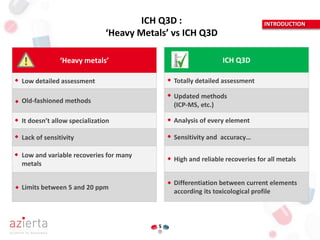
The document outlines the ICH Q3D guideline for evaluating risks related to elemental impurities in medicines, commonly referred to as 'heavy metals.' It emphasizes the need for updated methods for assessing these impurities, detailing their classification by toxicity, acceptable daily exposure limits, and the importance of risk analysis in managing their presence. The guideline aims to ensure that potentially toxic elemental impurities are limited in pharmaceuticals for safe human use.