Here are the key points about reverse repo rate from the document:
- Reverse repo rate is the rate at which the central bank of a country (Reserve Bank of India in case of India) borrows money from commercial banks.
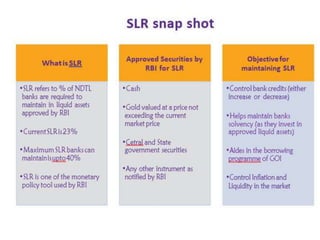
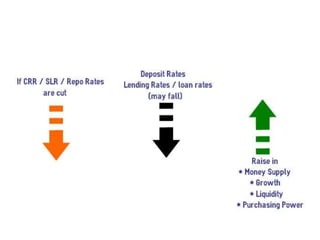
- It is a monetary policy instrument used by the central bank to control money supply. An increase in reverse repo rate will decrease money supply and vice versa.
- When reverse repo rate is increased, it provides more incentive for commercial banks to park their funds with the central bank, thus decreasing the money available in the market.