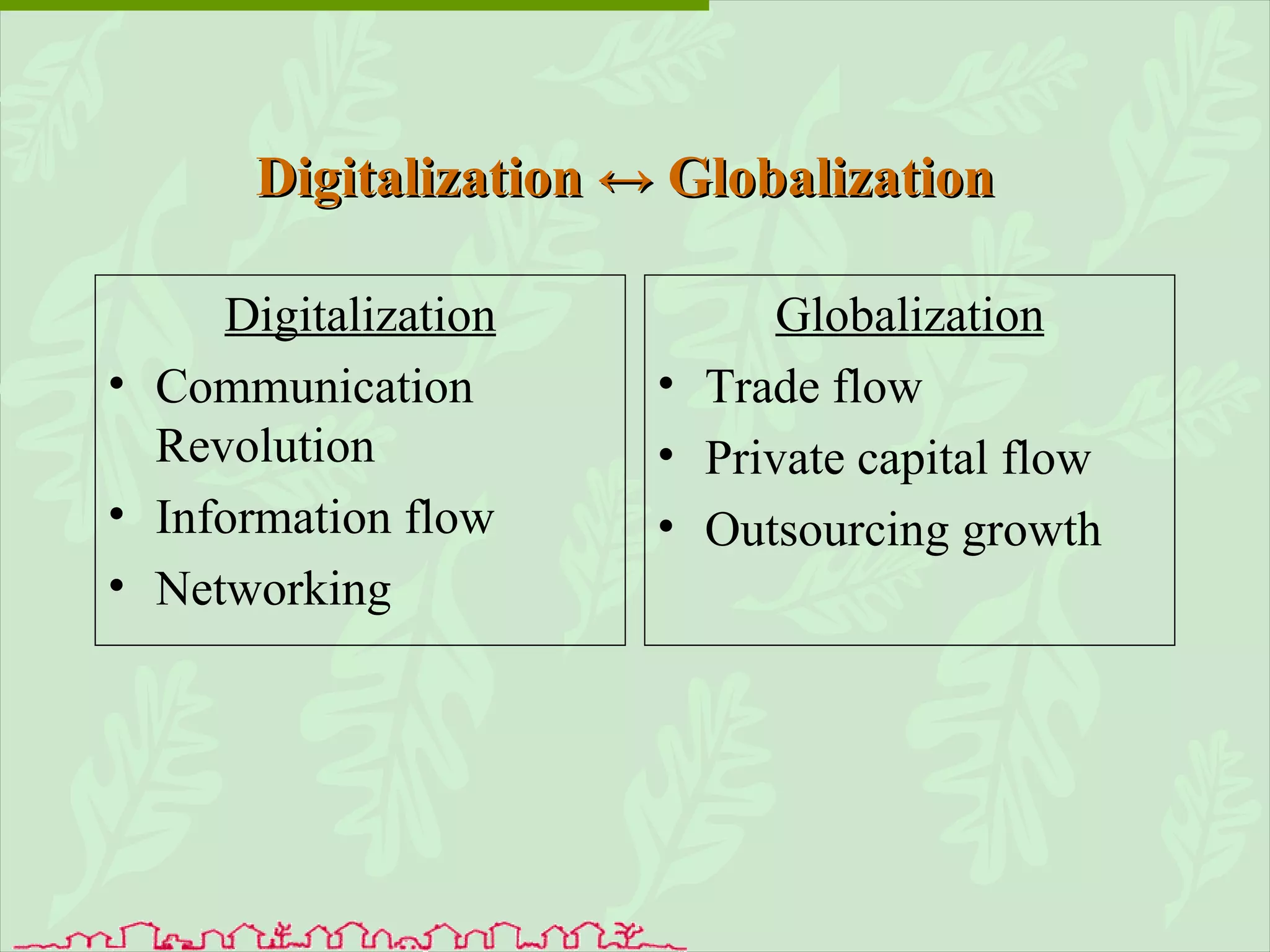
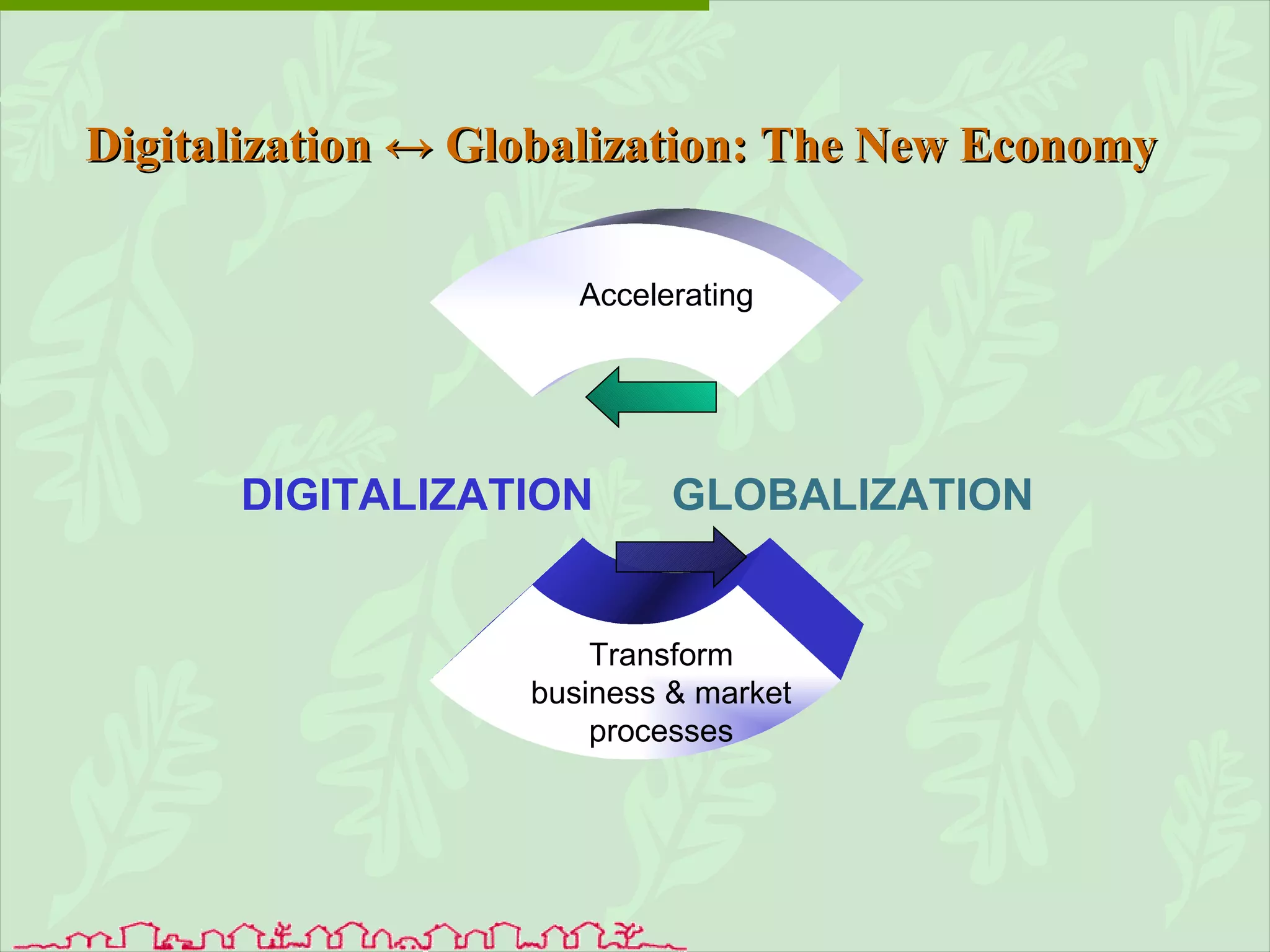
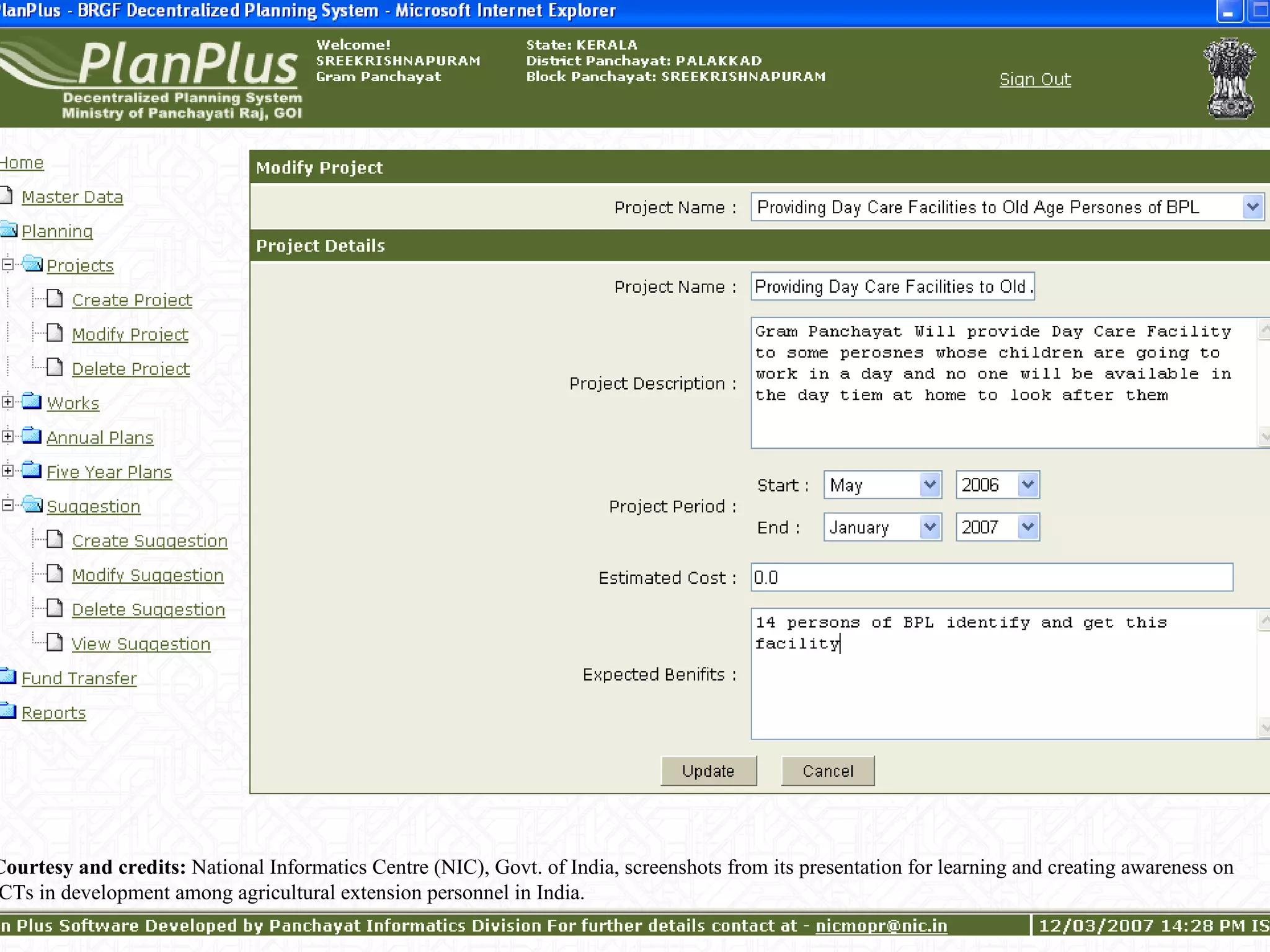
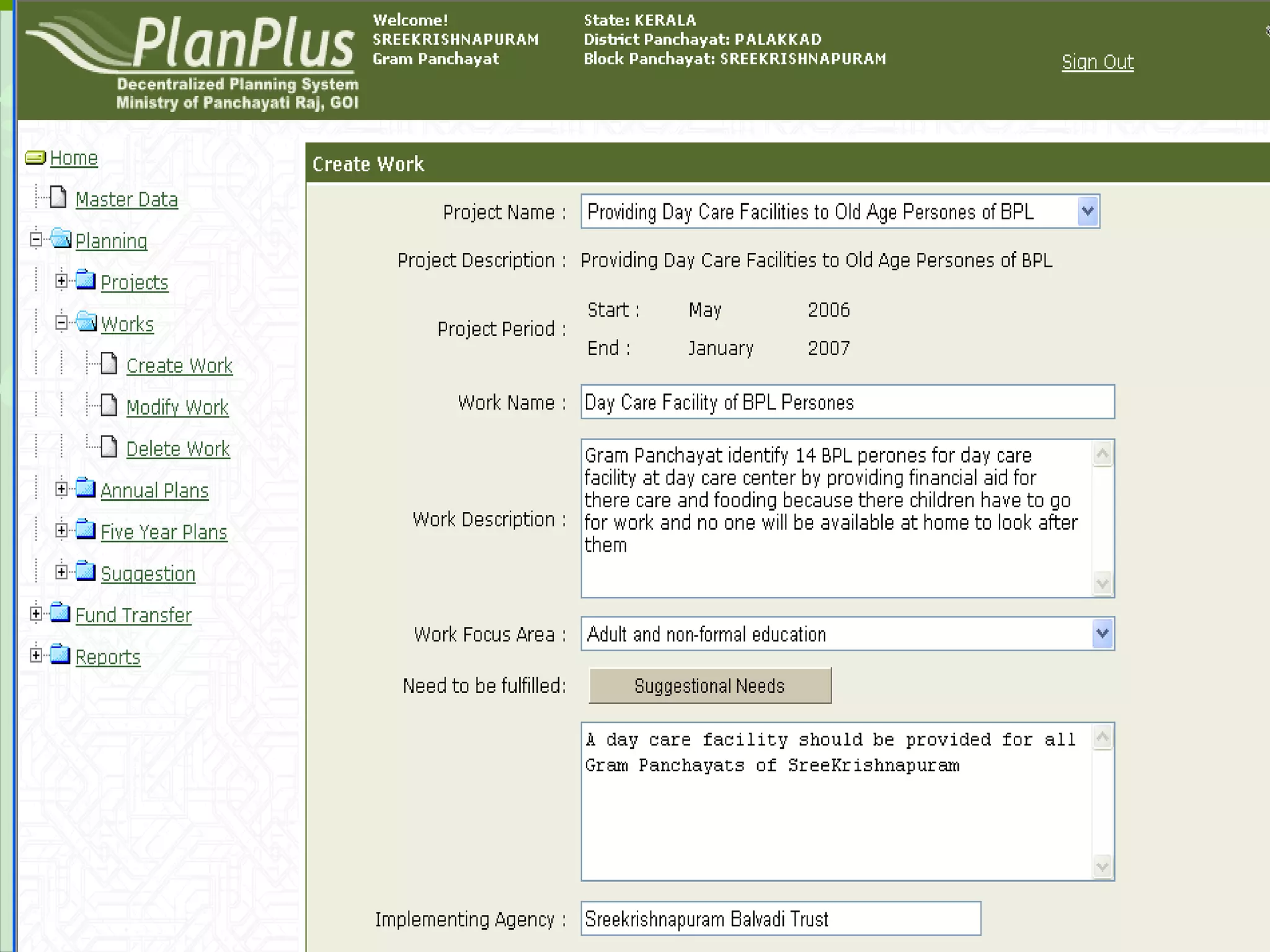
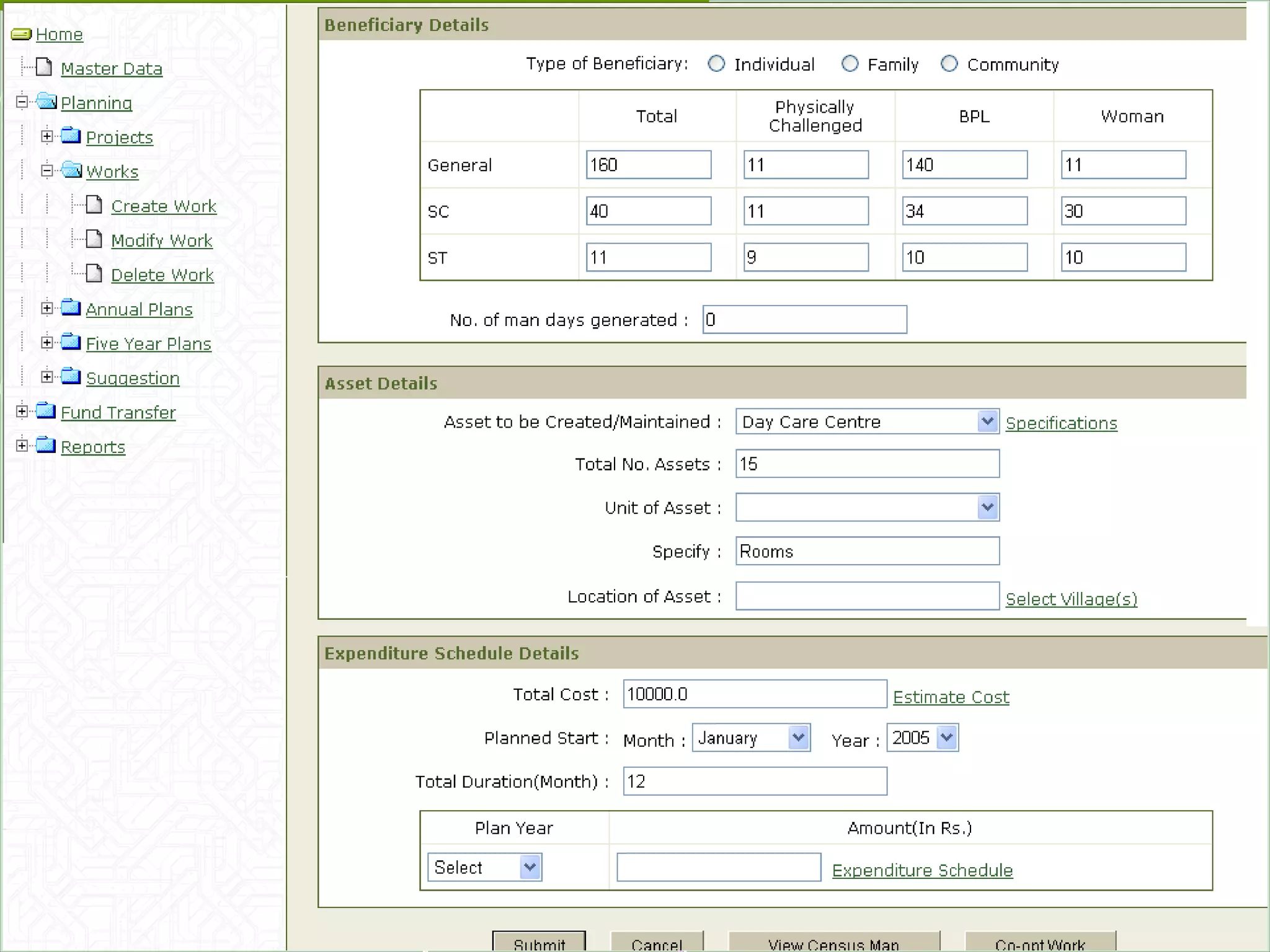
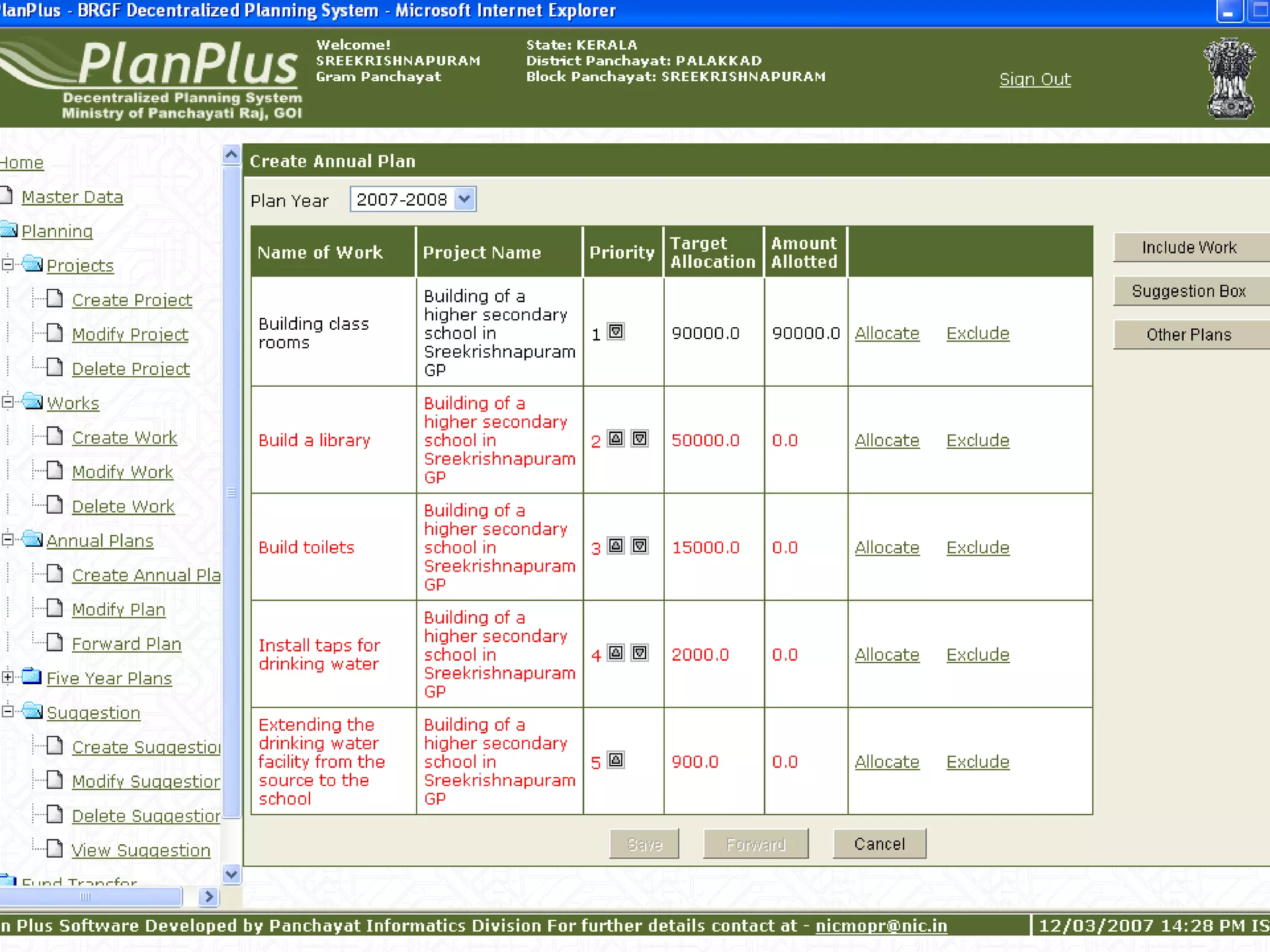
