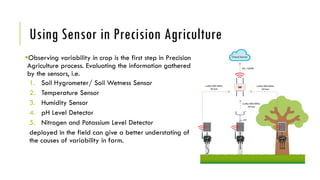
Precision agriculture is a farming management concept that uses technologies like GPS, sensors, satellites and drones to observe field variability and optimize the use of inputs like water, fertilizers and pesticides. This allows farmers to minimize costs, maximize yields, detect problems like pests and weeds precisely, and deal with different field conditions appropriately. Machine learning is also used to analyze data from sensors and images to provide automated recommendations and control devices like robots for efficient, precise farming. The goal is an optimized decision support system for farm management.