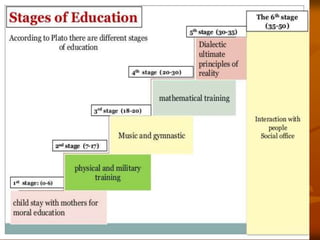
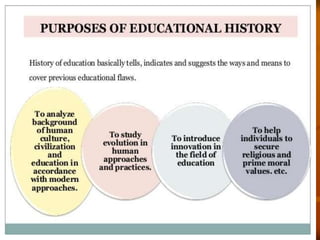
This document discusses the philosophical school of idealism. It defines idealism as the belief that ideas are the only true reality and that the material world is imperfect and changing. It notes that idealists believe we should be primarily concerned with the search for truth, which is found in perfect, eternal ideas rather than the material world. The document outlines some of the key exponents and principles of idealism, such as Plato, that spirit and mind constitute reality, and that values are absolute. It also discusses the epistemology, metaphysics, and axiology of idealism and how it influences education through a focus on character development, self-realization, and preservation of culture.