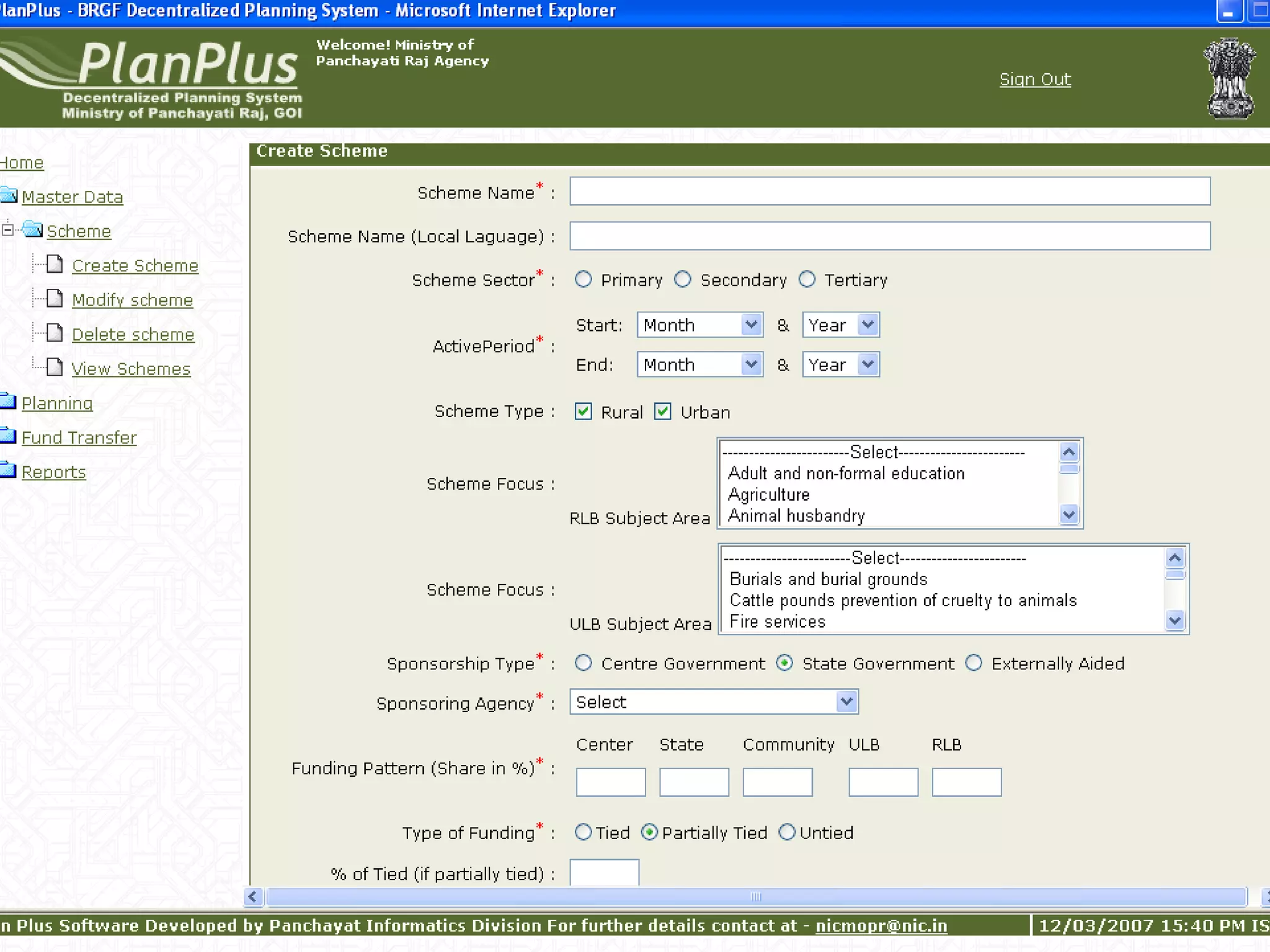
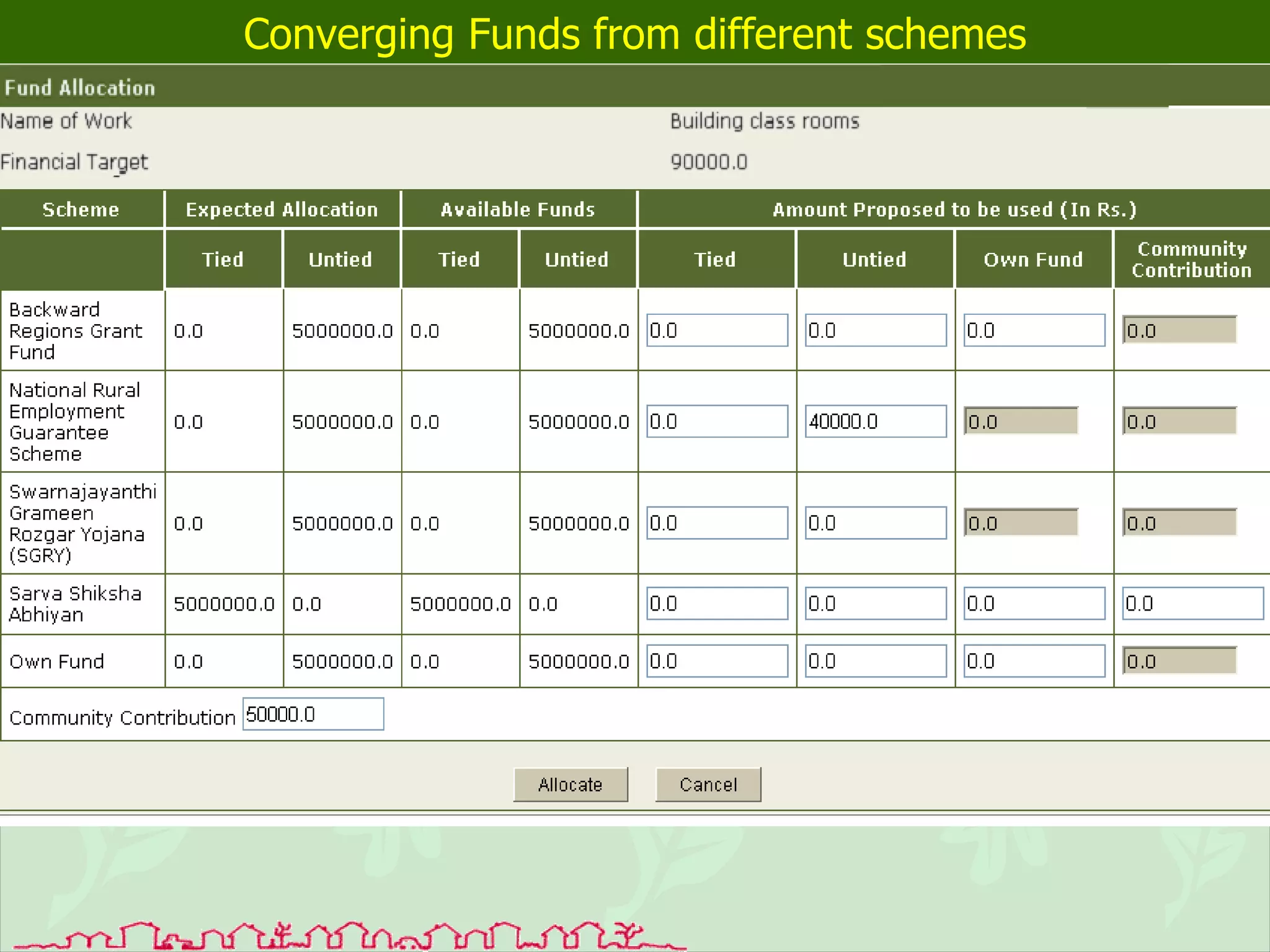
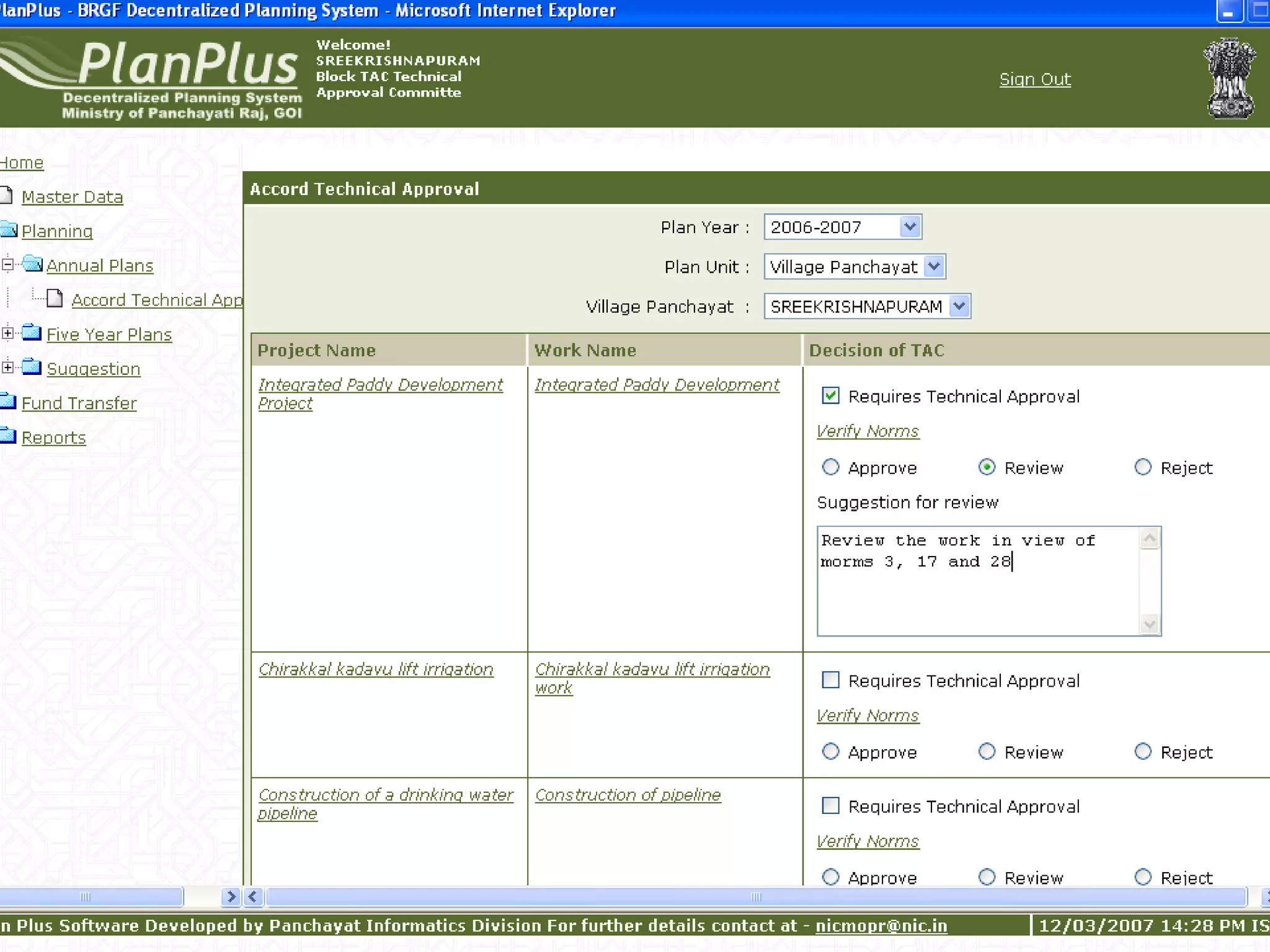
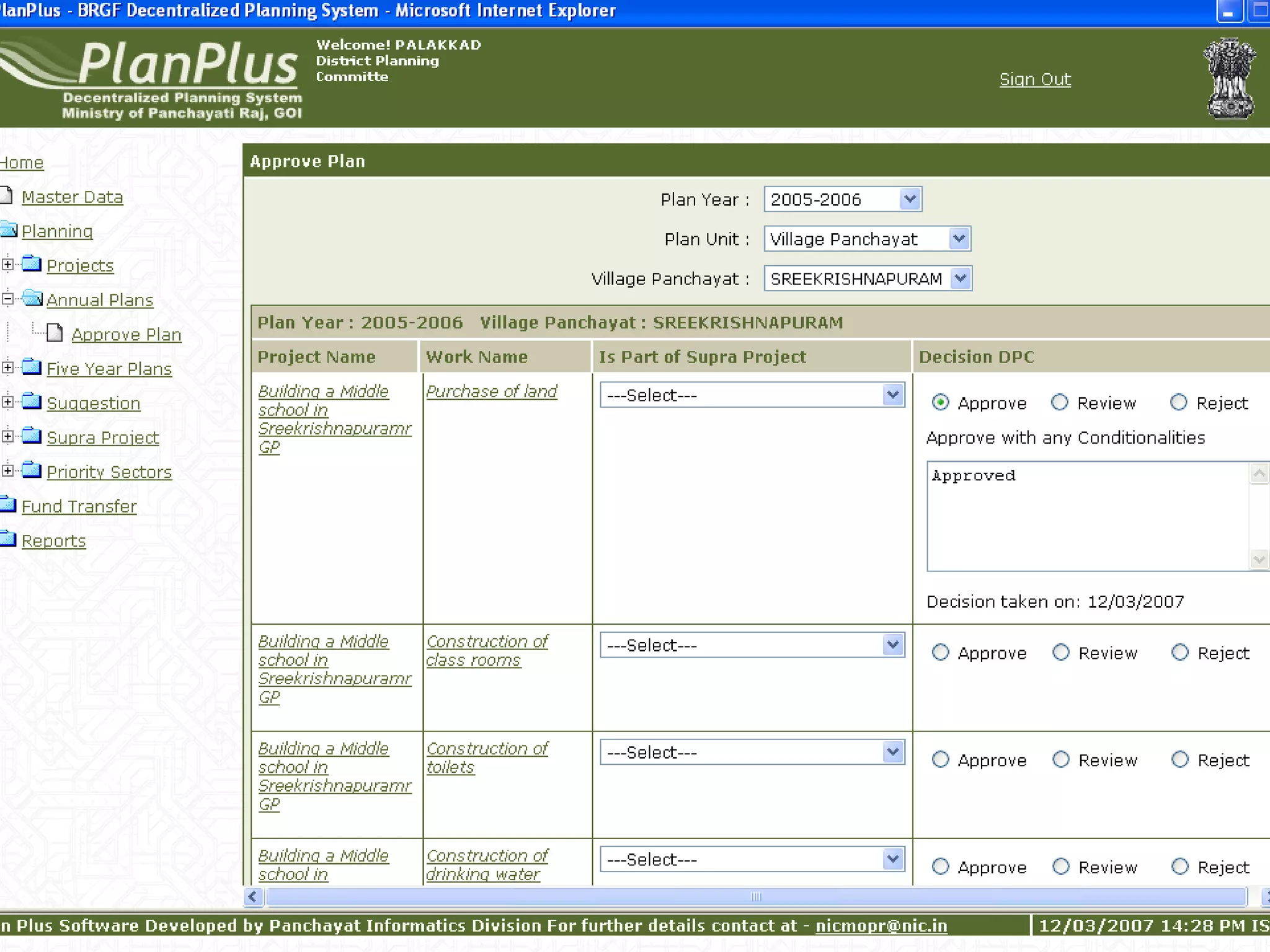
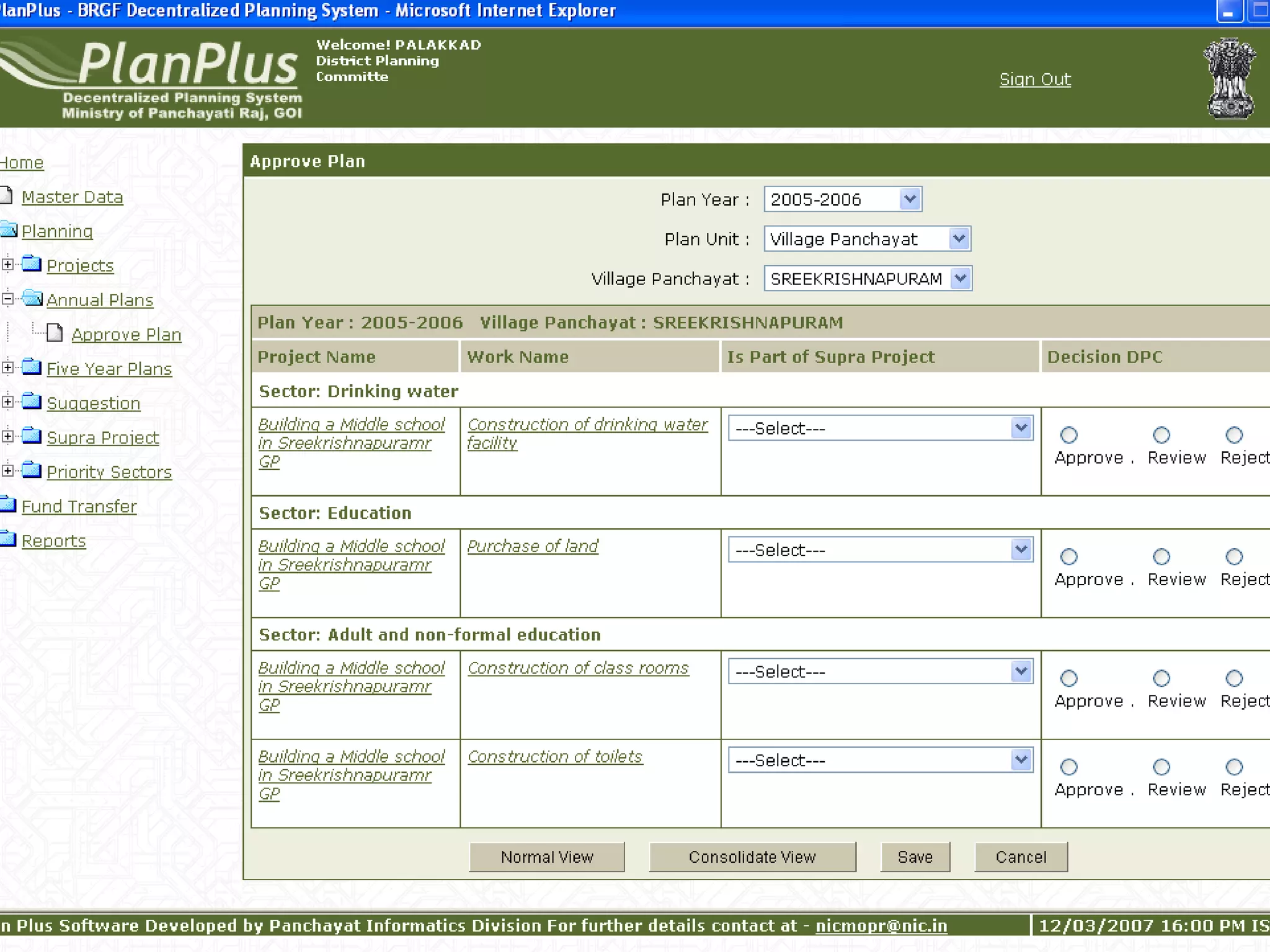
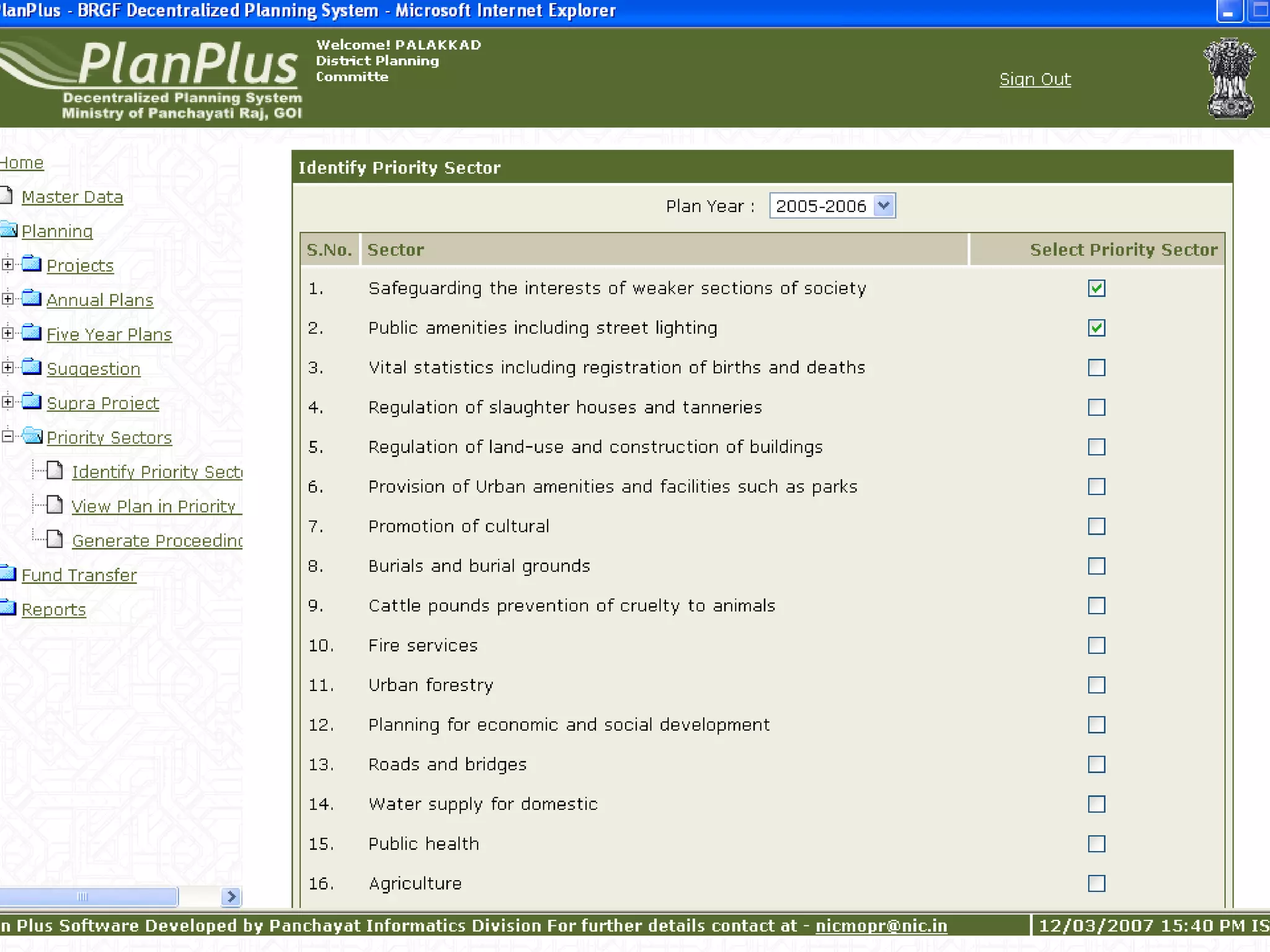
