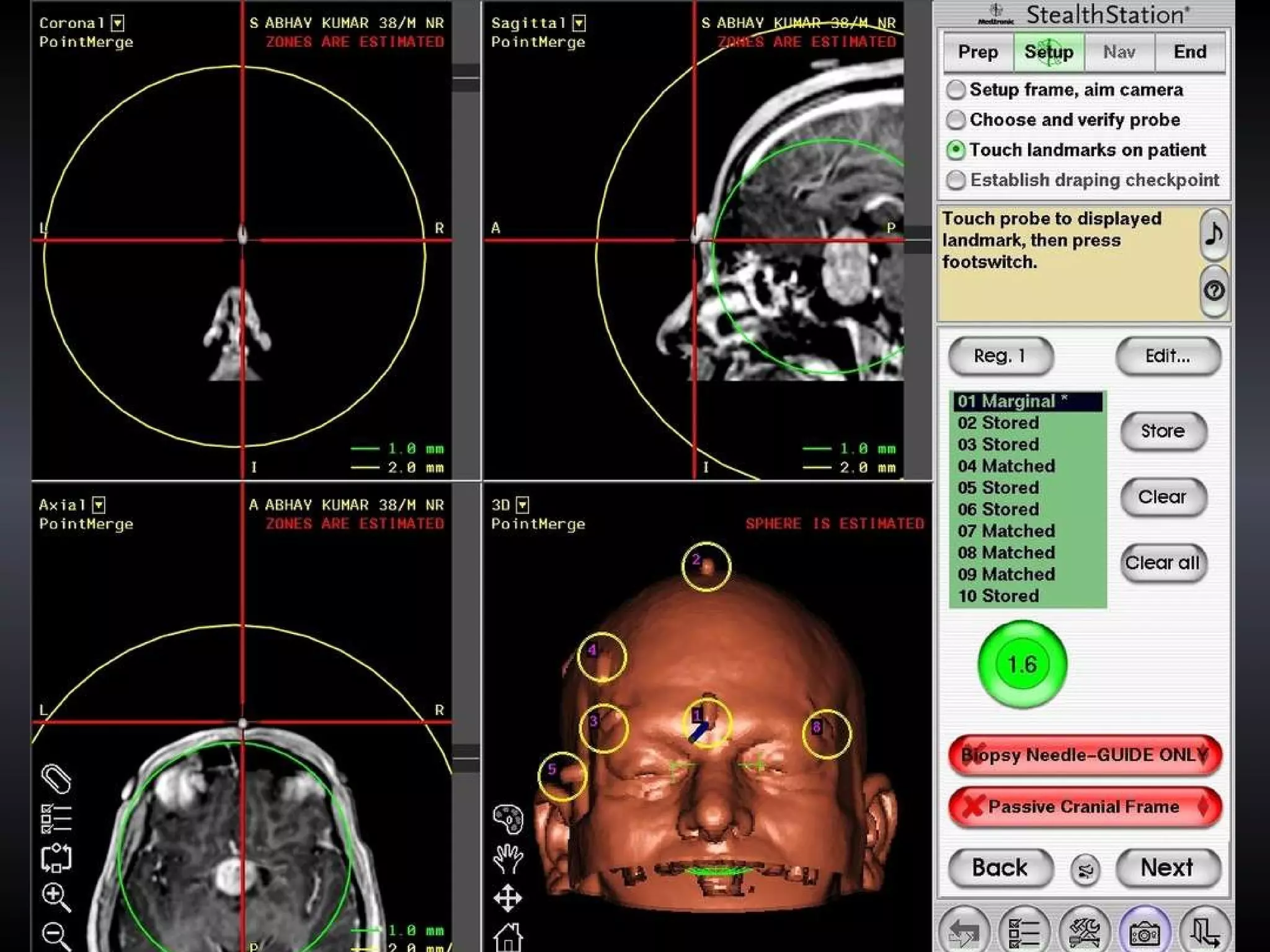
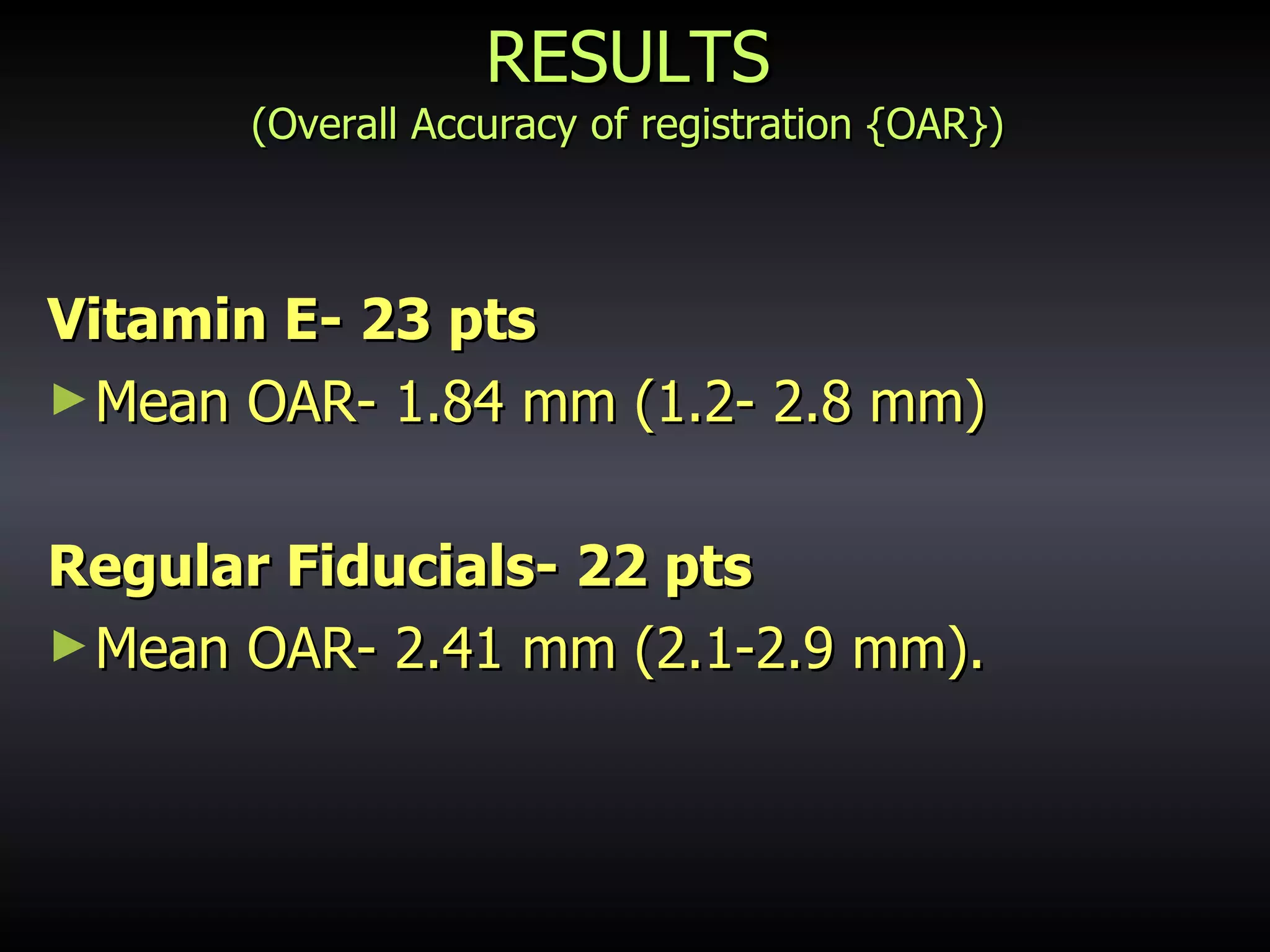
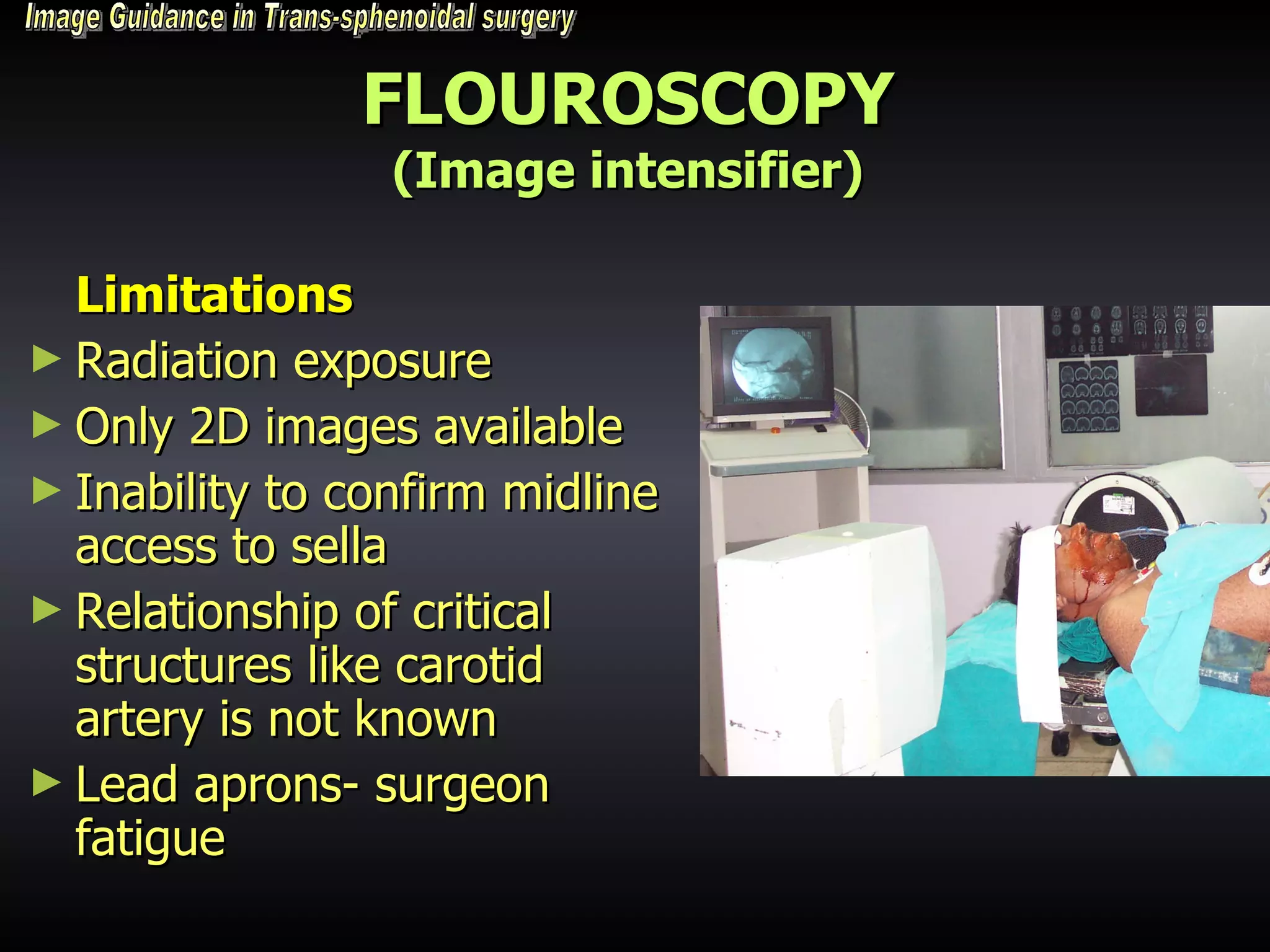
