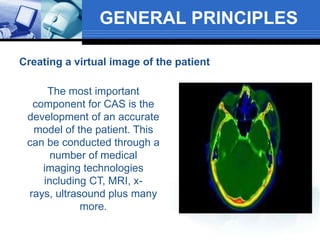
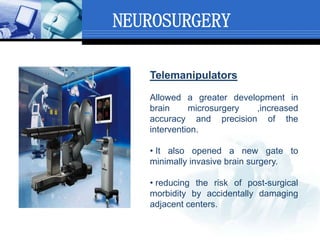
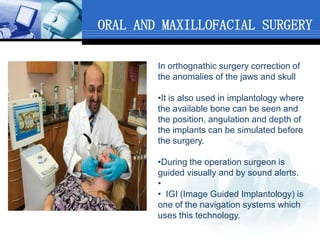
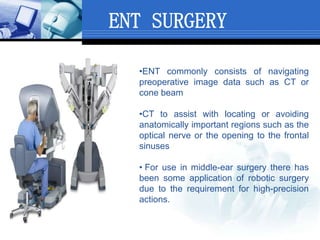
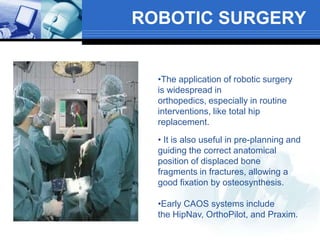
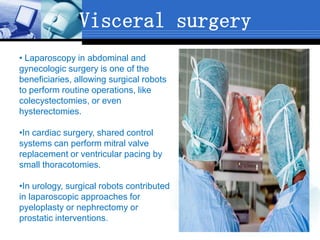
Computer assisted medical procedures use computer technology to assist with pre-surgical planning and guidance. This involves creating a virtual model of the patient using medical imaging like CT or MRI scans. The technology is used in various areas like neurosurgery where it increases precision, orthopedic surgery for joint replacements, and ENT surgery where it helps locate important anatomical structures. While it improves accuracy and reduces risks, computer assisted surgery is also very costly and its long term efficacy is still being established.