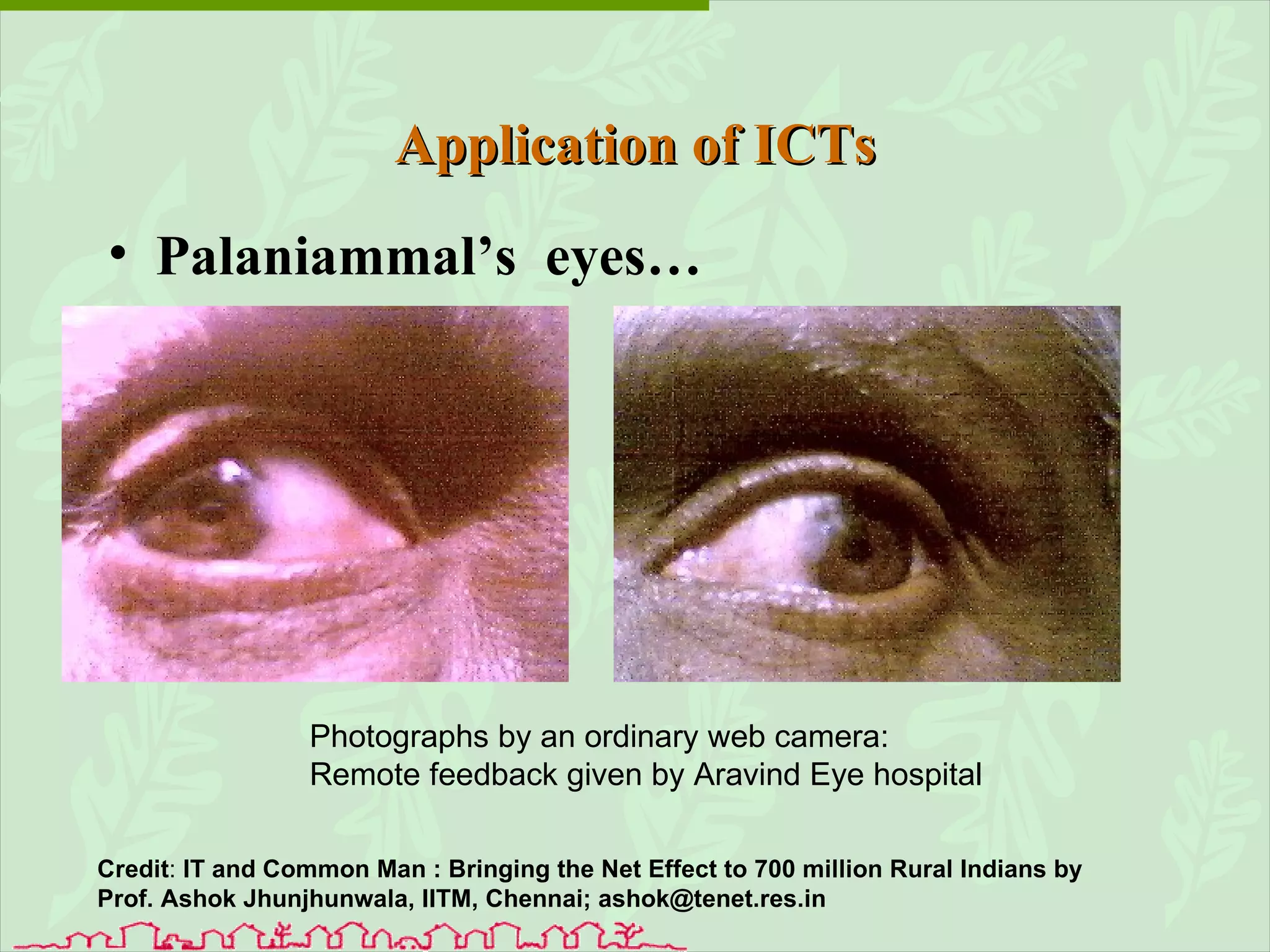
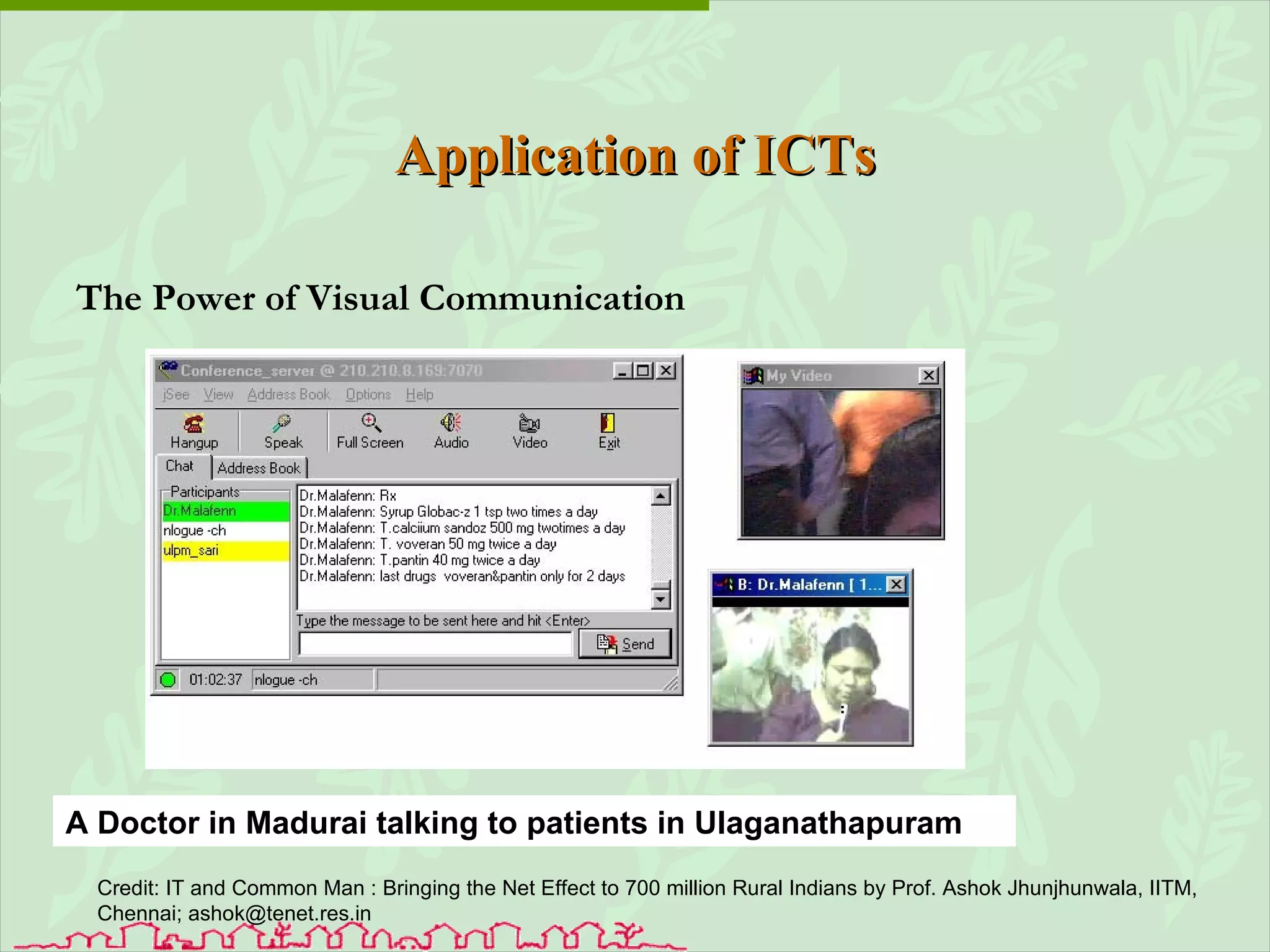
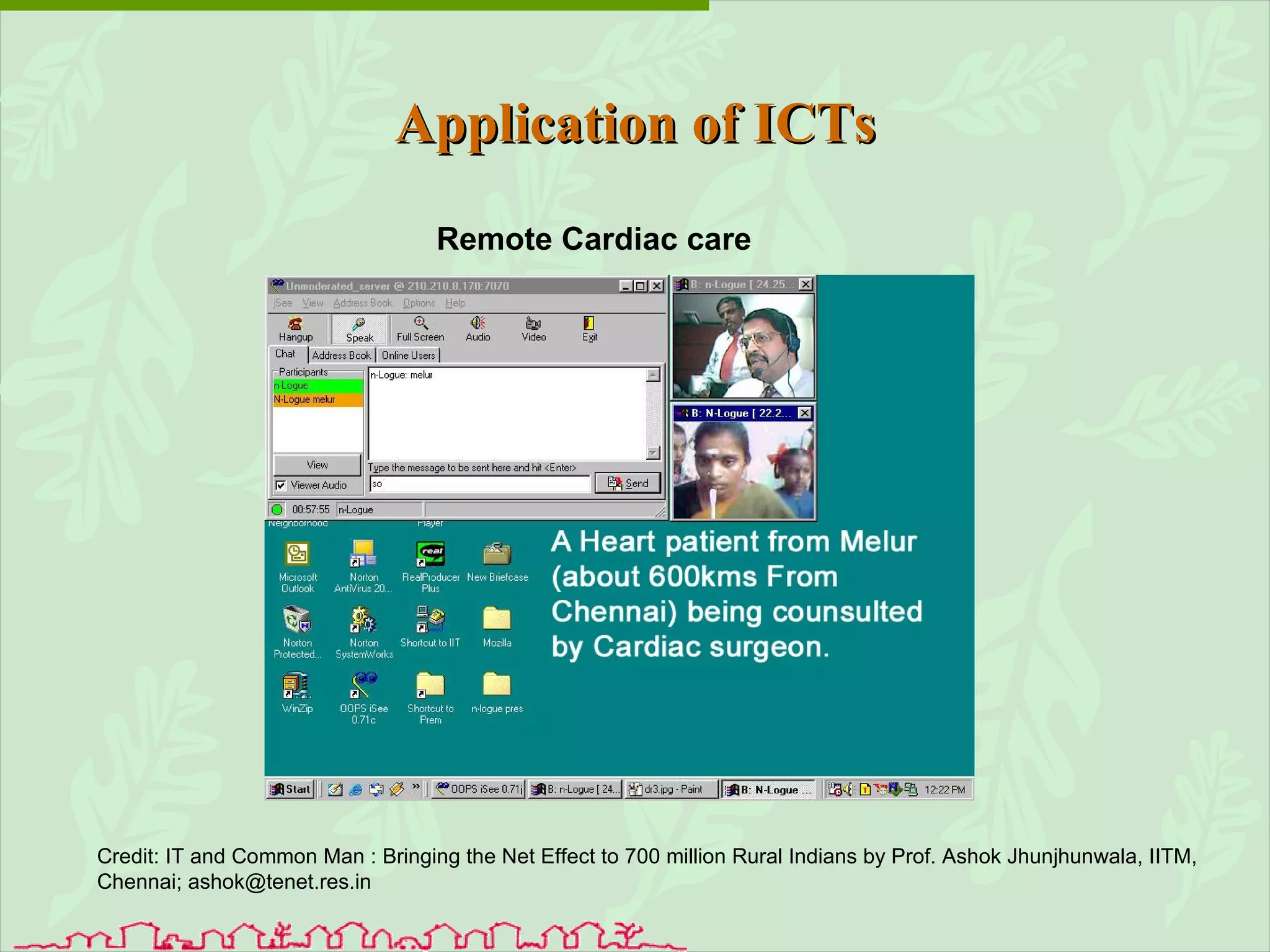
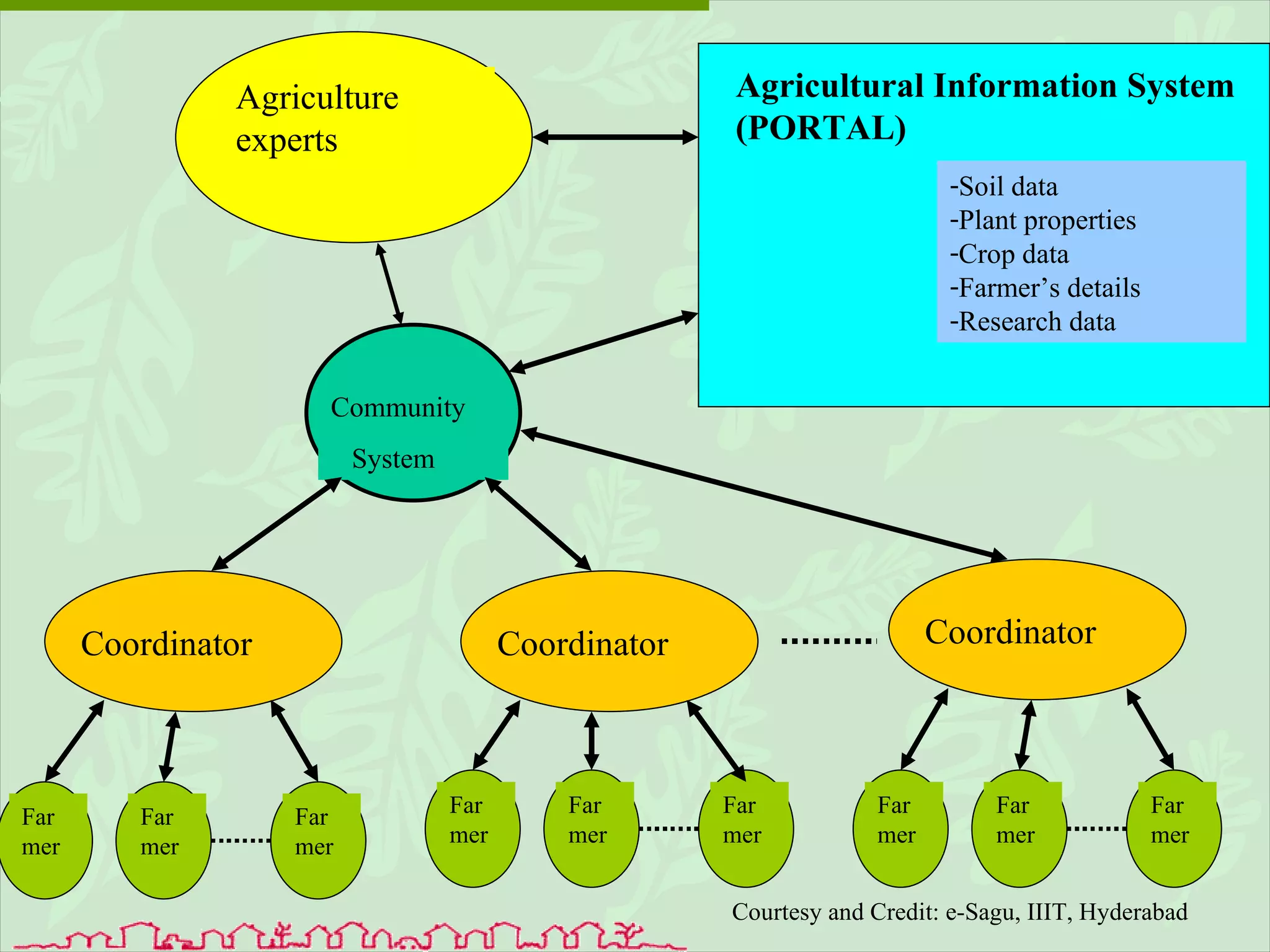
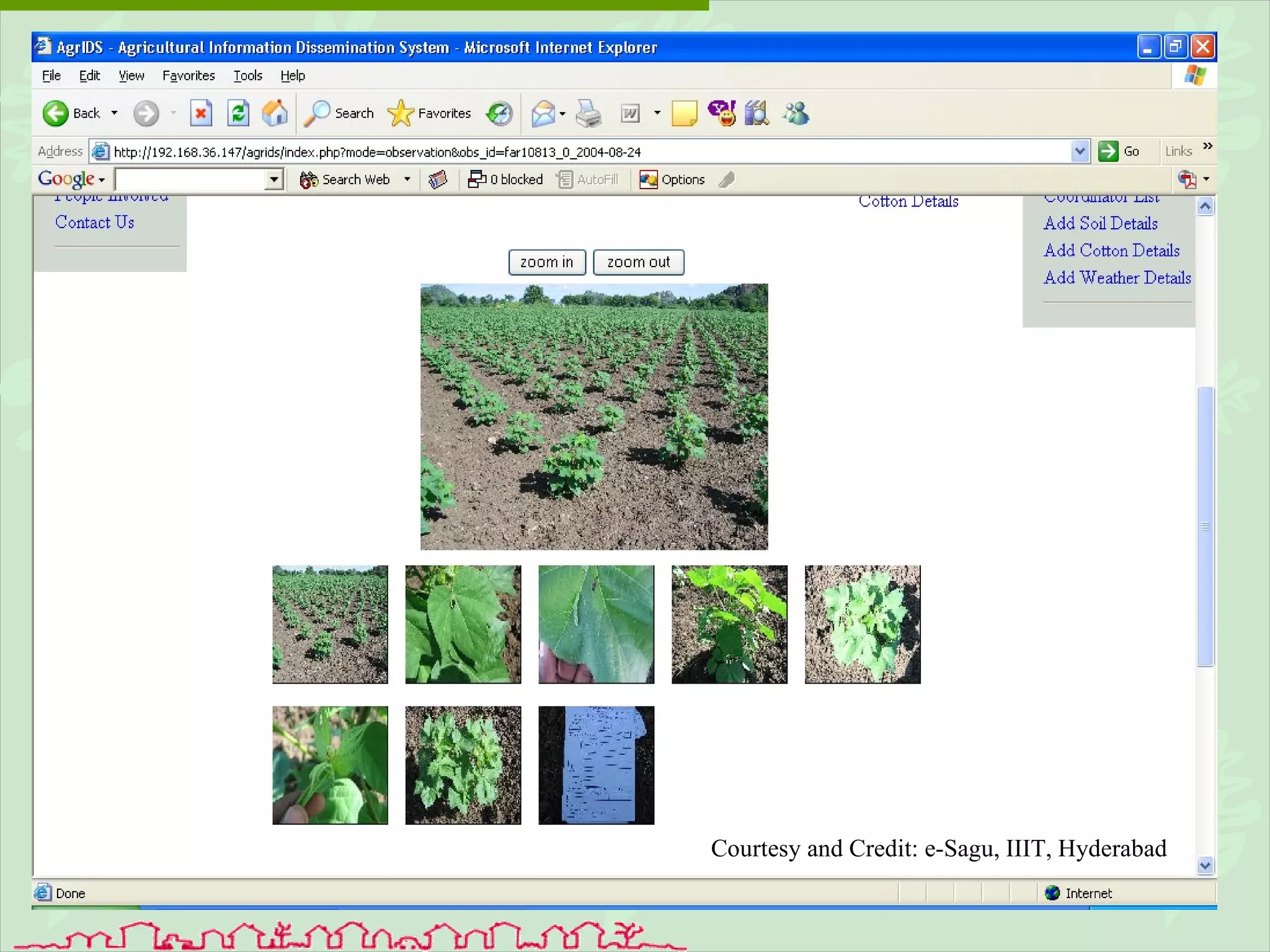
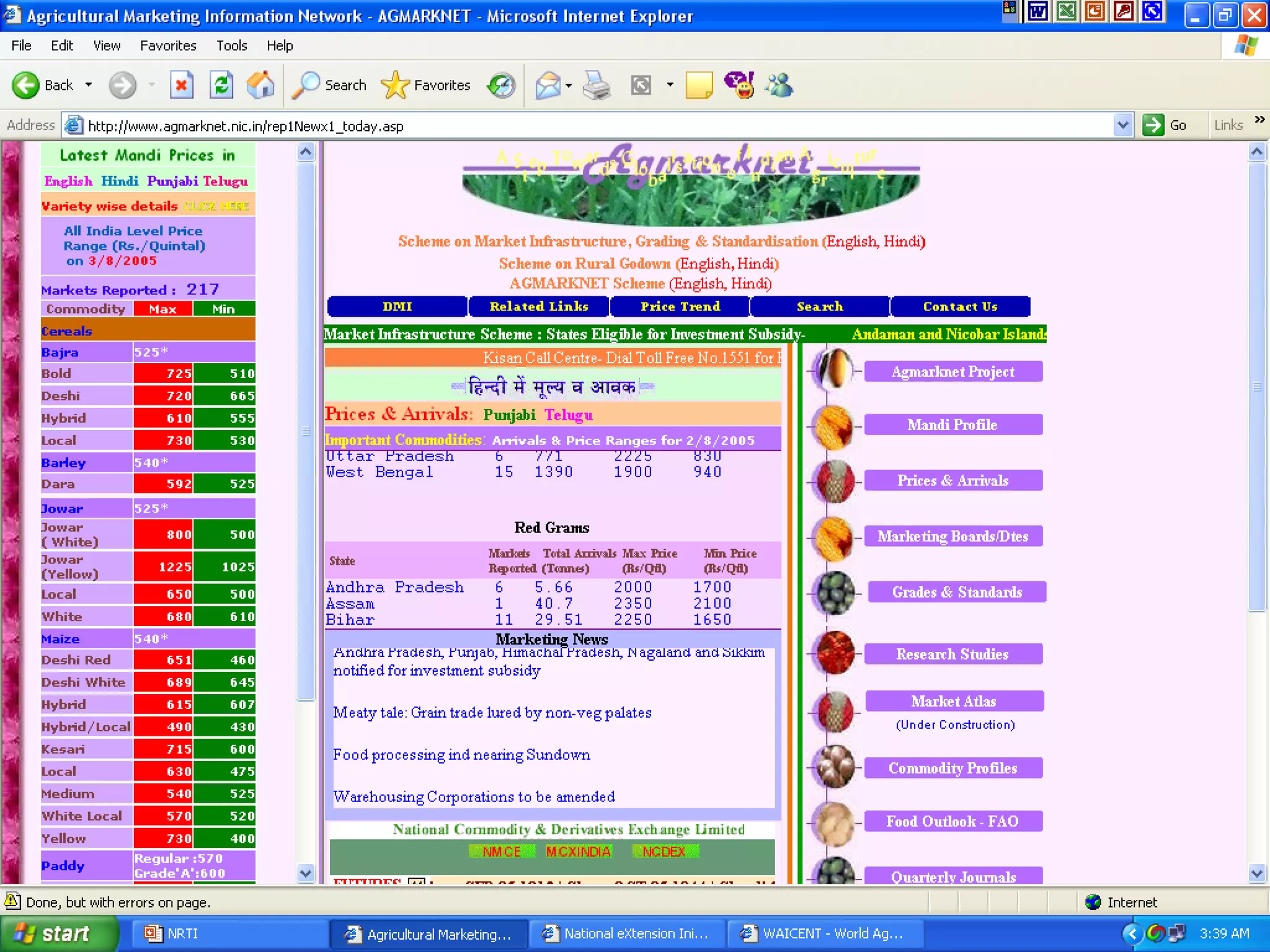