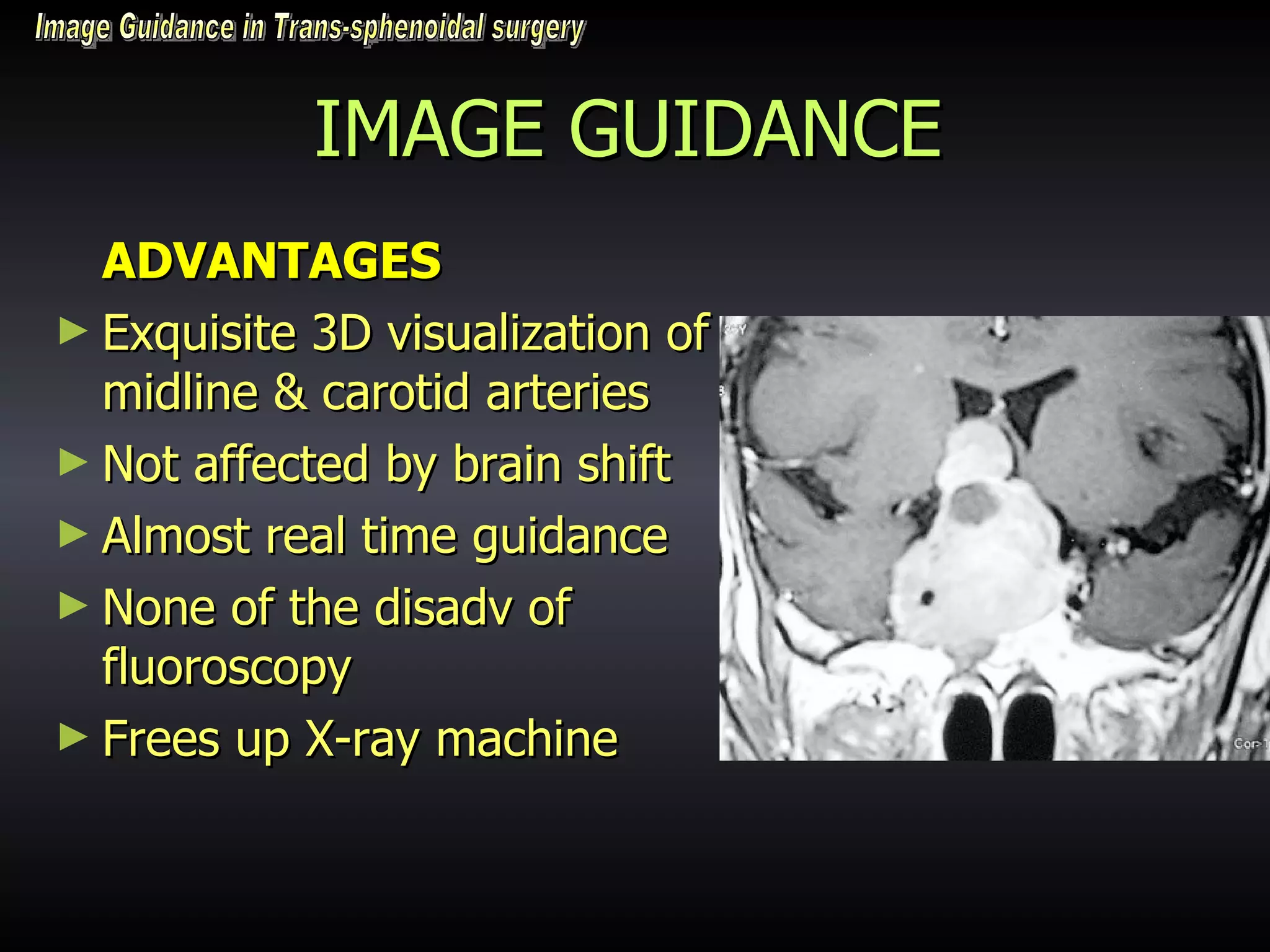
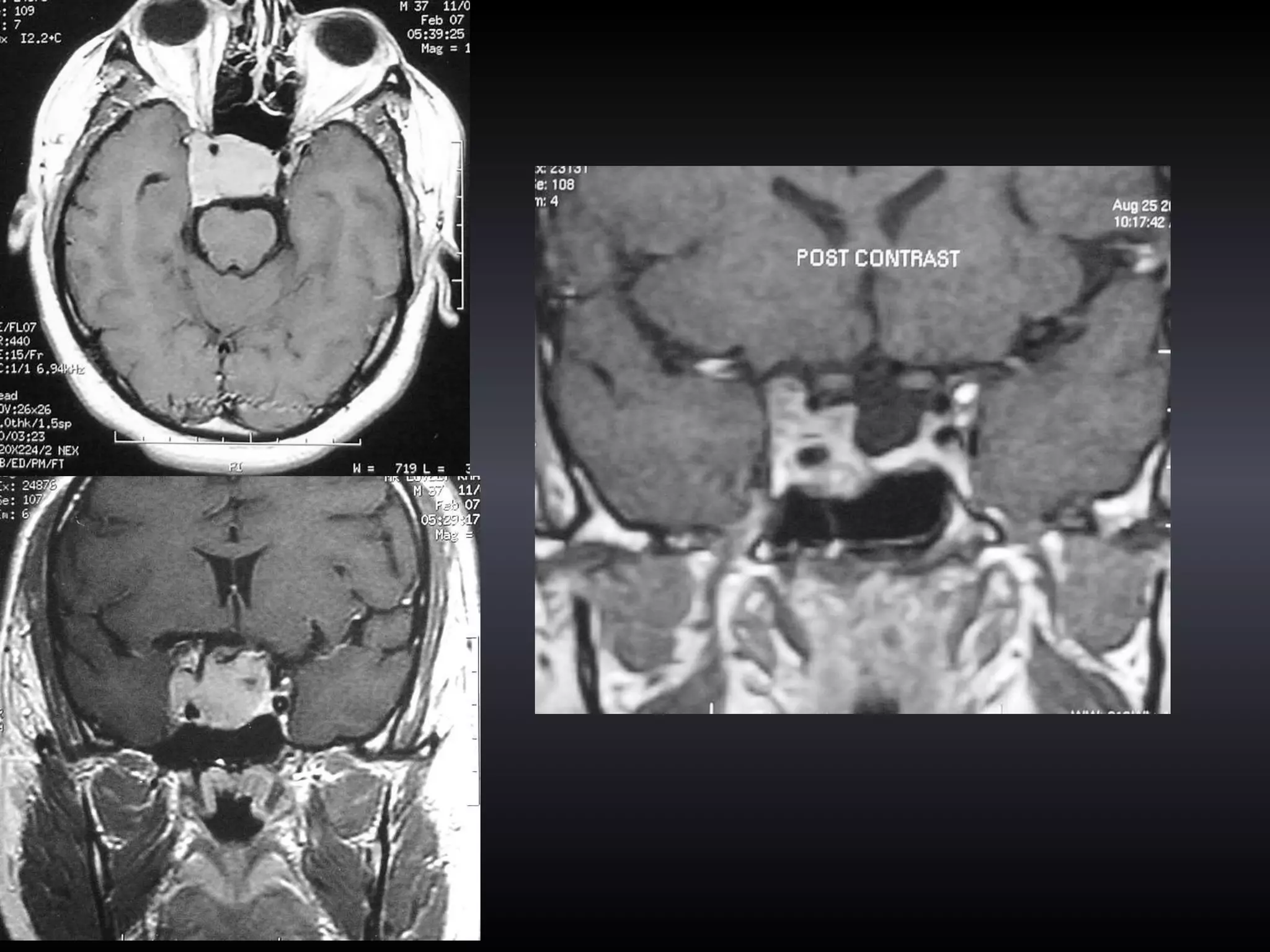
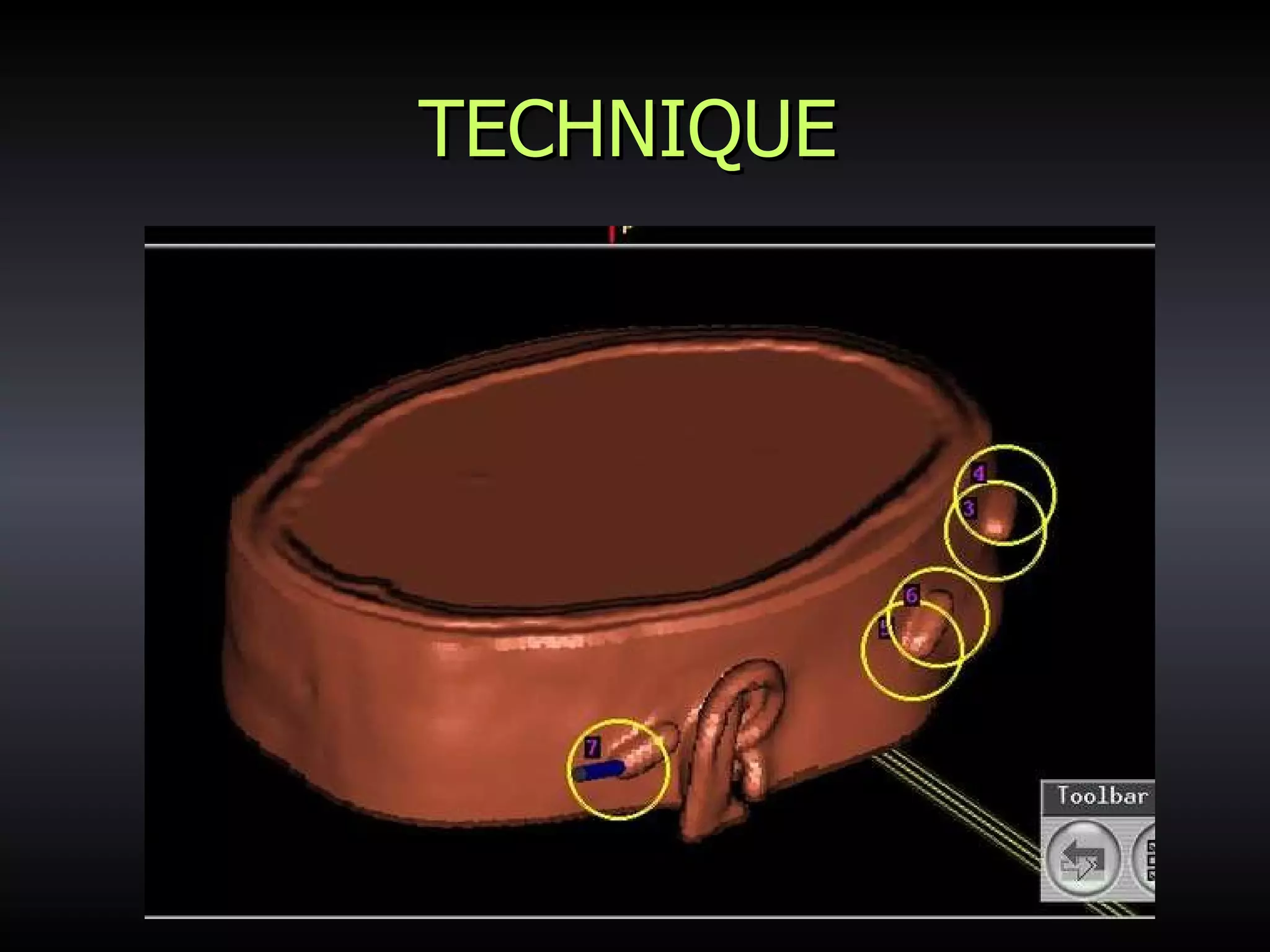
