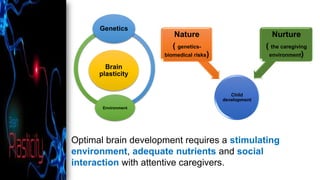
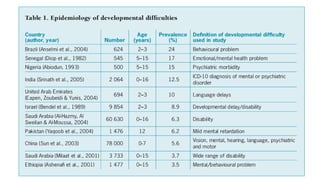
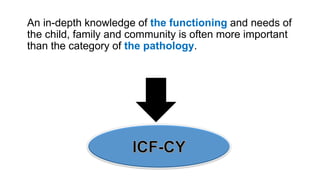
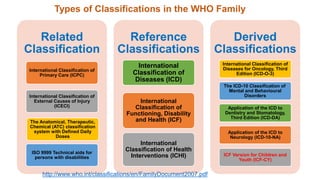
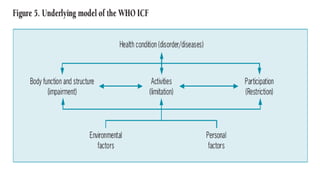
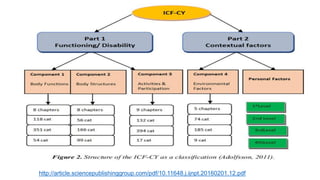
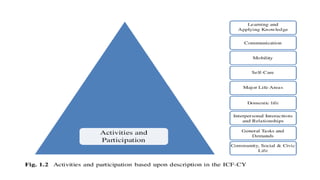
This document discusses early childhood development and developmental delays. It begins by explaining the importance of early childhood development between birth and age 8. It then discusses the current status of early childhood development globally and in Egypt. Key points include developmental delays being common, affecting 1 in 6 children, and early childhood education attendance and quality varying greatly between socioeconomic groups. The document also defines developmental delay and developmental quotients. It discusses international classification systems like ICD and ICF and their application to early childhood. Early identification, assessment, and intervention services are important for children with developmental delays or disabilities.

![,
which spans the period
up to 8 years of age, is
critical for cognitive,
social, emotional and
physical development.
The formative years: UNICEF’s work on measuring early childhood [internet]. 1st ed. New York: UNICEF; 2014 [cited 14 March
2017]. Available from:
https://data.unicef.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/Measuring-ECD-Brochure-HR-10_8_116.pdf.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icf-cyandchildhooddevelopment-180413123755/85/ICF-CY-and-early-childhood-development-3-320.jpg)







![➢The true prevalence of developmental difficulties in children aged 0–3
years is unknown.
➢The percentage of children screening positive for, or at risk of,
disability in Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (MICSs) carried out in
18 countries in 2005–2006 was a median 23% (range 3–48%) of
children aged 2–9 years screened positive for disability (Gottlieb et al.,
2009).
Developmental difficulties in early childhood: Prevention, early identification, assessment and intervention in low- and middle-
income countries [internet]. 1st ed. Geneva: WHO; 2012 [cited 14 March 2017]. Available from:
http://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/documents/development_difficulties_early_childhood/en/.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icf-cyandchildhooddevelopment-180413123755/85/ICF-CY-and-early-childhood-development-12-320.jpg)

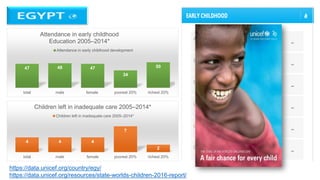
![In Egypt, children under 9 years old constitute 21.8% of total
population (11.3% are under five years old) in 2015.
unfortunately, there are no population based specific data about early
childhood developmental difficulties and the only early childhood
development indicators that had been examined, were:
• prenatal care
• skilled attendant at
delivery
• neonatal mortality
• infant mortality
• fully immunized
• stunting/height-for-age
• salt iodization
• early childhood care and
education.
Early childhood development in Egypt [Internet]. World Bank. 2017 [cited 14 March 2017]. Available from:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icf-cyandchildhooddevelopment-180413123755/85/ICF-CY-and-early-childhood-development-15-320.jpg)

![“Developmental delay” is often defined as a deviation of
development from the normative milestones in the areas of
cognitive, language, social, emotional and motor functioning.
Developmental difficulties in early childhood: Prevention, early identification, assessment and intervention in low- and middle-
income countries [internet]. 1st ed. Geneva: WHO; 2012 [cited 14 March 2017]. Available from:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icf-cyandchildhooddevelopment-180413123755/85/ICF-CY-and-early-childhood-development-18-320.jpg)


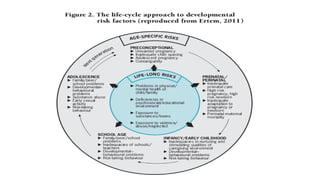
![Biological & psychosocial
Categorical
DC 0-3R: “psychosocial and environmental stressors”
The Bright Futures guidelines (Council on Children with
Disabilities, 2006): risks related to the child, family and
community
Developmental difficulties in early childhood: Prevention, early identification, assessment and intervention in low- and middle-
income countries [internet]. 1st ed. Geneva: WHO; 2012 [cited 14 March 2017]. Available from:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icf-cyandchildhooddevelopment-180413123755/85/ICF-CY-and-early-childhood-development-21-320.jpg)













![contributes in serving individuals with intellectual
and developmental disabilities as it is:
1. a unifying framework for interdisciplinary work,
2. a classification of dimensions of functioning and health,
3. profiles of functional characteristics and limitations,
4. clarification of diagnoses and comorbidity, functional
indicators for framing intervention and outcomes,
Simeonsson R. ICF-CY: A universal tool for documentation of disability. J Policy Pract Intellect Disabil. 2009 [cited 15 March
2017];6(2):70-72.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icf-cyandchildhooddevelopment-180413123755/85/ICF-CY-and-early-childhood-development-42-320.jpg)




![ICF-CY Developmental Code Sets
• Identify limited ICF-CY codes by expert consensus to
document essential physical and developmental
characteristics, functions and skills of children by four
developmental age groups (0-2, 3-5, 6-12, 13-17)
Birth-2
3-5
6-12
13-17
Ellingsen K, Simeonsson R. ICF-CY developmental code sets [Internet]. WHO ICF-CY
developmental code sets. 2011 [cited 8 March 2017]. Available from:
http://www.icfcydevelopmentalcodesets.com/.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icf-cyandchildhooddevelopment-180413123755/85/ICF-CY-and-early-childhood-development-48-320.jpg)