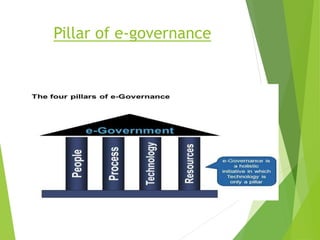
The document presents a detailed overview of e-governance, its history, pillars, phases, sectors, benefits, limitations, and challenges. It defines e-governance as the electronic facilitation of government processes and outlines its evolution in India from the 1970s. The four phases of e-governance identified are presence, interaction, transaction, and transformation, aimed at improving government services to citizens, businesses, and employees.