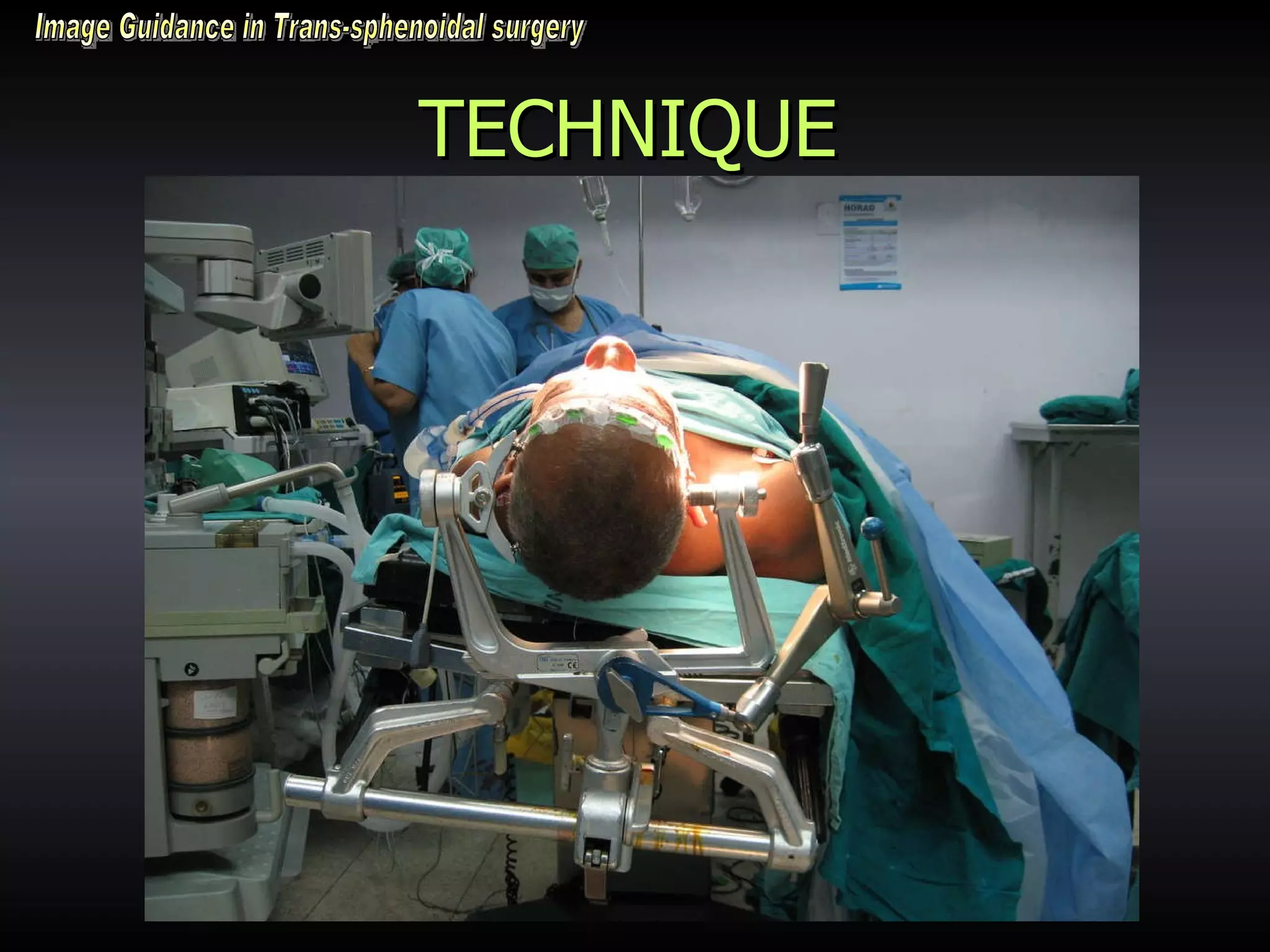
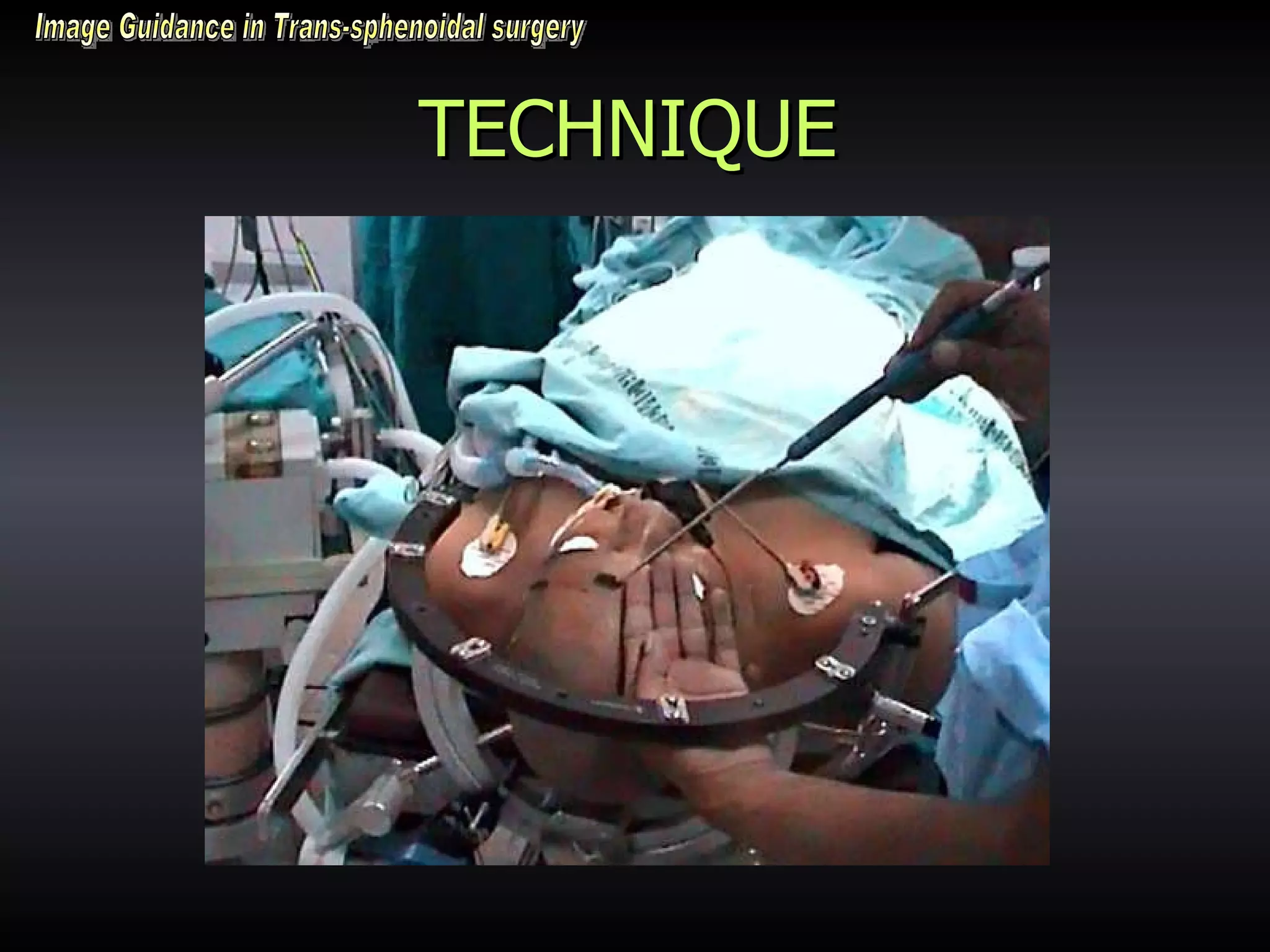
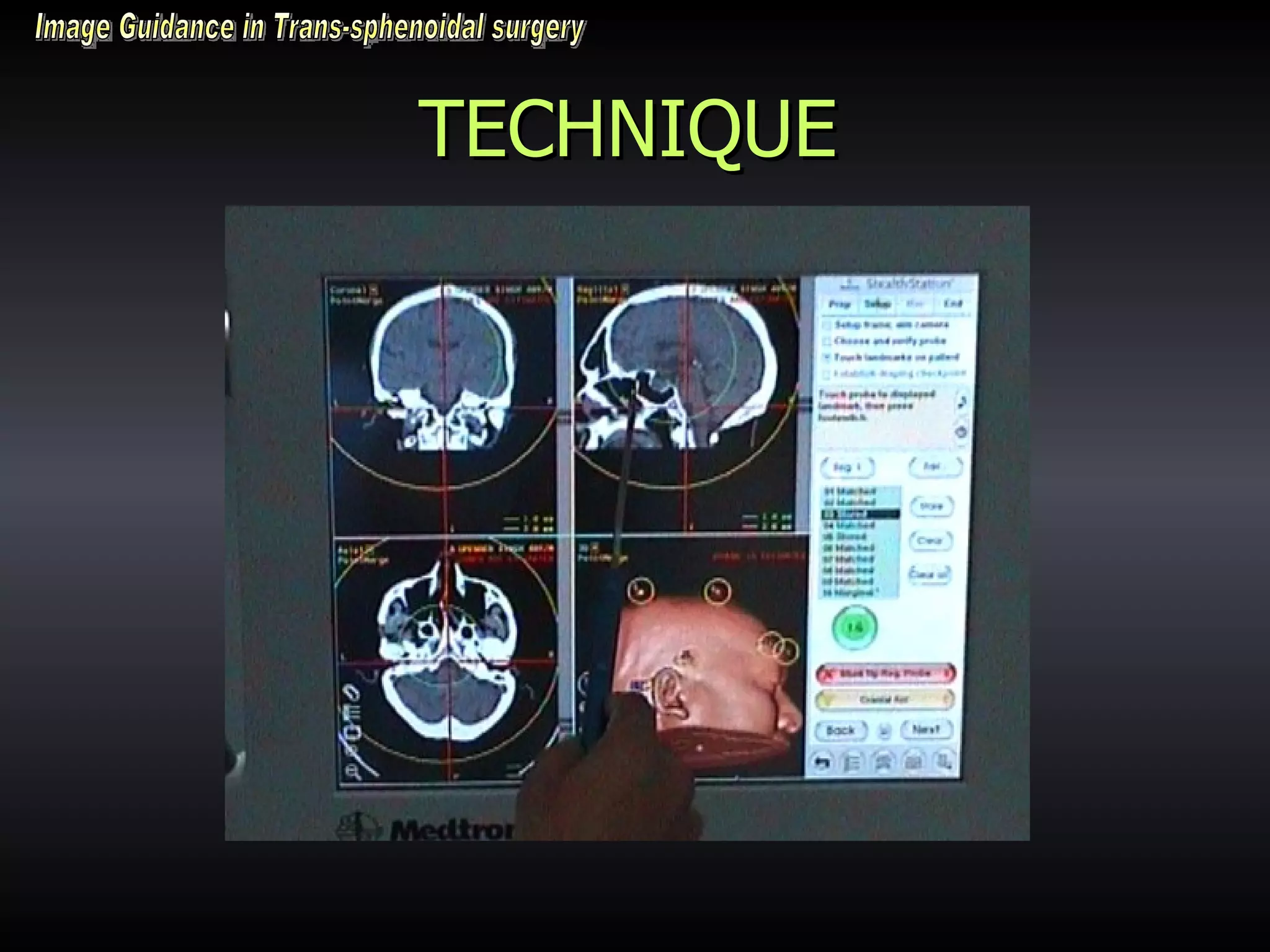