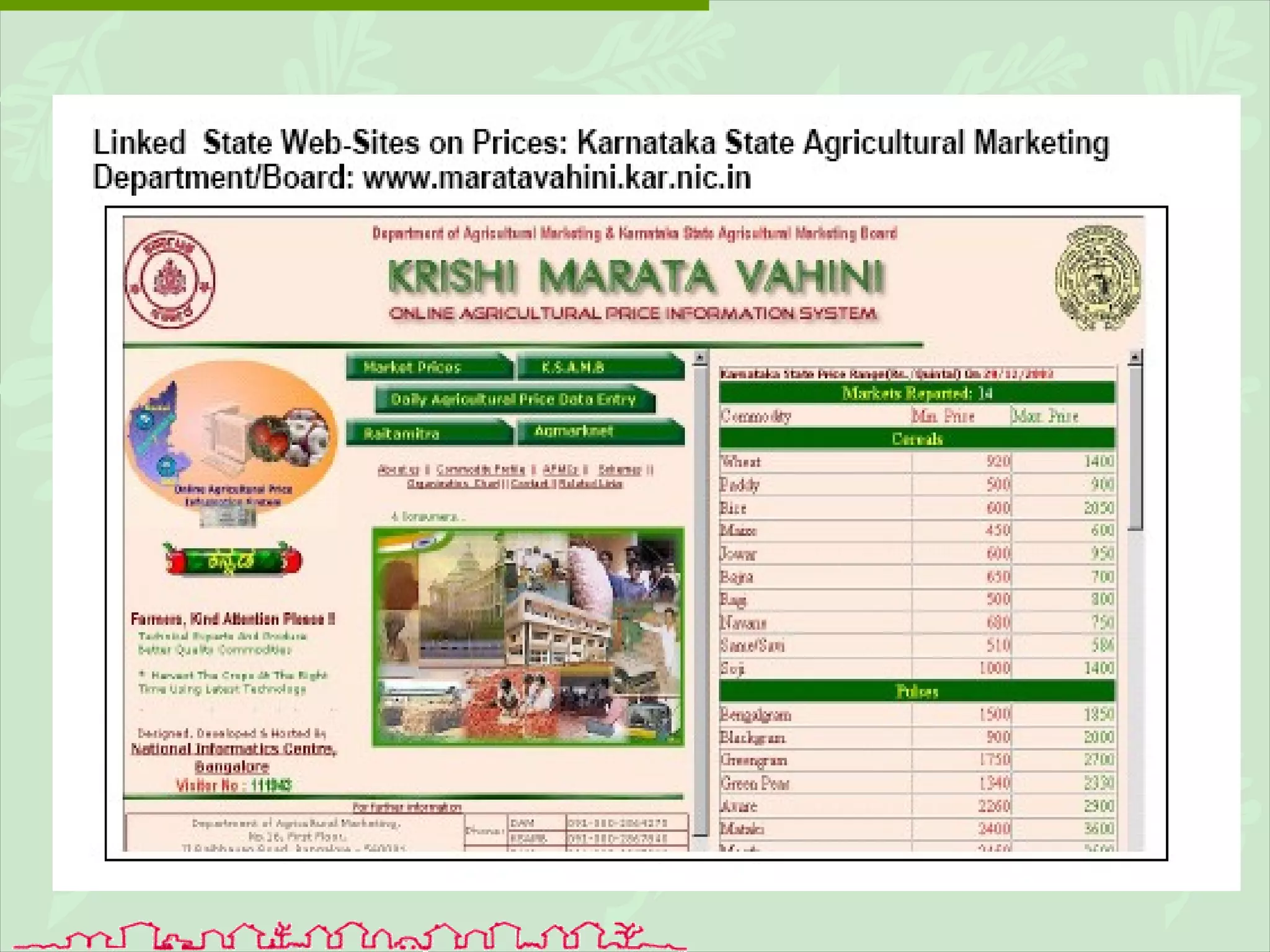
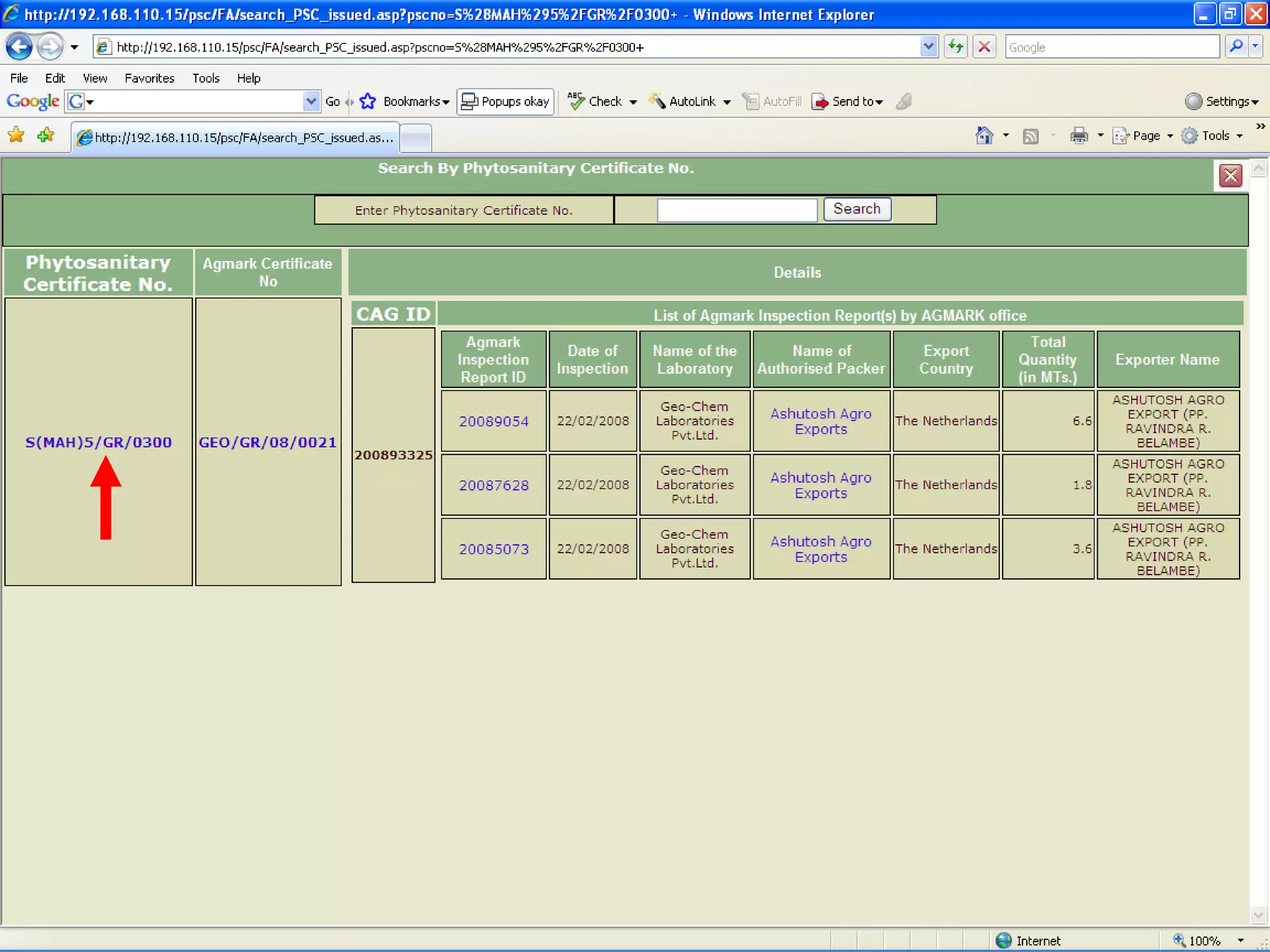
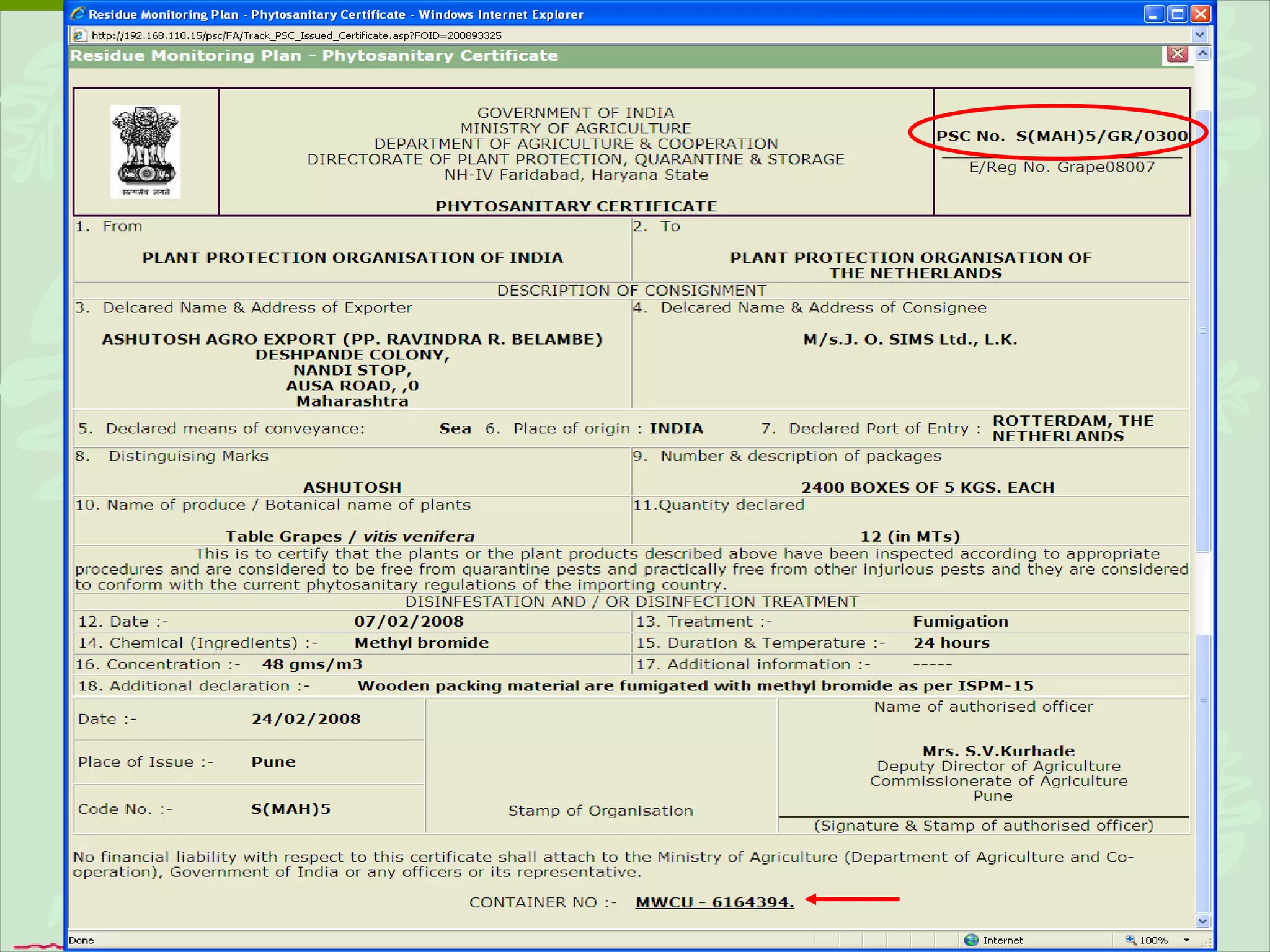
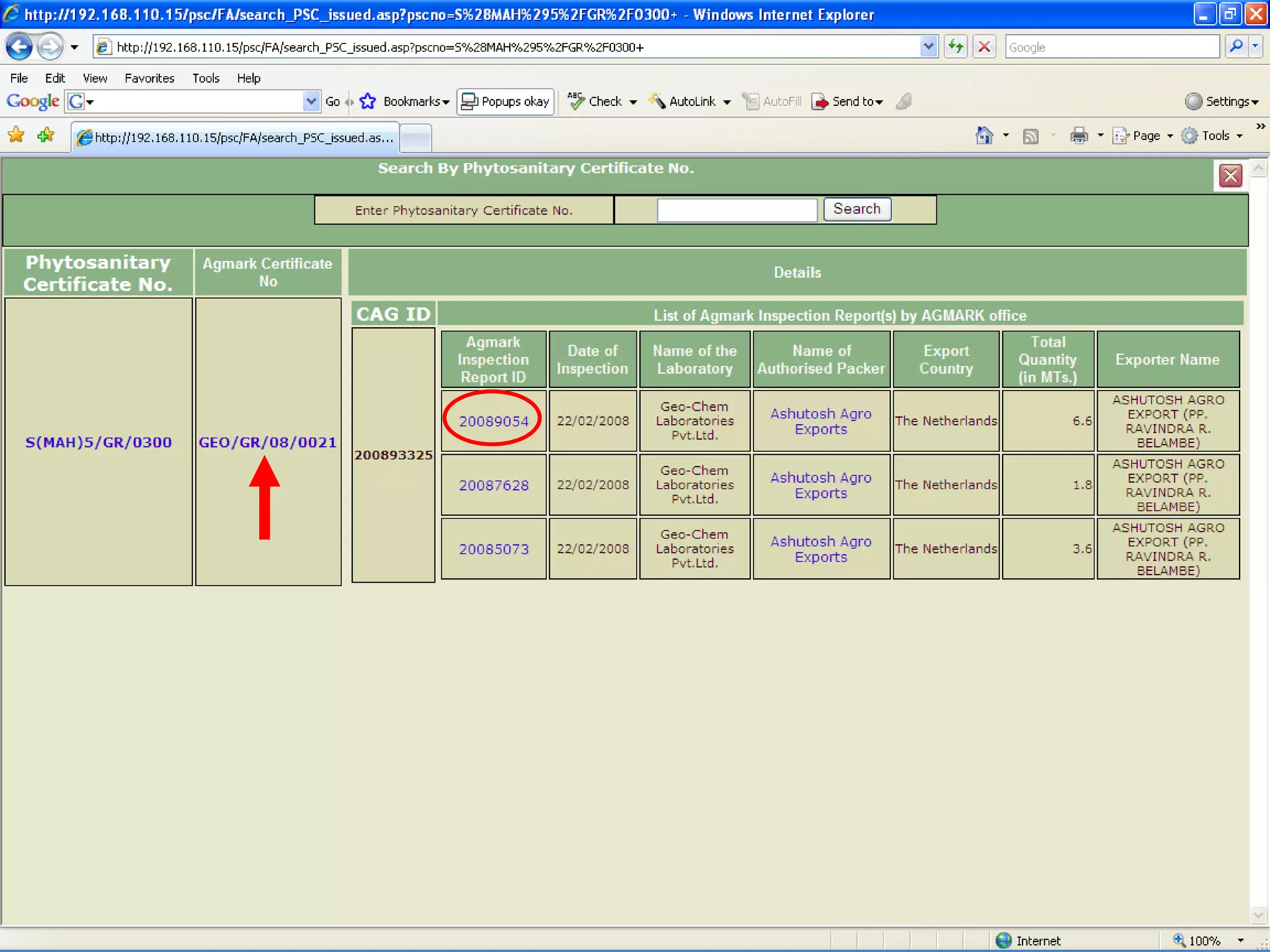
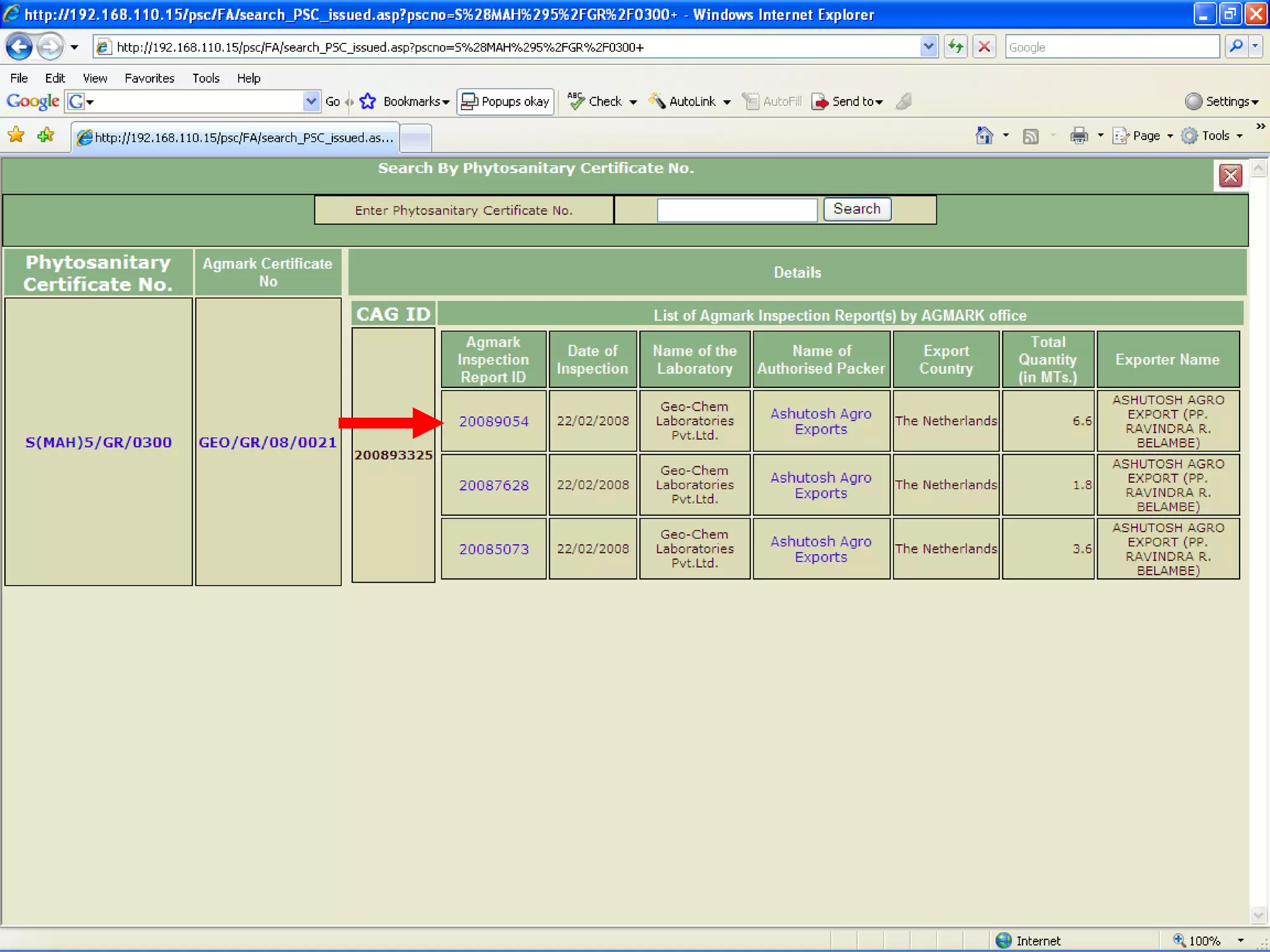
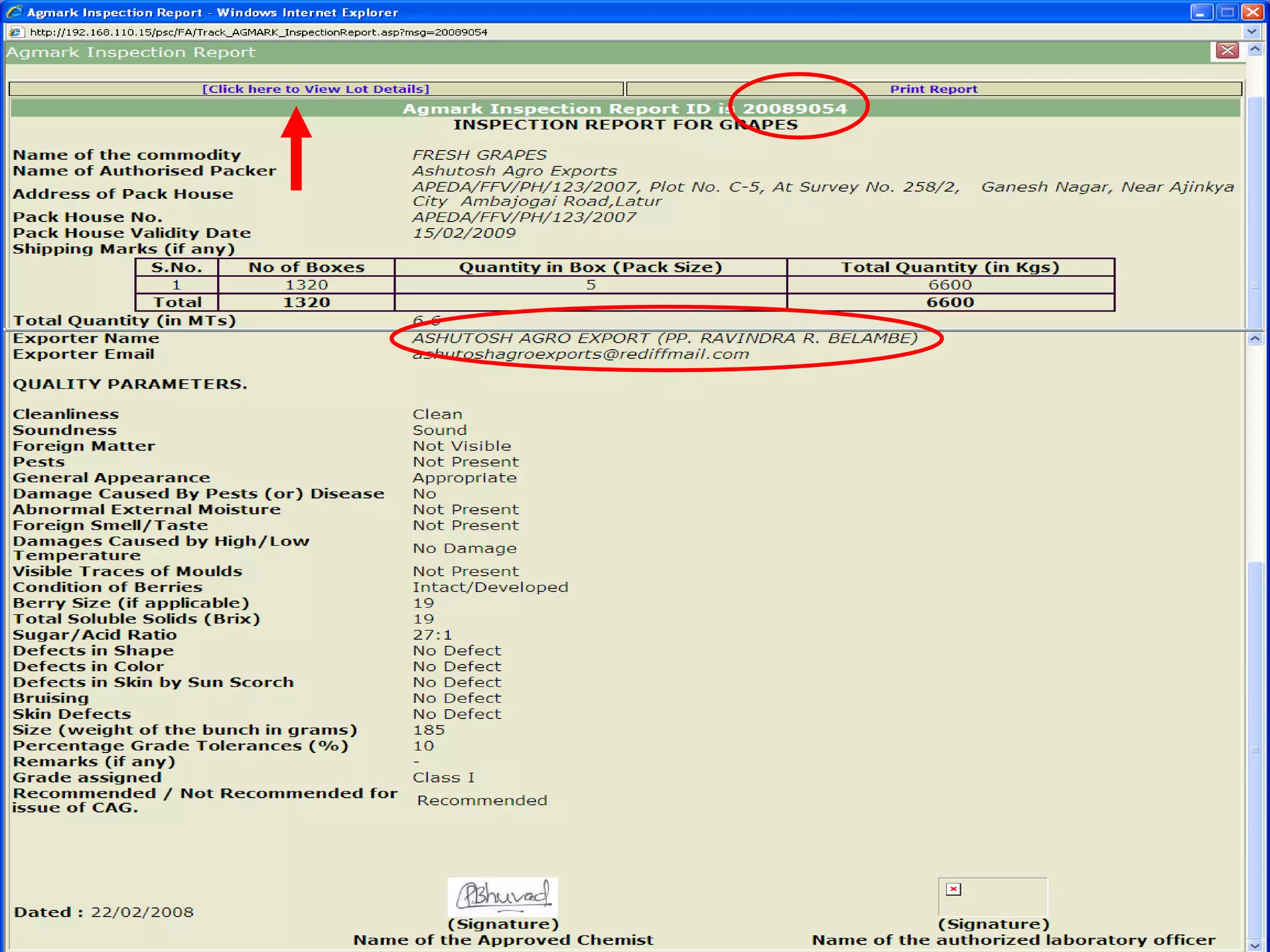
