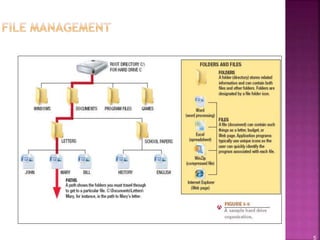
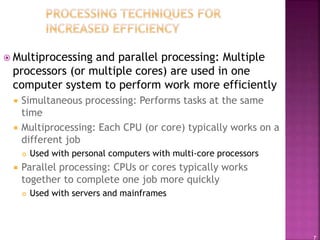
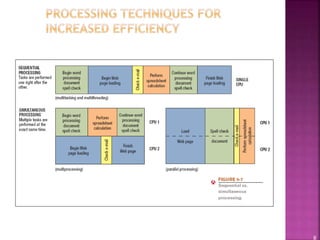
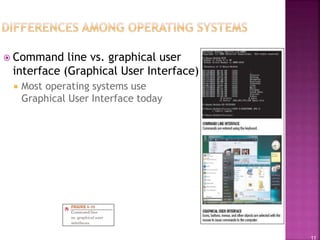
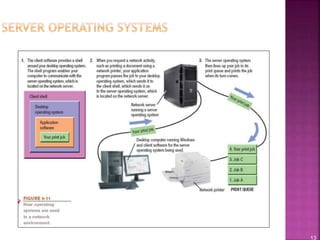
This document provides an overview of operating systems and their components. It discusses how operating systems manage hardware resources, allow for multitasking of programs, and provide interfaces for users. Different types of operating systems are covered, including Windows, Mac OS, Linux, mobile operating systems, and those used for servers and large computers. The document traces the evolution and versions of prominent operating systems like Windows and Android.