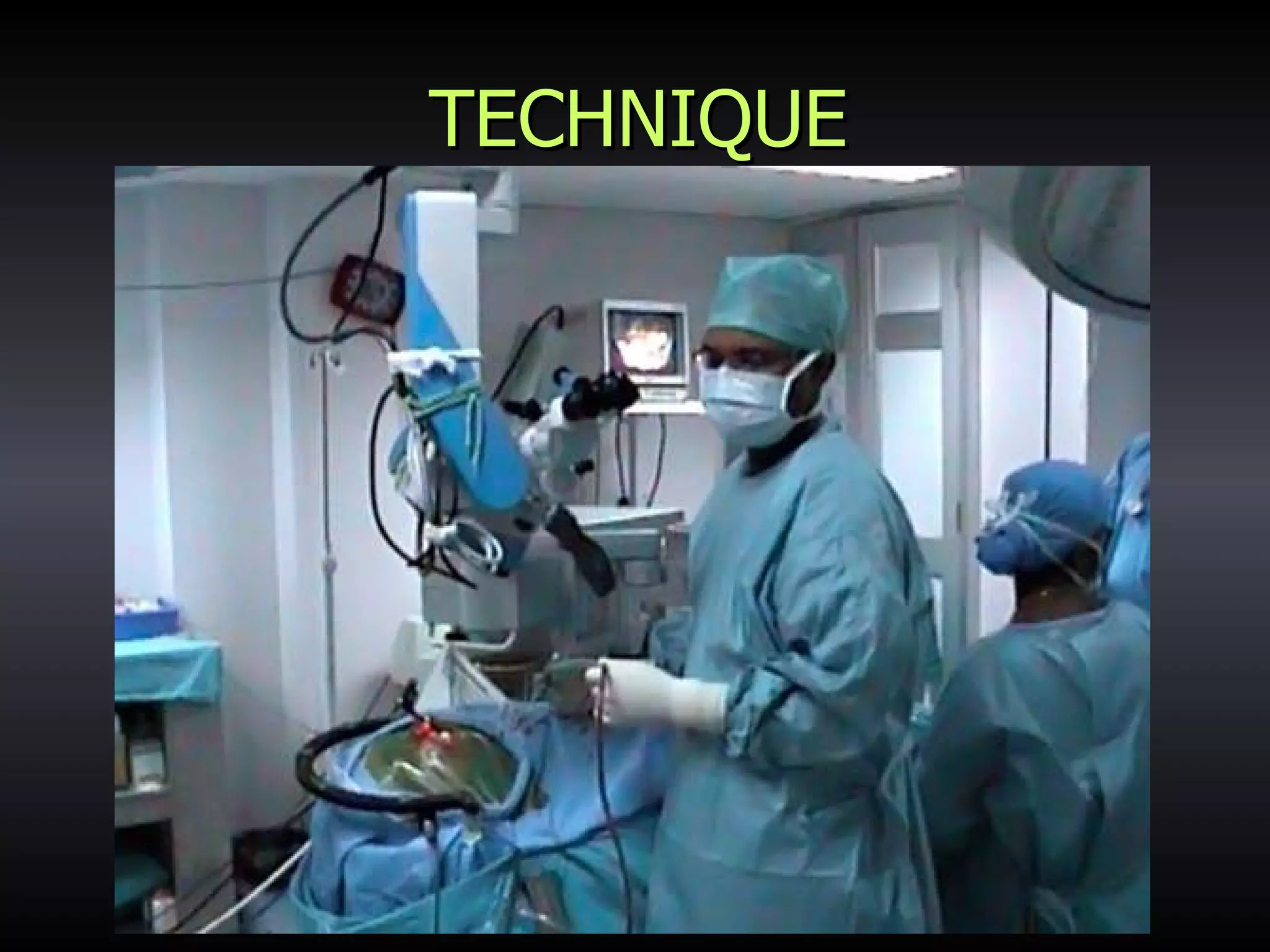
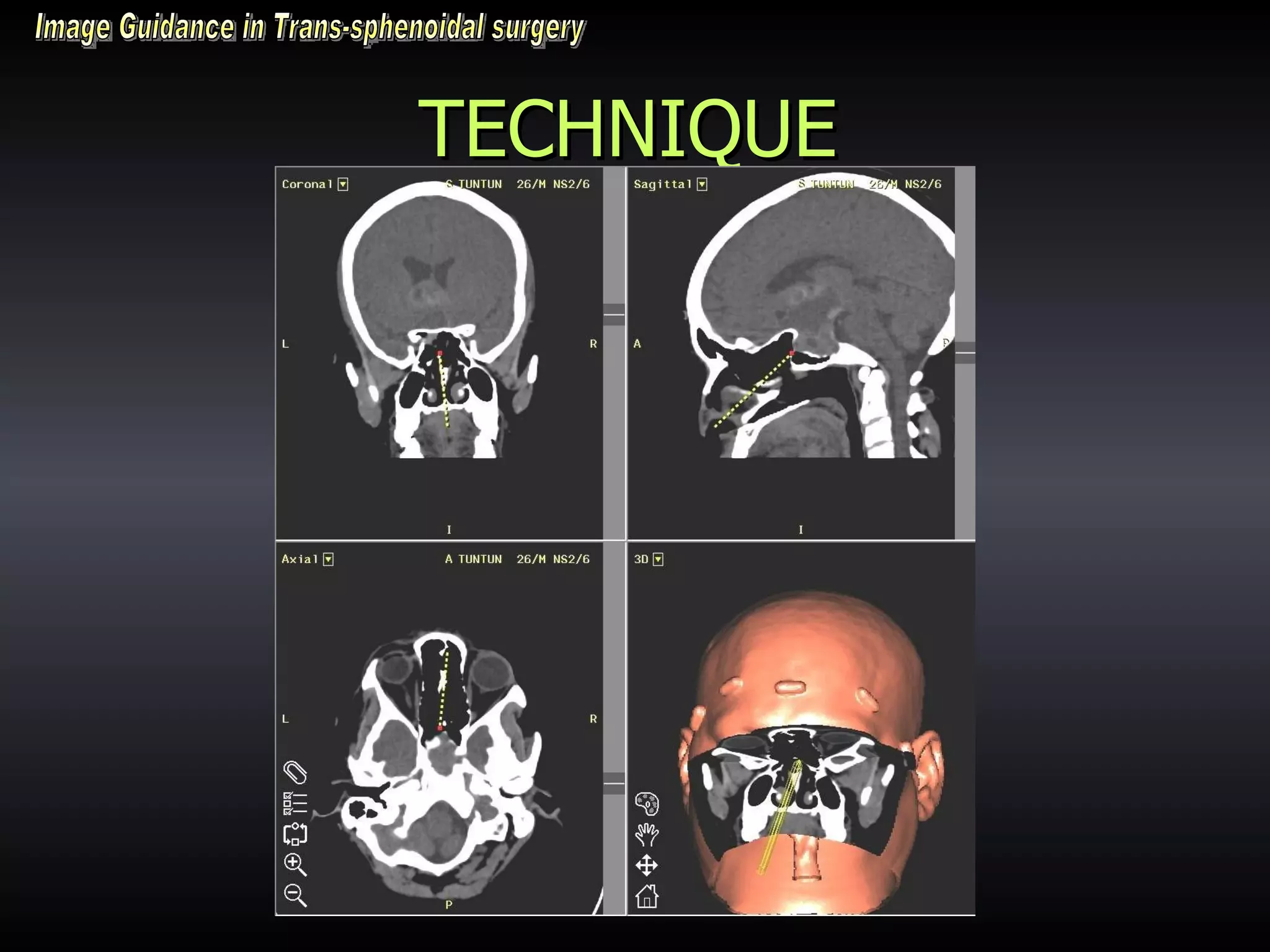
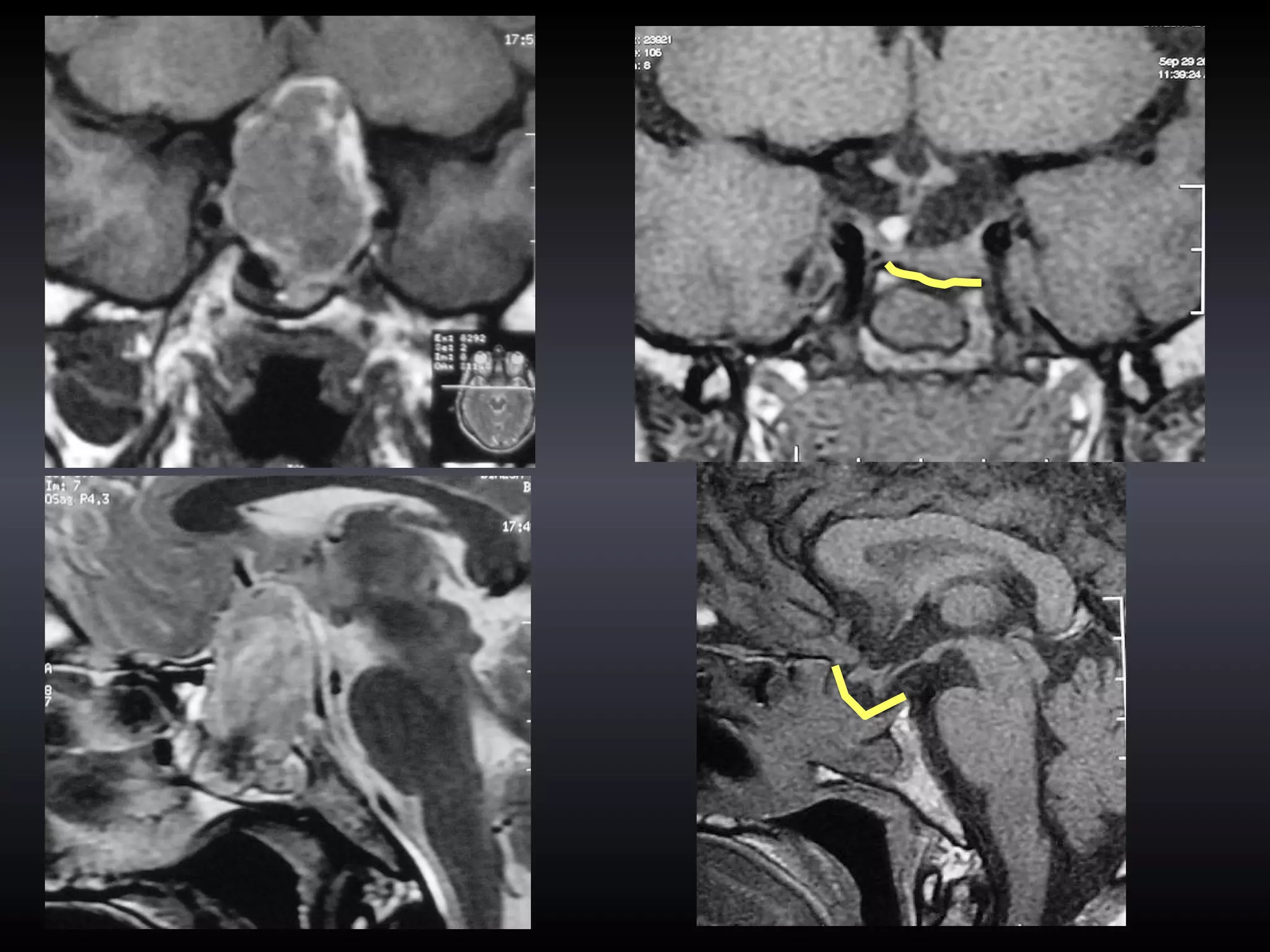
Vitamin E capsules can effectively be used as fiducial markers for image-guided neurosurgery, providing accurate registration while significantly reducing costs compared to proprietary fiducials. The use of Vitamin E capsules for registration resulted in a mean overall accuracy of 1.84 mm, compared to 2.41 mm for regular fiducials. Image guidance improves the safety, accuracy, and visualization for trans-sphenoidal pituitary surgeries compared to fluoroscopy alone.