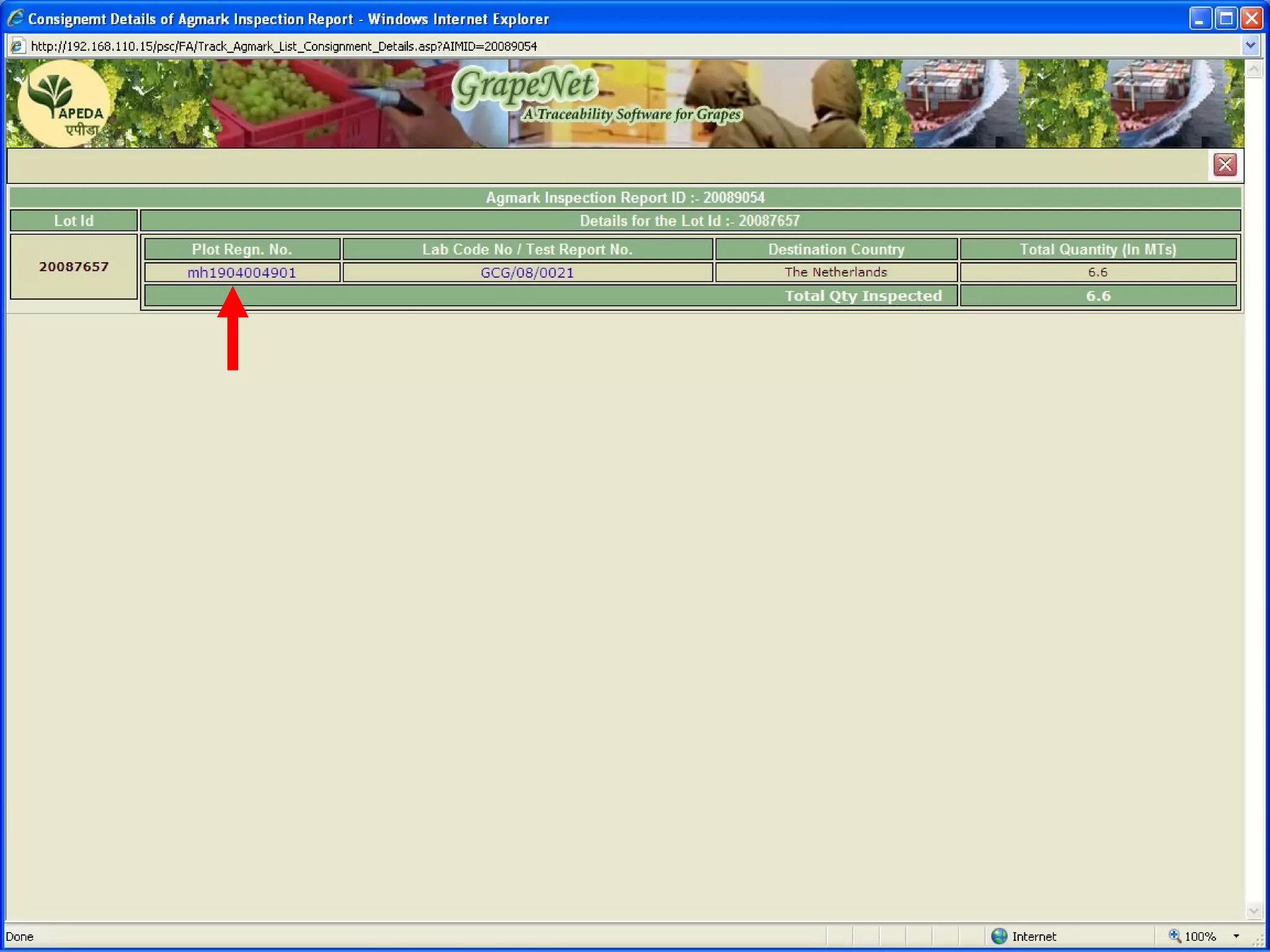
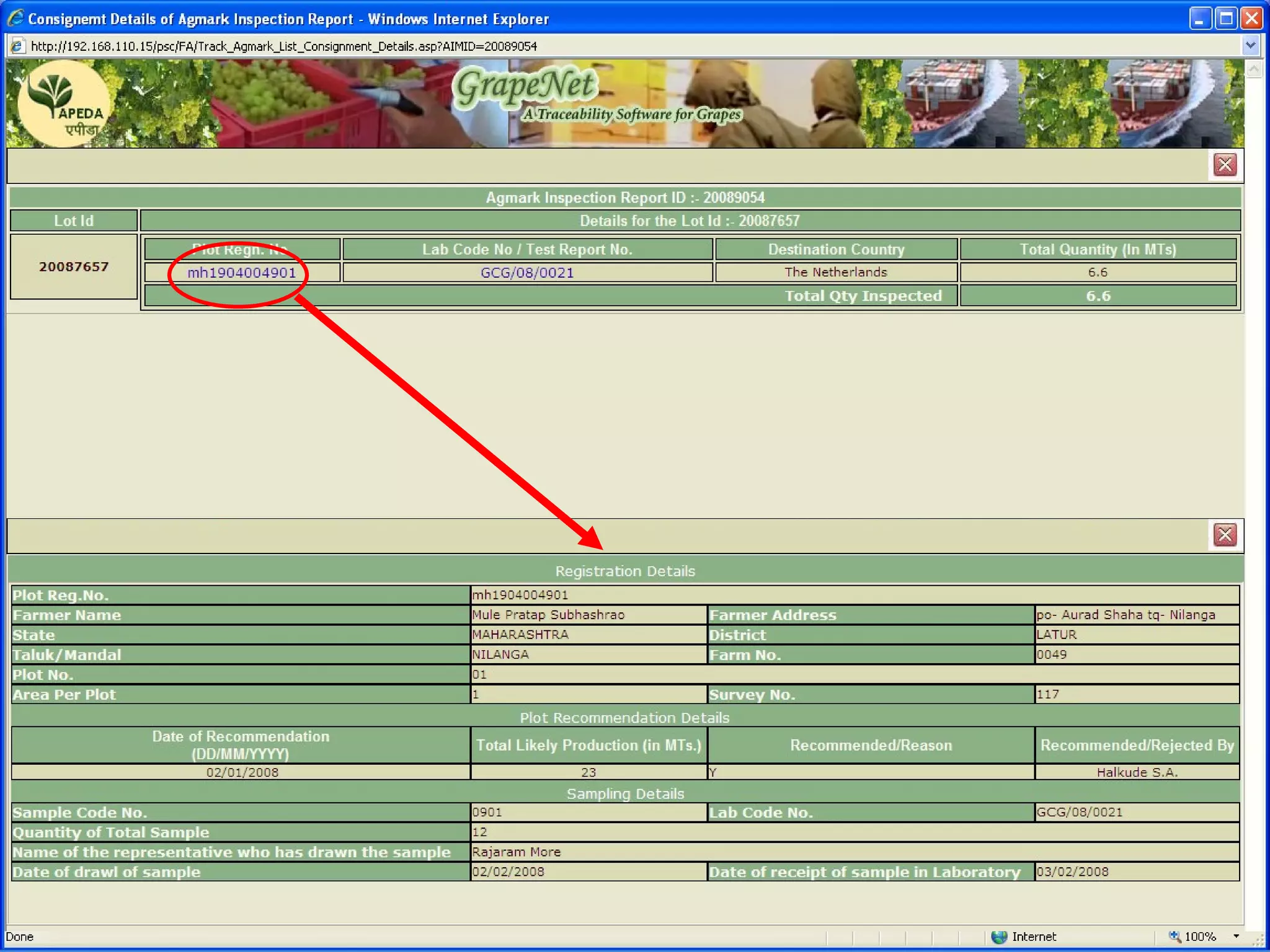
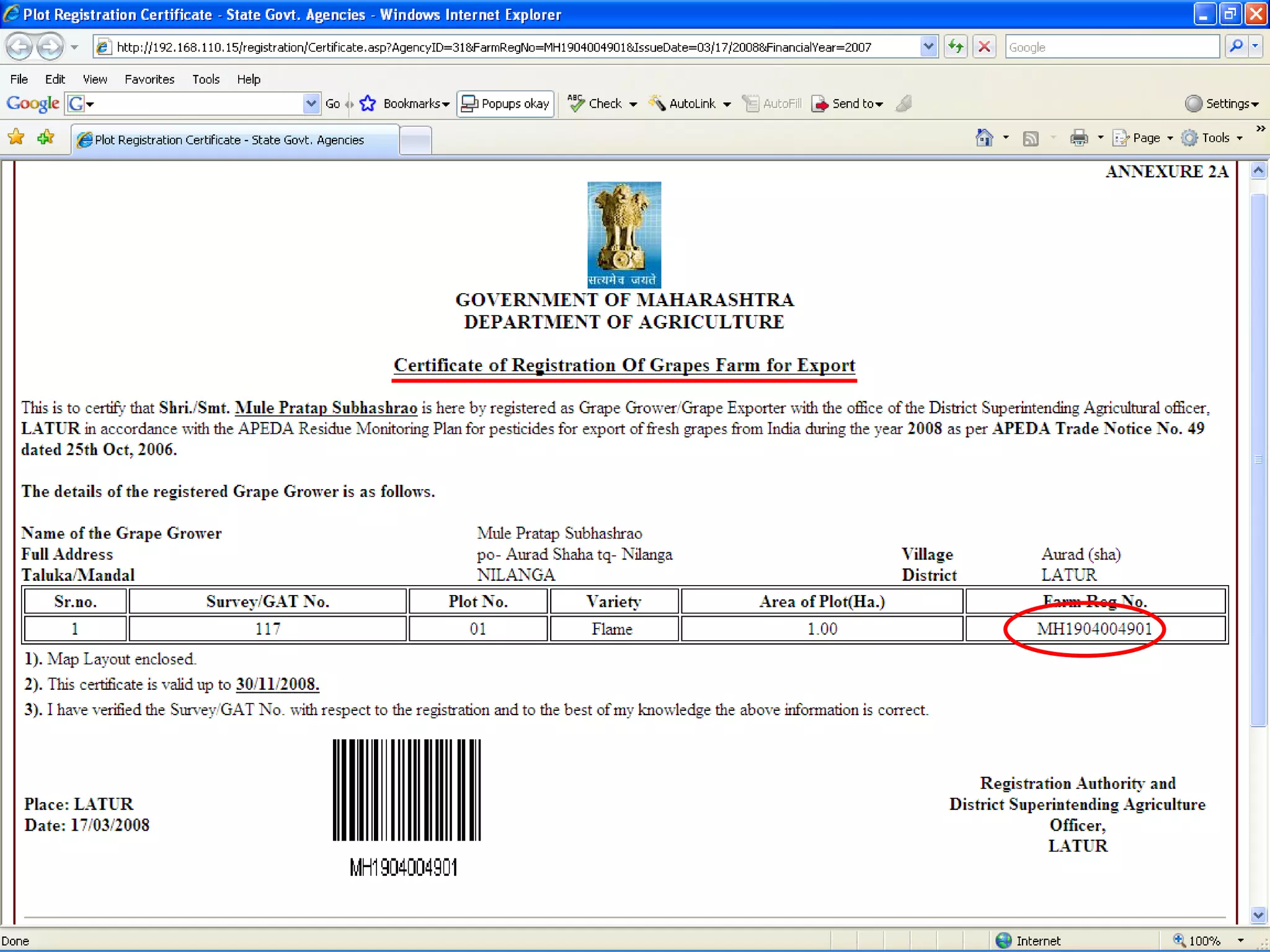
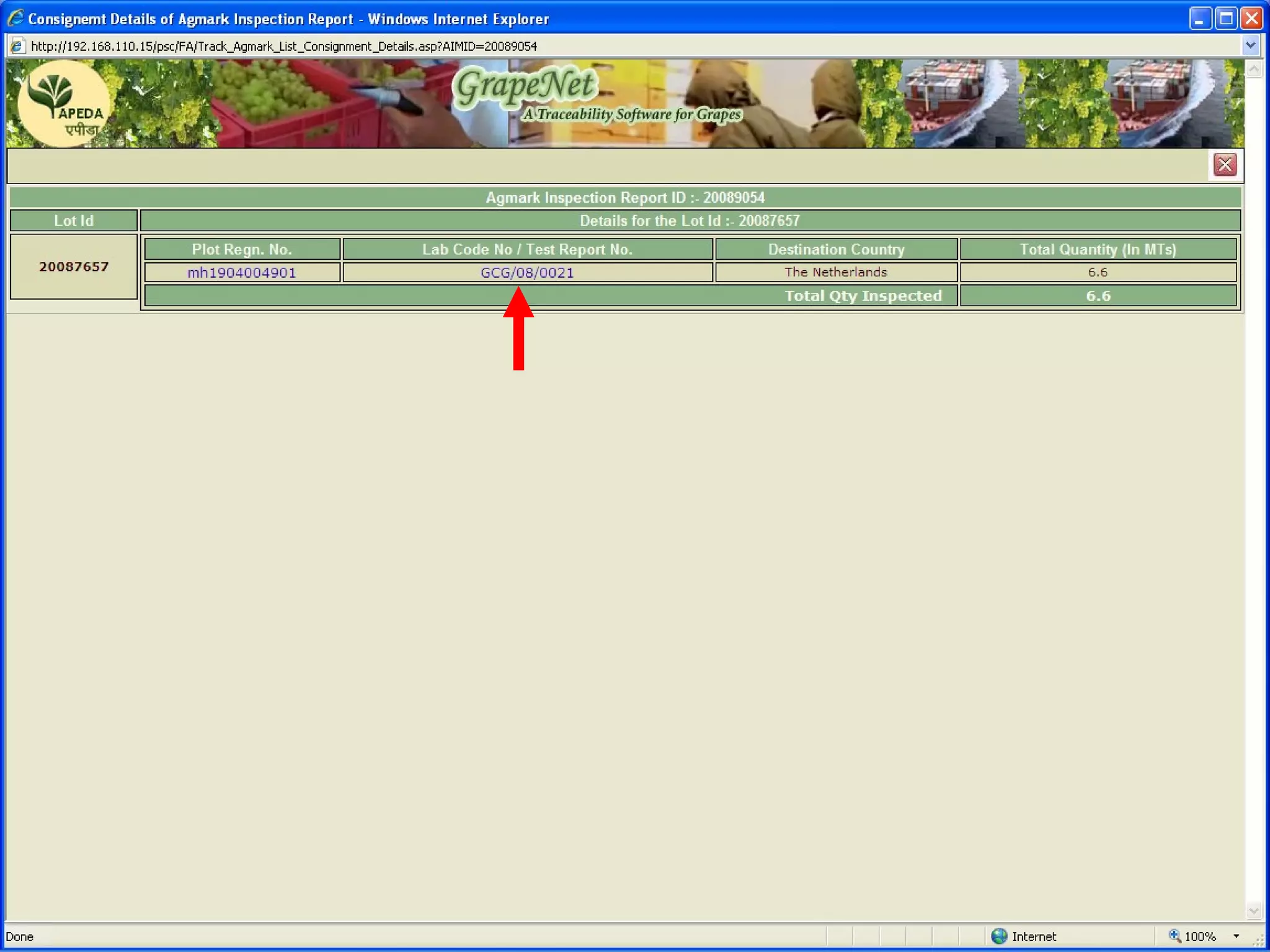
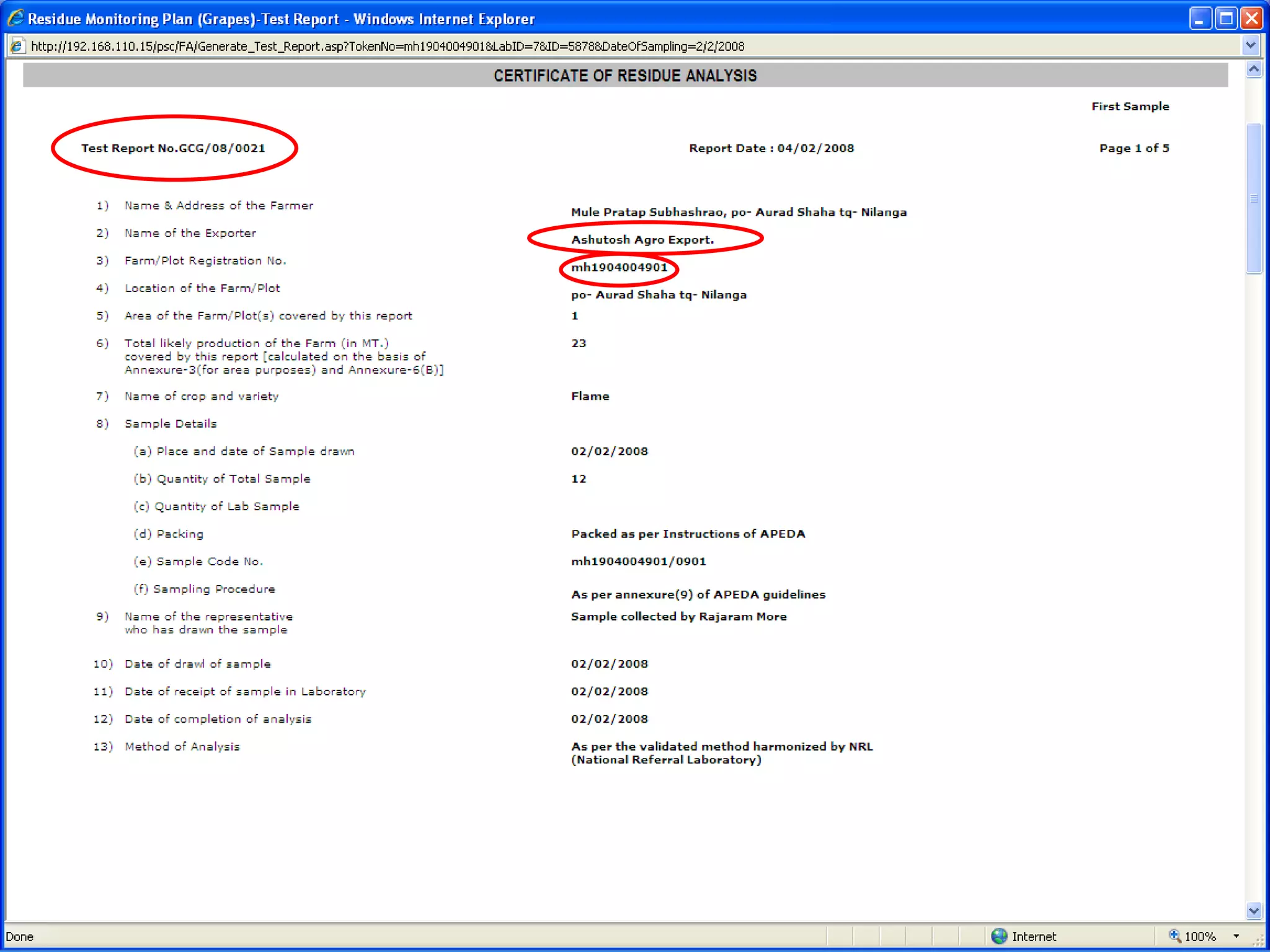
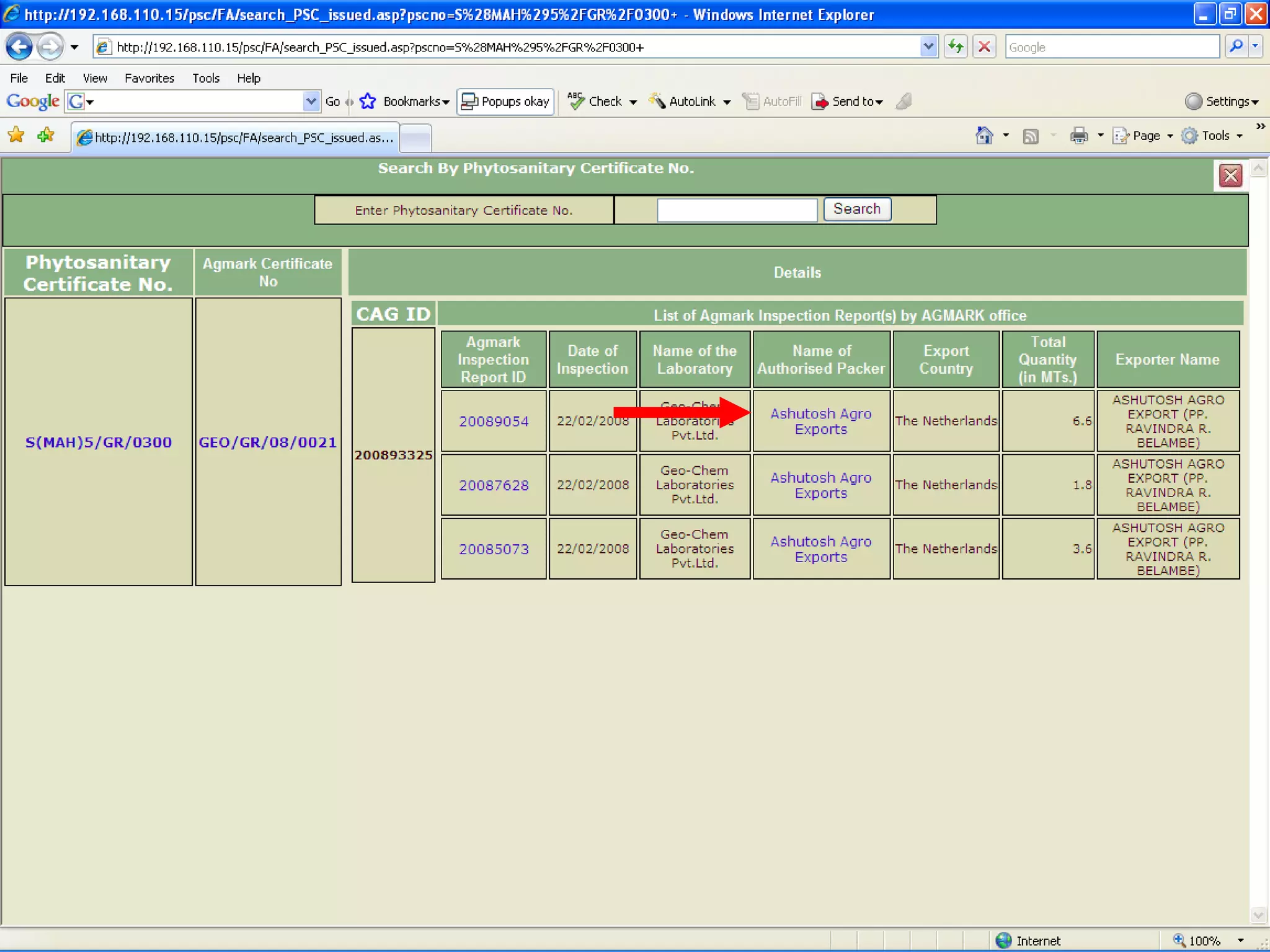
