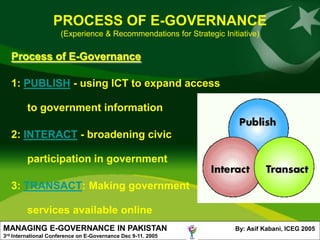
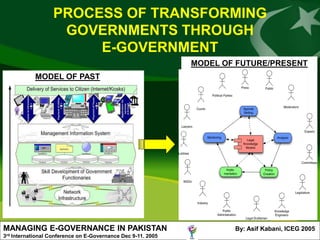
The document discusses e-governance initiatives in Pakistan. It defines e-governance as using technology, especially the internet, to achieve better government. The author outlines Pakistan's vision for e-government, including increasing citizens' access to government information and services. Key e-governance processes discussed are publishing information online, enabling civic participation, and making government services available transactionally online. The author provides recommendations for successful e-governance transformation, including leadership, strategic investment, and civic engagement.