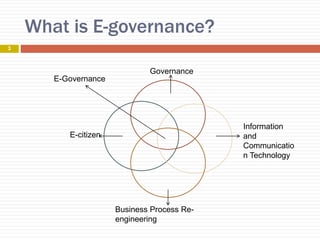
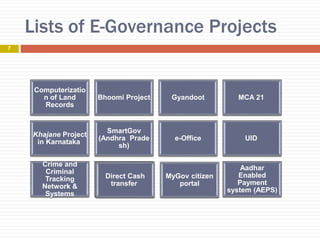
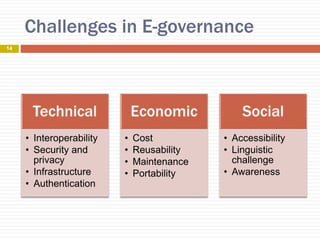
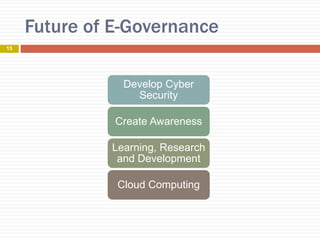
E-governance refers to the use of information and communication technology to enhance government processes and improve public service delivery across various levels. Its objectives include increasing transparency, citizen participation, and interaction between government and citizens or businesses. Key components include connectivity, knowledge, data content, and funding, with various implementation projects across urban and rural sectors in areas like health and education.











![References
[1] Dr. Dinesh Chandra Misra, I.A.S,(Retd.), Feb 2-3, 2006, “Defining
E-government : a citizen-centric criteria-based approach”, 10th
National Conference on E-Governance, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh,
India
[2] Nikita Yadav and V.B.Singh, “E-Governance: Past, Present and
Future in India”, Sep 2012, International Journal of Computer
Applications(0975-8887), Vol.53- No.7,
[3] Shailendra C. Jain Palvia and Sushil S.Sharma, “E-government and
E-governance: Defintions/Domain Framework and Status around
the World”, “Foundations of E-government”, Computer Society of
India
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e-governance-190719202845/85/E-governance-management-information-system-16-320.jpg)
![References (Contd.)
17
[4] “E-governance in India: Issues and Challenges”, Nagaraja. K, IOSR
Journal of Economics and Finance (IOSR-JEF), Vol 7, Issue 5,
Version IV, Sep-Oct, 2016
[5] https://www.nic.in/projects-all/
[6] Ake Gronlund, Thomas A. Horan, Orebo, “Introducing E-Gov:
History, Definitions and Issues”, Communications of the Association
for Information Systems (Volume 15, 2004)713-729.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e-governance-190719202845/85/E-governance-management-information-system-17-320.jpg)