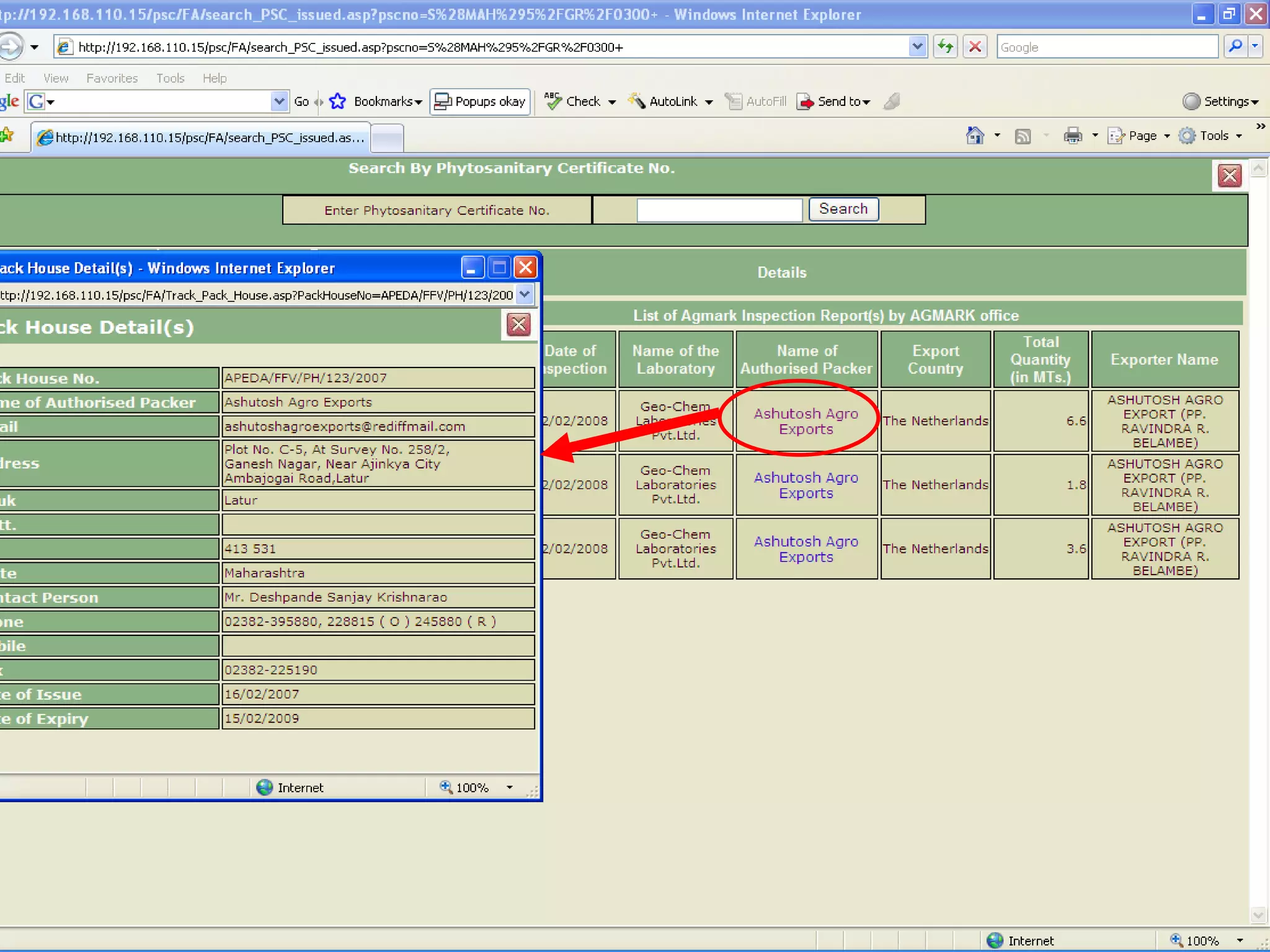
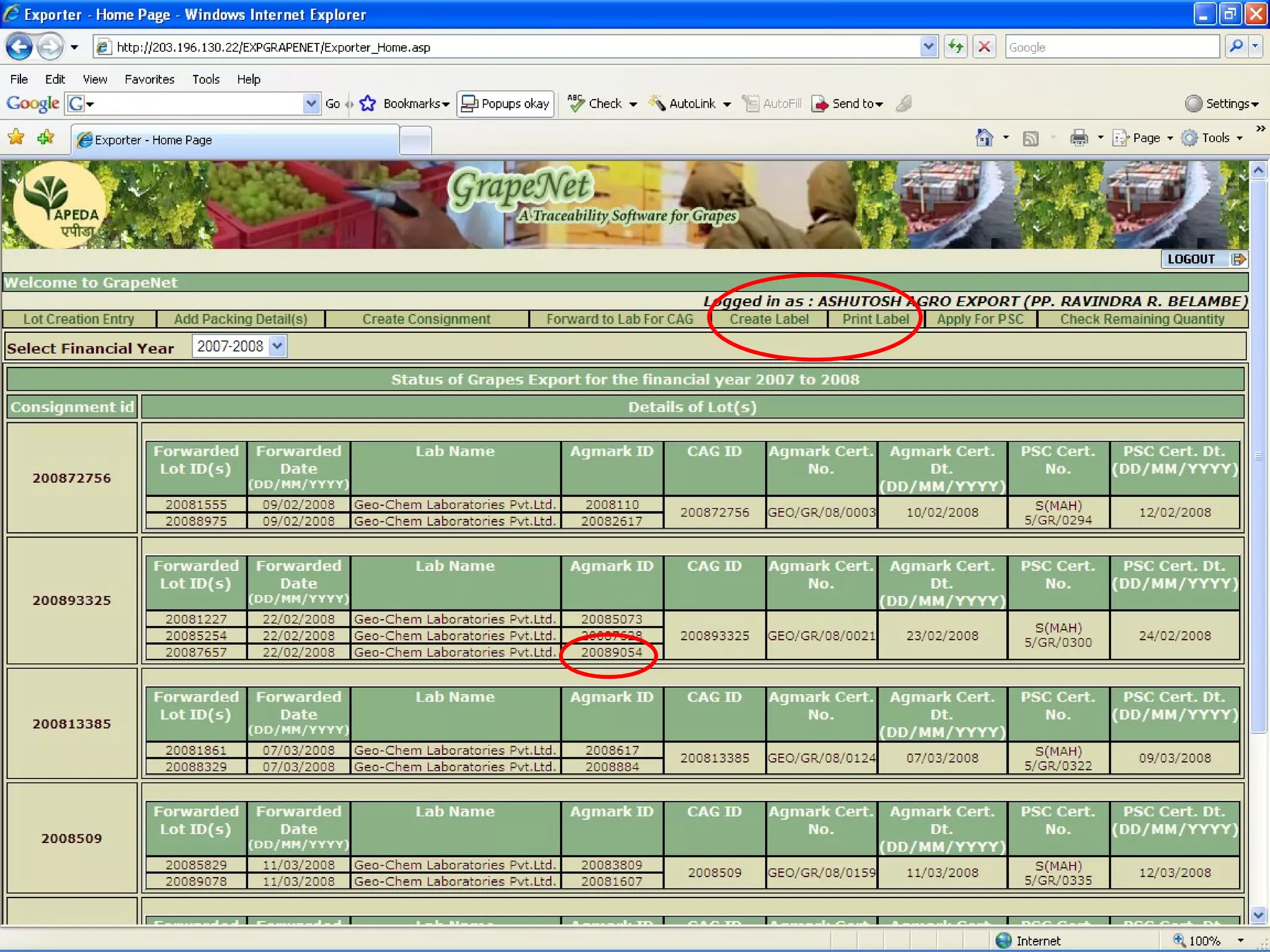
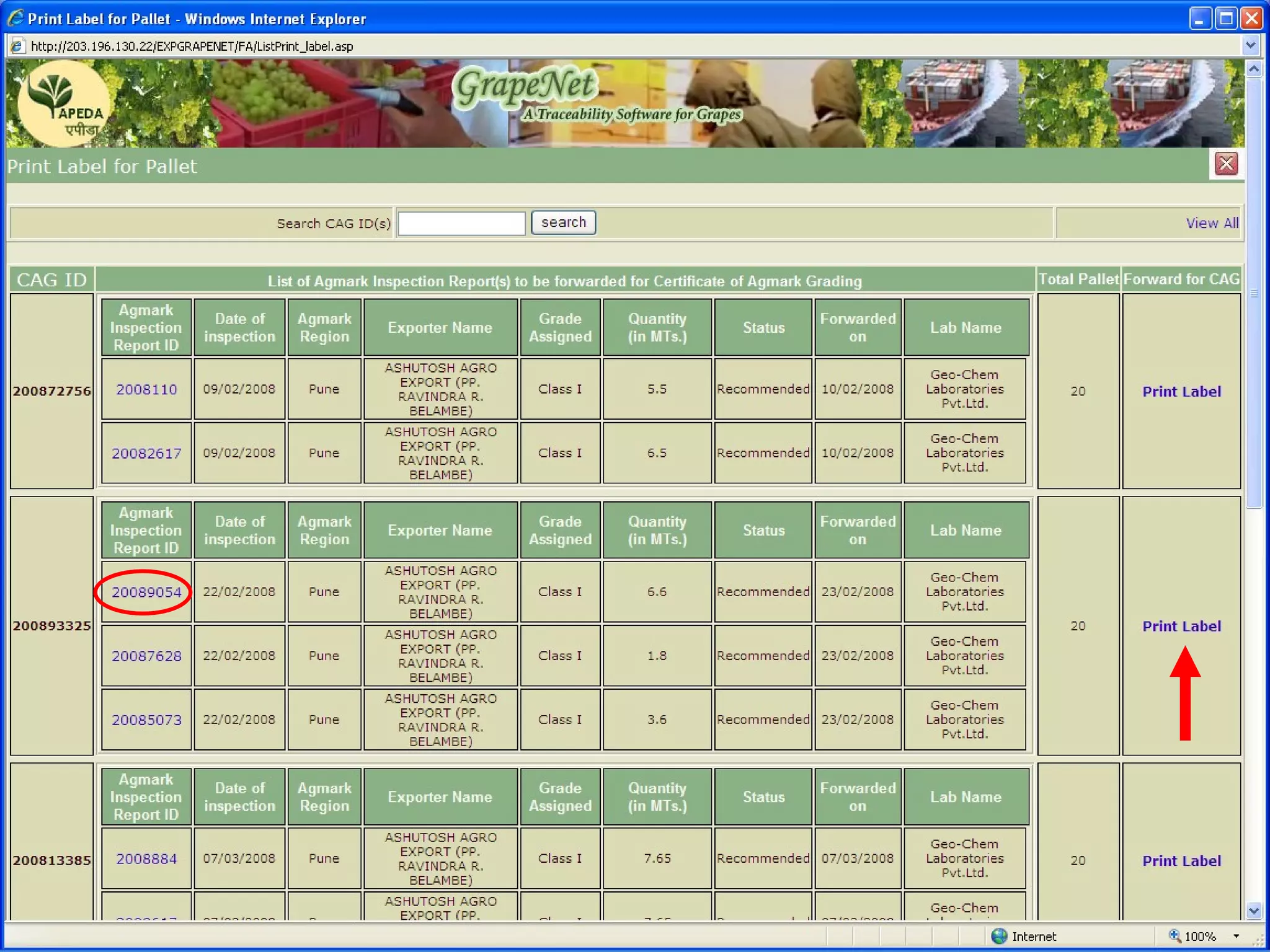
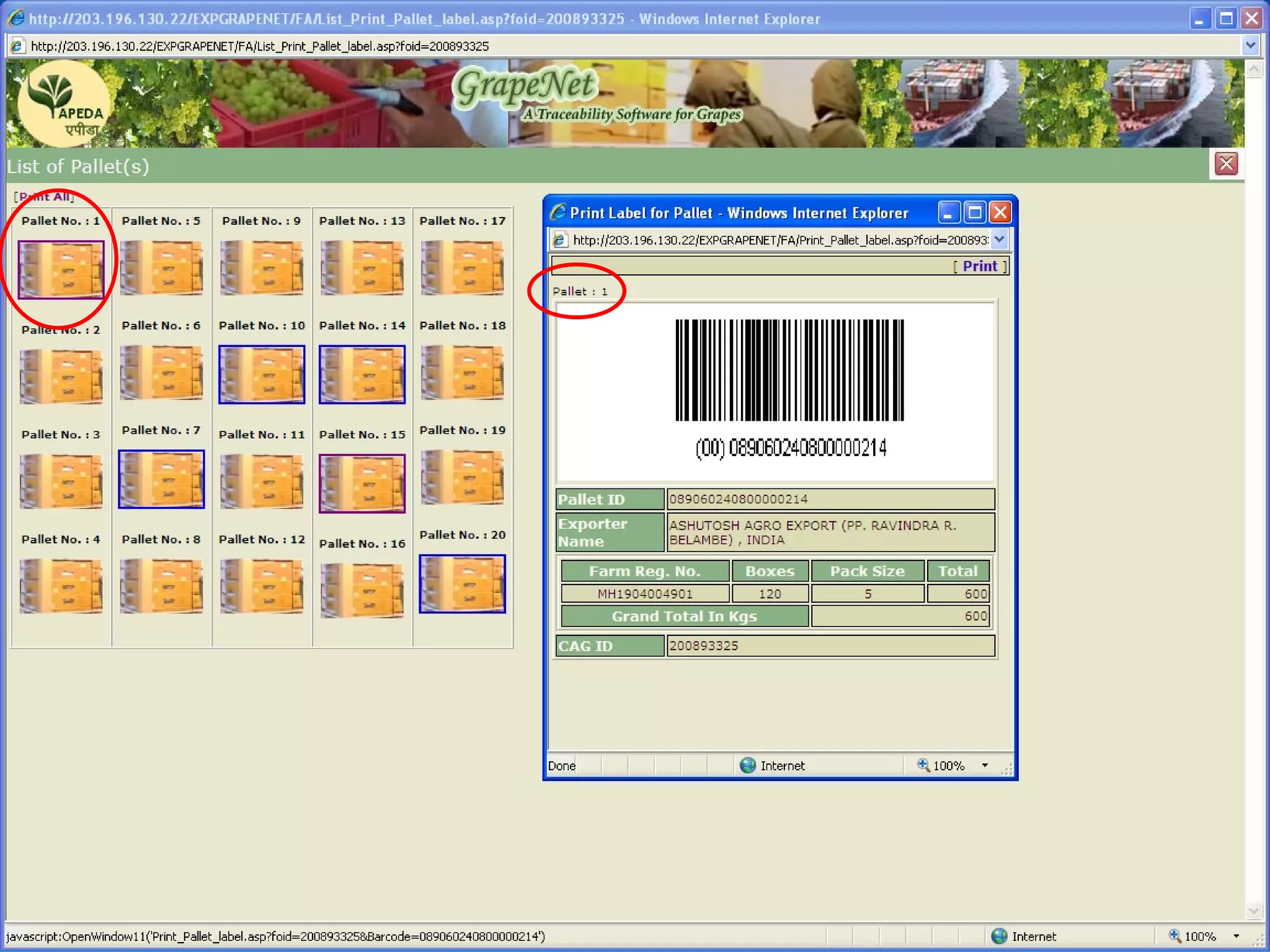
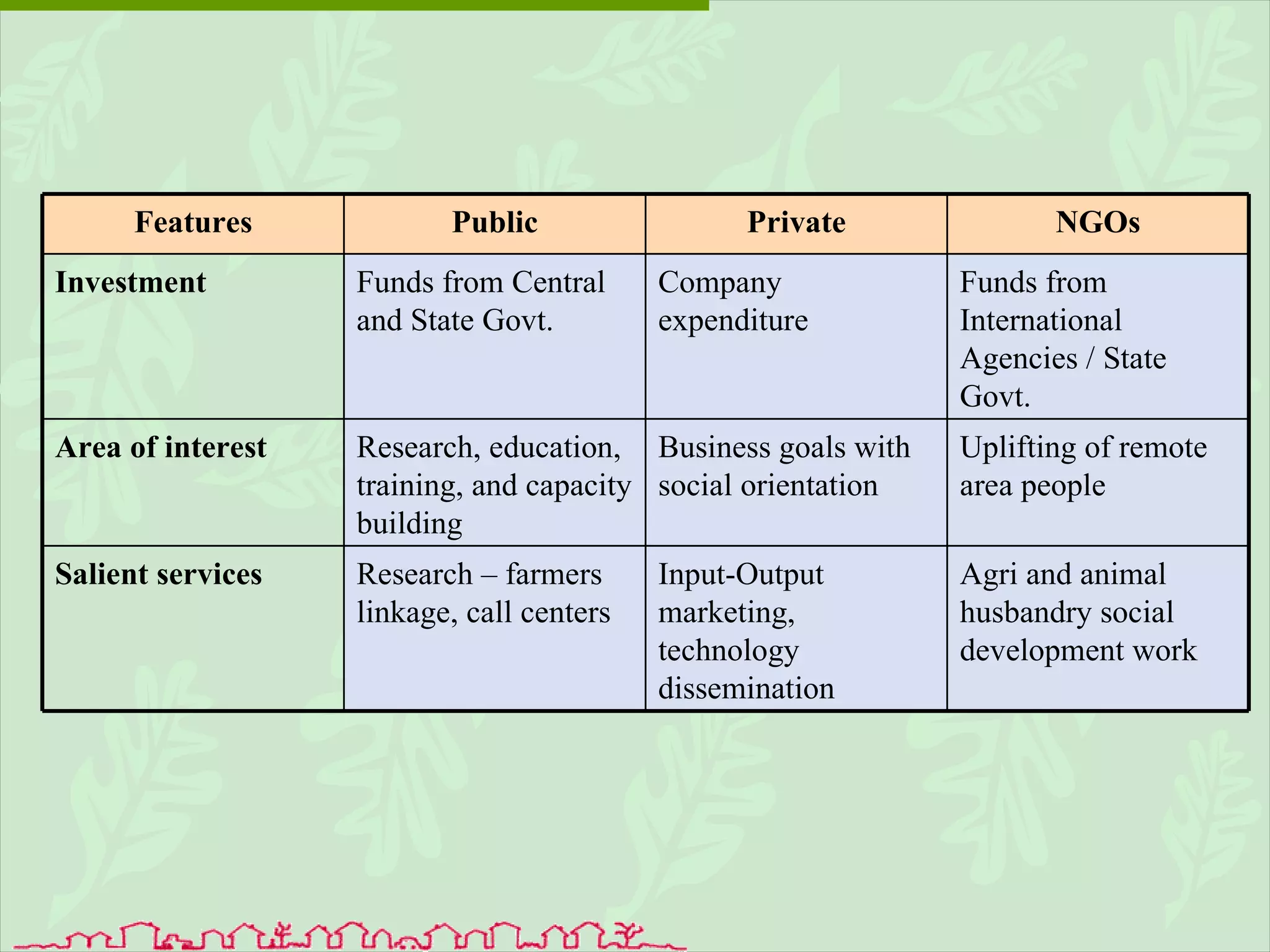
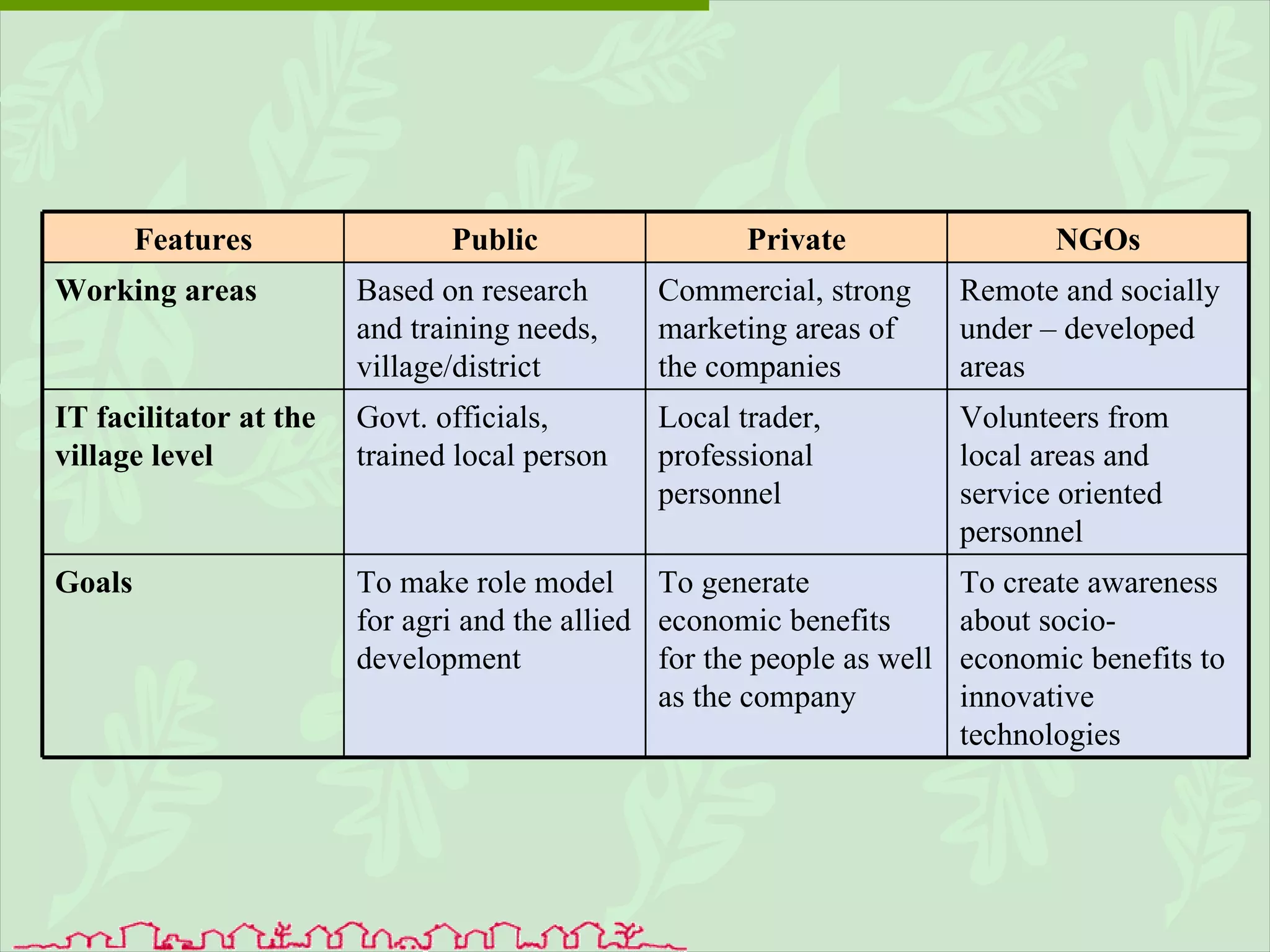
The document discusses various ways that information and communication technologies (ICTs) can help support agricultural development in India. It describes how ICTs such as mobile phones, computers, and the internet are being used to improve access to information for farmers, strengthen agricultural extension services, and help manage agricultural supply chains. It provides several examples of ICT initiatives in India that are aimed at bridging the digital divide between rural and urban areas.