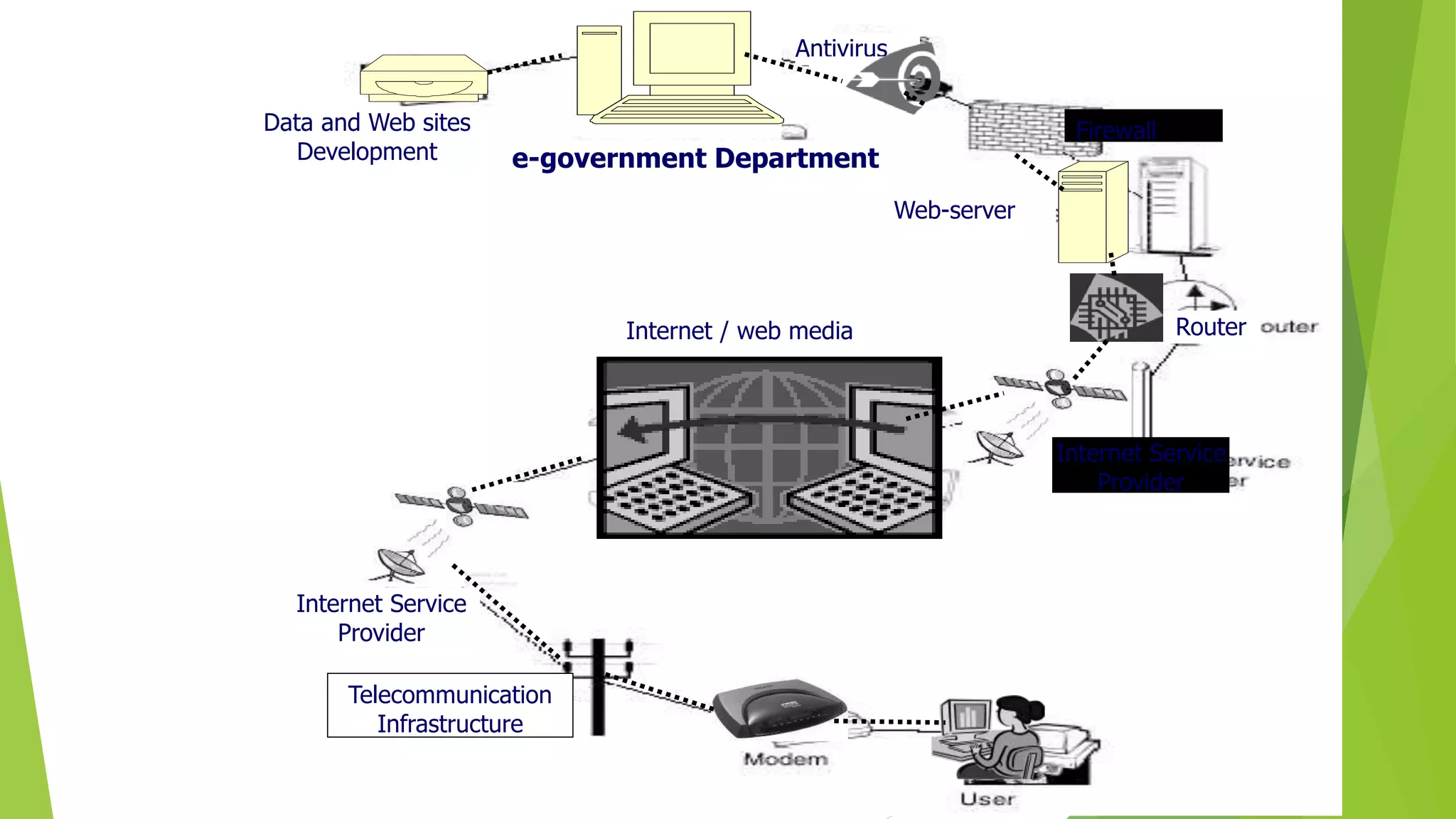
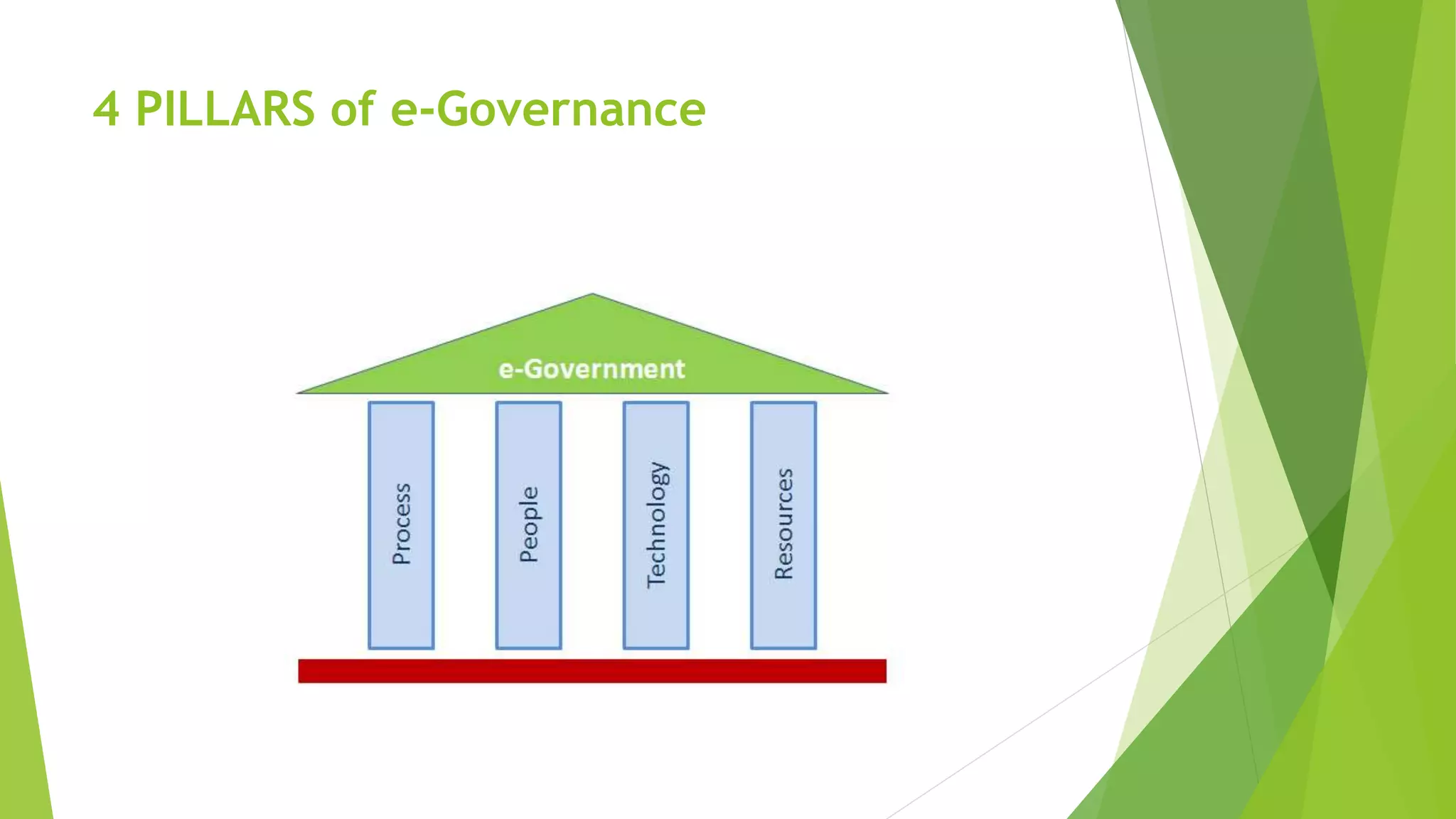
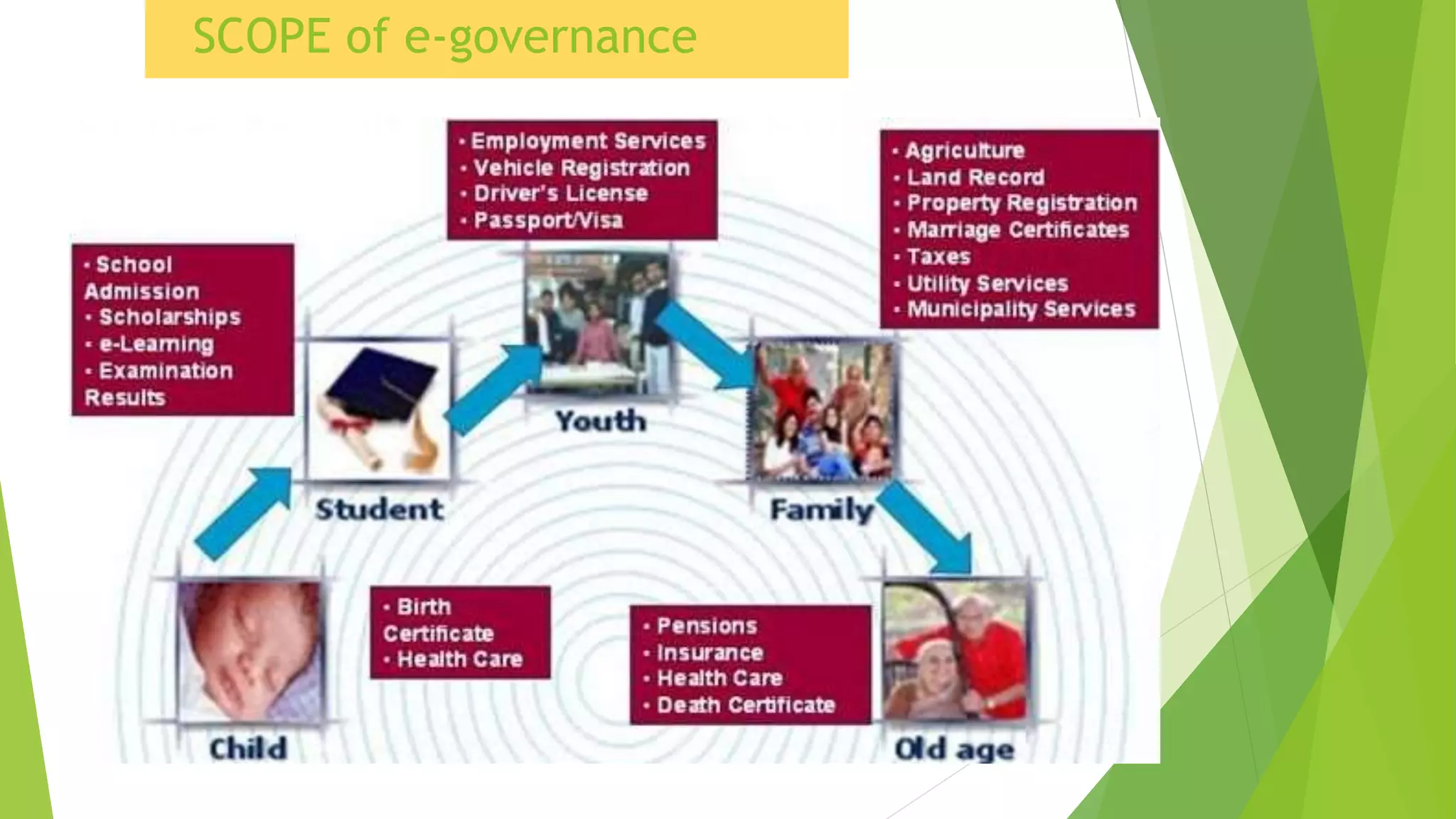
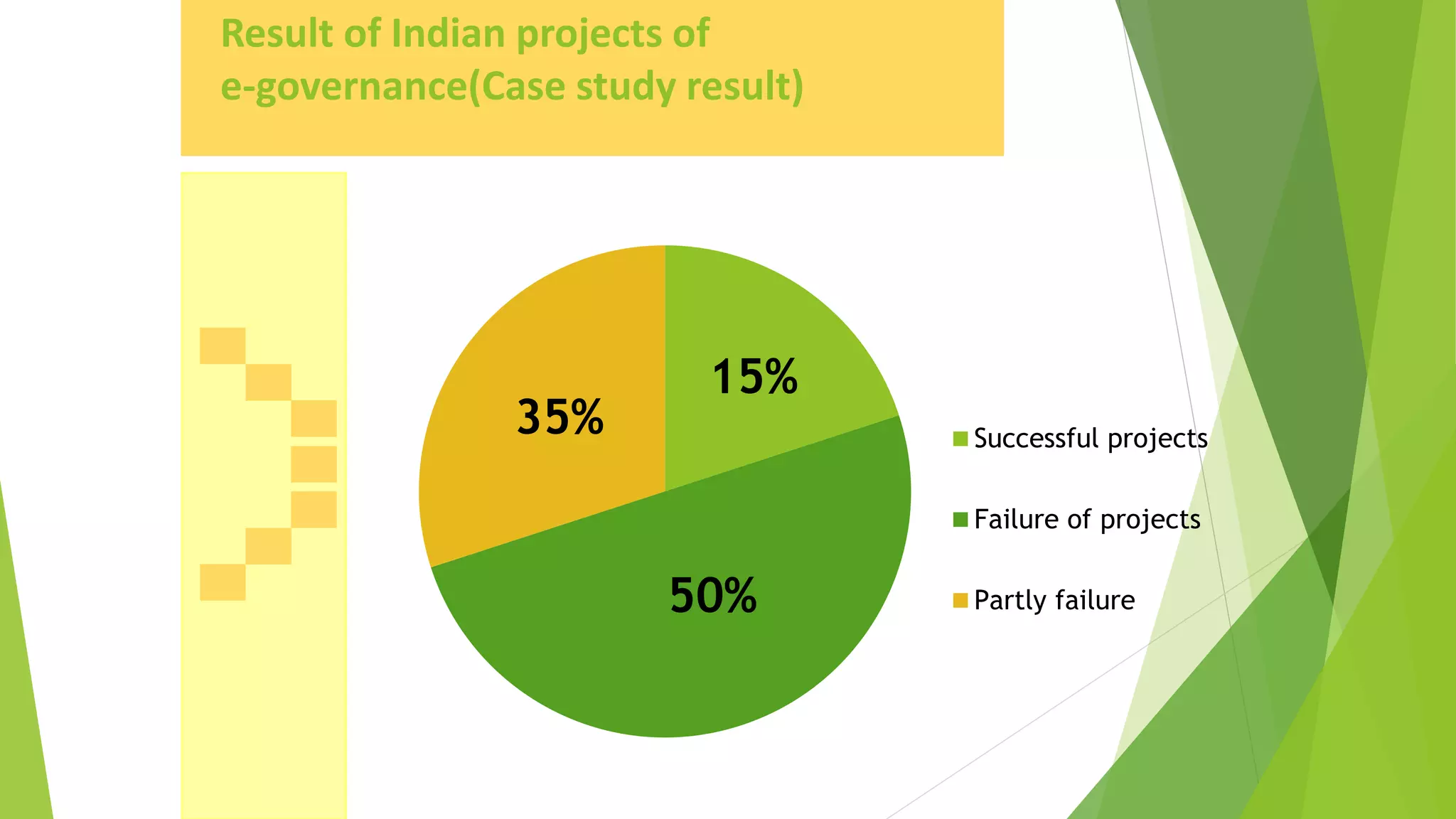
The document discusses e-governance and India's Digital India initiative. E-governance uses information technologies to make government more efficient and transparent for citizens. India implemented e-governance in phases from the late 1980s onward. Digital India, launched in 2015, aims to transform India into a digitally empowered society through initiatives like expanding broadband internet access nationwide, digitizing government services, and improving digital literacy. The nine pillars of Digital India focus on areas like digital infrastructure, governance, healthcare, education, and financial inclusion to promote digital transformation across India.