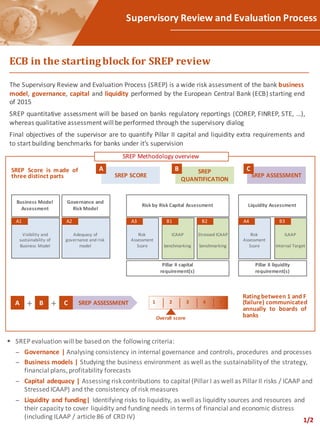
The document outlines the Supervisory Review and Evaluation Process (SREP) undertaken by the European Central Bank (ECB), focusing on assessing banks' business models, governance, capital, and liquidity. It describes the methodology for evaluating banks, including governance analyses, business model sustainability, capital adequacy, and liquidity risks. Additionally, it highlights challenges faced by financial institutions in adhering to SREP requirements and offers approaches to mitigate these challenges through benchmarking and preparatory work plans.