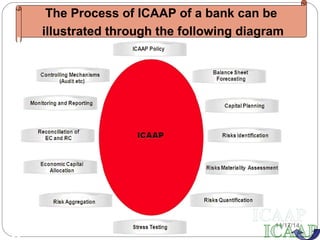
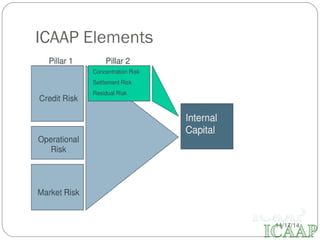
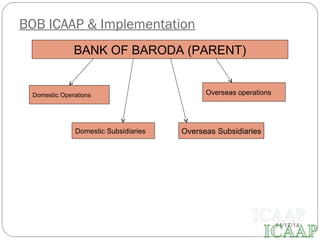
This document provides an overview of the Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process (ICAAP) under Basel II Pillar 2 requirements. It discusses the purpose of Pillar 2 in complementing Pillar 1 by addressing bank-specific risks. The ICAAP process involves identifying and quantifying all risks, conducting stress tests, and assessing capital adequacy. The document then outlines Bank of Baroda's implementation of ICAAP, including its risk policy, data collection from various departments, and quarterly reporting to internal committees and regulators.