This document provides an overview of e-governance including definitions, history, purpose, benefits, types, services, models, pillars, phases, projects, and challenges. The key points are:
1. E-governance refers to the use of information technologies to enhance the ability of government to serve citizens and businesses.
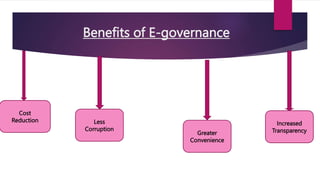
2. It aims to simplify processes, promote transparency and accountability, and make governance more responsive.
3. Major e-governance projects in India include SUWIDHA in Punjab and various departmental automation initiatives in states like Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, and Gujarat.